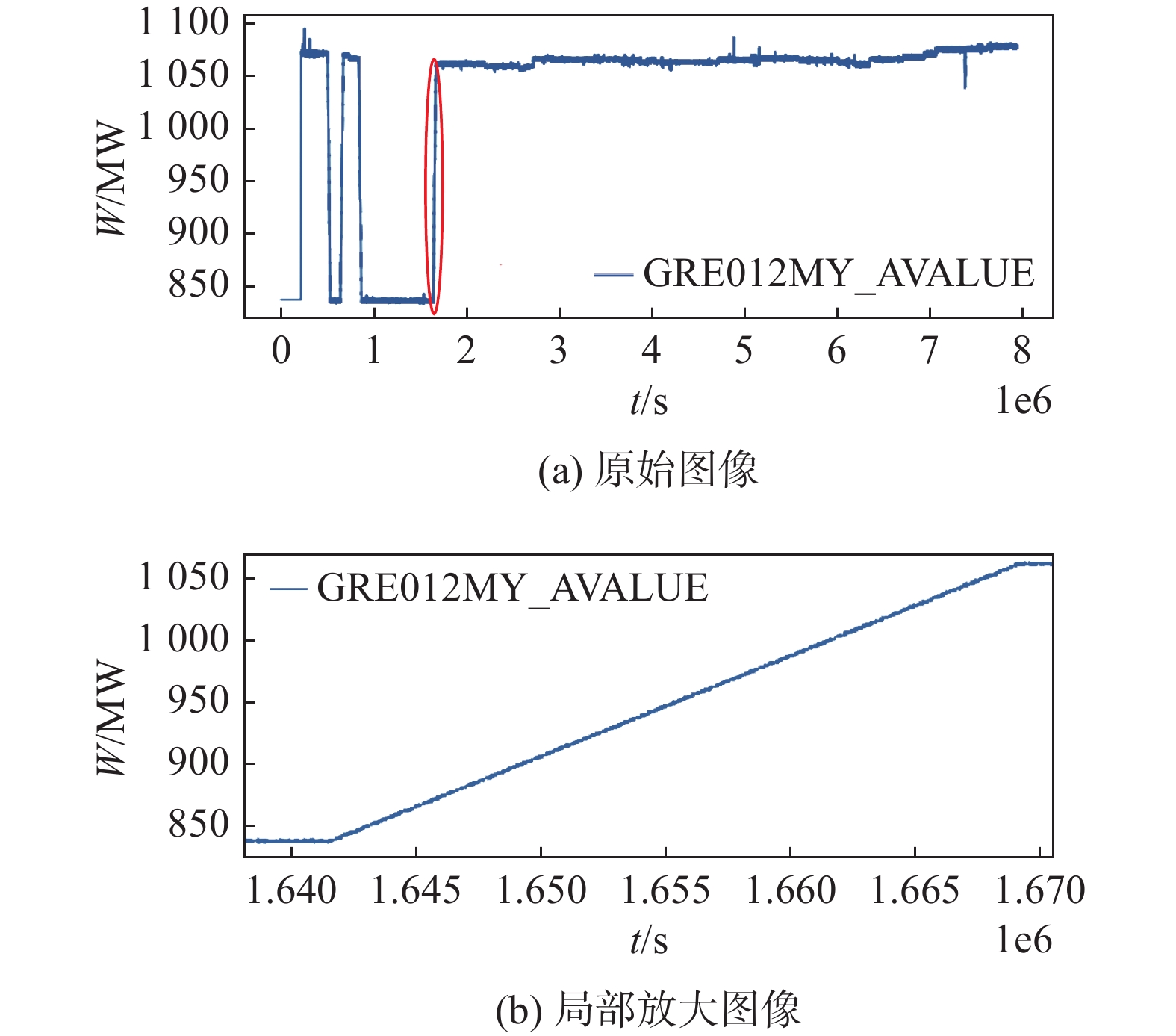
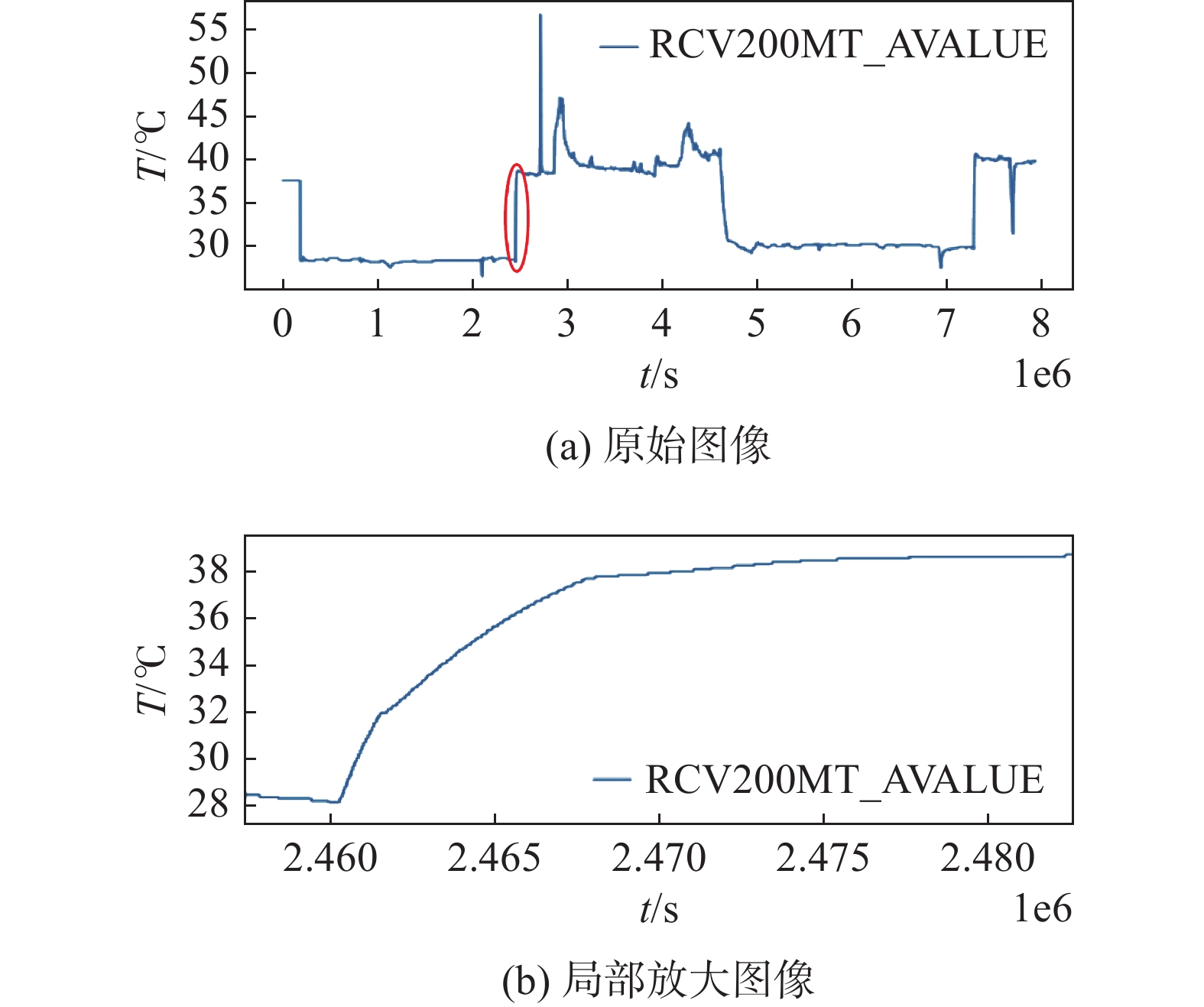
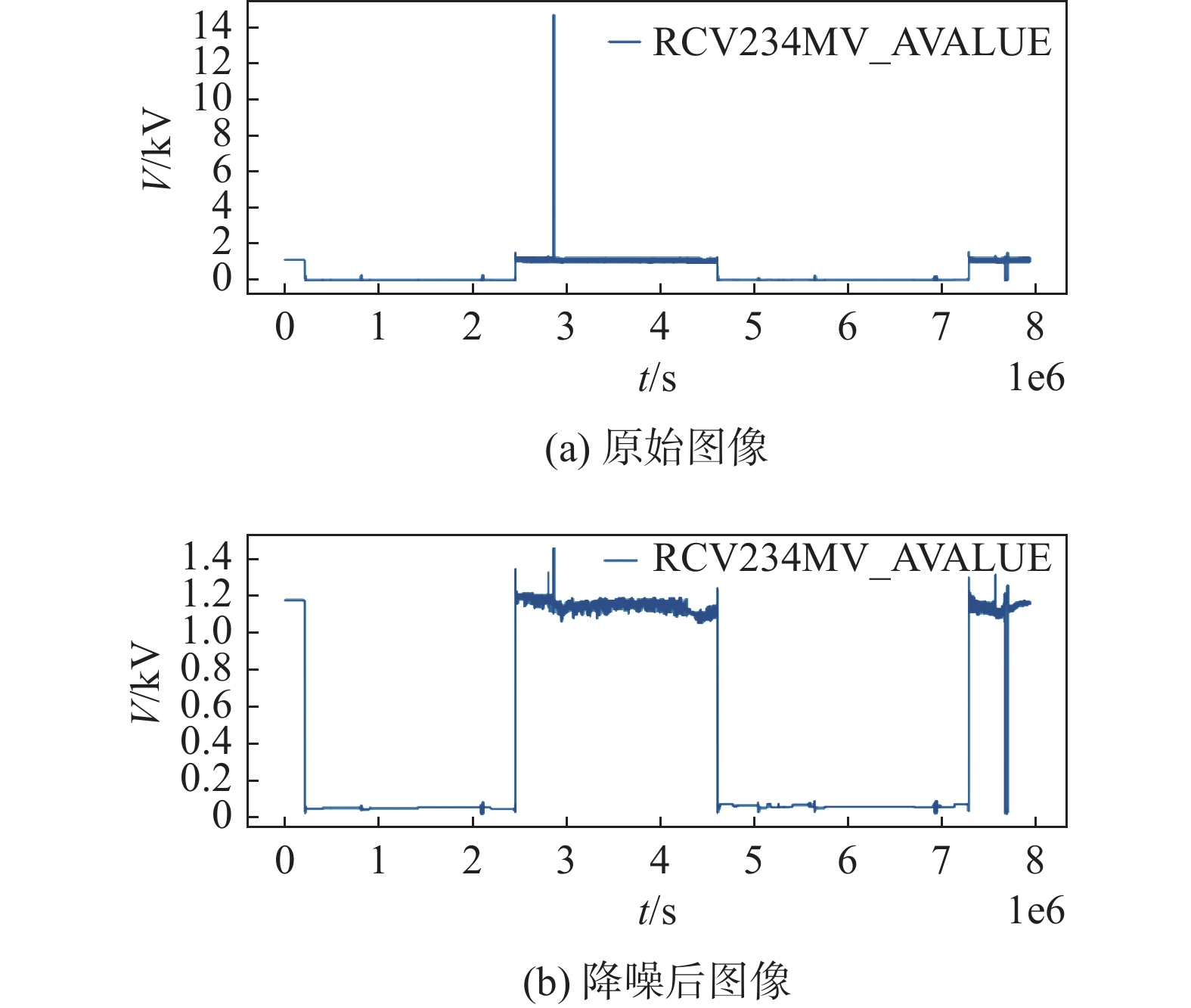
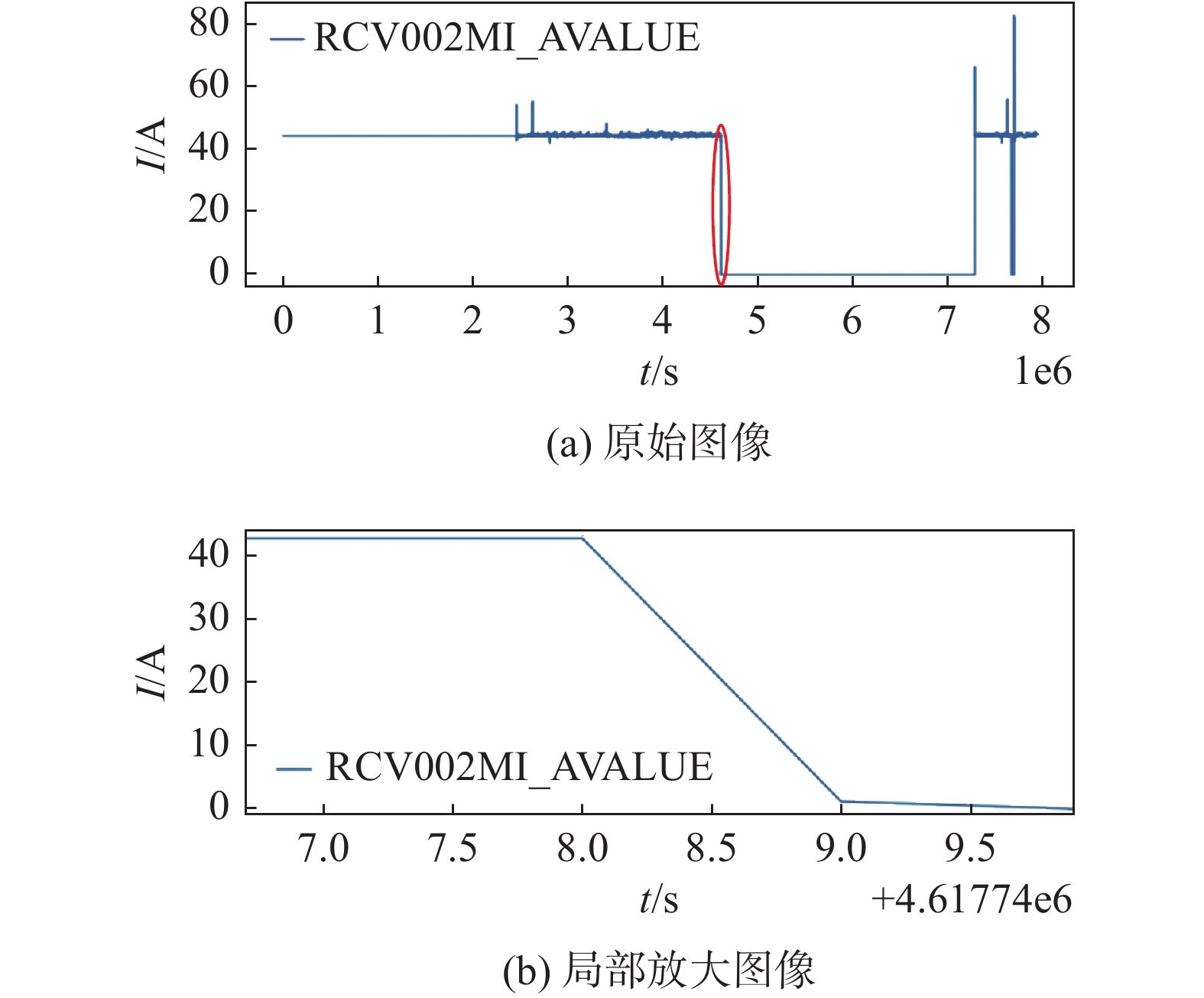
-
摘要:目的 核电运行数据具有维度高、体量大等特点,而核电厂内部系统的复杂性导致难以构建相应的机理模型,因此依靠人工从核电数据中筛选出具有关联性的参数非常困难,而非关联性参数的混入将极大地影响模型精度,通过提高模型精度以达到精准建模的目的。方法 文章提出了一种基于多尺度时间窗口的关联分析方法,该方法对目标参数进行状态切换点提取,依据不同传感器所记录数据的特点对各个传感器进行分类,再针对不同种类的传感器设计符合其特点的检测窗口,利用从目标参数所提取到的状态切换时间点,对各个传感器的相应时间邻域进行状态切换检测,计算各个传感器与目标传感器的关联匹配率来判断其关联性大小。结果 利用真实的核电厂历史运行数据展开实验,通过建立的关联匹配率规则,成功地筛选出了与目标传感器具有关联性的传感器参数。结论 实验结果表明,文章所提出的方法可以更为准确地筛选出关联性参数,与常用的皮尔逊相关系数相比,文章所提出的方法准确性更高。Abstract:Introduction Nuclear power operation data is characterized by high dimension and large volume, and the complexity of the internal system of nuclear power plant makes it difficult to build a corresponding mechanism model. Therefore, it is very difficult to manually screen out relevant parameters from nuclear power data, and the introduction of non-relevant parameters will greatly affect the accuracy of the model. By means of improving the model accuracy, the purpose of accurate modeling can be reached.Method This paper proposed a correlation analysis method based on multi-scale time window. This method extracted state switch points for target parameters, classifies each sensor according to the characteristics of the data recorded by different sensors, and then designs detection windows for different kinds of sensors that meet their characteristics. The state switch detection was carried out in the corresponding time neighborhood of each sensor, and the correlation matching rate between each sensor and the target sensor was calculated to judge the correlation.Result Based on the actual historical operation data of nuclear power plant, the sensor parameters associated with the target sensor are selected successfully by the established correlation matching rate rule.Conclusion The experimental results show that the proposed method can screen out the correlation parameters more accurately. Compared with the commonly used Pearson correlation coefficient, the proposed method is more accurate.
-
表 1 状态切换时间点
Table 1 Status switch time point
序号 时间点 序号 时间点 1 2019-10-03T 11:31:39.00 7 2019-11-23T 10:37:51.00 2 2019-10-29T 11:22:42.00 8 2019-11-23T 10:42:56.00 3 2019-11-02T 13:45:35.00 9 2019-12-23T 10:50:18.00 4 2019-11-02T 13:54:07.00 10 2019-12-27T 21:30:28.00 5 2019-11-03T 05:11:15.00 11 2019-12-28T 06:03:17.00 6 2019-11-03T 05:14:37.00 — — 表 2 各传感器匹配度
Table 2 Matching degree of each sensor
序号 传感器名称 匹配度 序号 传感器名称 匹配度 1 RCV202MT 81.82% 15 RCV231MV 54.55% 2 RCV203MT 81.82% 16 RCV232MV 54.55% 3 RCV205MT 81.82% 17 RCV002MI 36.36% 4 RCV206MT 81.82% 18 DVH001ZV 9.09% 5 RCV223MT 81.82% 19 DVH002ZV 9.09% 6 RCV226MT 81.82% 20 RCV001MI 9.09% 7 RCV200MT 72.73% 21 RCV002PO 9.09% 8 RCV201MT 72.73% 22 GRE012MY 0.00% 9 RCV204MT 72.73% 23 RCP009VE 0.00% 10 RCV222MT 72.73% 24 RCP602KM 0.00% 11 RCV210MT 63.64% 25 RCP624KM 0.00% 12 RCV224MT 63.64% 26 RCV001PO 0.00% 13 RCV233MV 63.64% 27 RCV003MI 0.00% 14 RCV254MT 63.64% 28 RCV003PO 0.00% 表 3 各传感器皮尔逊系数
Table 3 Pearson coefficient of each sensor
% 序号 传感器名称 系数值 序号 传感器名称 系数值 1 RCV202MT 98.05 15 RCV231MV 96.47 2 RCV203MT 97.36 16 RCV232MV 97.78 3 RCV205MT 98.31 17 RCV002MI 66.57 4 RCV206MT 98.36 18 DVH001ZV 9.09 5 RCV223MT 22.89 19 DVH002ZV 9.09 6 RCV226MT 81.82 20 RCV001MI 4.40 7 RCV200MT 94.50 21 RCV002PO 16.93 8 RCV201MT 96.87 22 GRE012MY 17.24 9 RCV204MT 97.99 23 RCP009VE 16.84 10 RCV222MT 22.47 24 RCP602KM 0.00 11 RCV210MT 99.36 25 RCP624KM 16.97 12 RCV224MT 16.86 26 RCV001PO 4.56 13 RCV233MV 98.39 27 RCV003MI 68.75 14 RCV254MT 99.40 28 RCV003PO 49.24 表 4 检测准确率
Table 4 Accuracy of detection
方法 正确检出数/
个复核认定数/
个误检数/
个实际数/
个准确率/
%本文算法 16 1 0 17 100 皮尔逊系数 14 0 4 17 82.35 -
[1] 荣健, 刘展. 先进核能技术发展与展望 [J]. 原子能科学技术, 2020, 54(9): 1638-1643. DOI: 10.7538/yzk.2020.youxian.0348. RONG J, LIU Z. Development and prospect of advanced nuclear energy technology [J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2020, 54(9): 1638-1643. DOI: 10.7538/yzk.2020.youxian.0348.
[2] 王海洋, 荣健. 碳达峰、碳中和目标下中国核能发展路径分析 [J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54(6): 86-94. DOI: 10.11930/j.issn.1004-9649.202103141. WANG H Y, RONG J. Analysis on China's nuclear energy development path under the goal of peaking carbon emissions and achieving carbon neutrality [J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54(6): 86-94. DOI: 10.11930/j.issn.1004-9649.202103141.
[3] 蔡绍宽. 双碳目标的挑战与电力结构调整趋势展望 [J]. 南方能源建设, 2021, 8(3): 8-17. DOI: 10.16516/j.gedi.issn2095-8676.2021.03.002. CAI S K. Challenges and prospects for the trends of power structure adjustment under the goal of carbon peak and neutrality [J]. Southern Energy Construction, 2021, 8(3): 8-17. DOI: 10.16516/j.gedi.issn2095-8676.2021.03.002.
[4] 王鑫, 吴继承, 朴磊. “双碳”目标下核能发展形势思考 [J]. 核科学与工程, 2022, 42(2): 241-245. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0918.2022.02.001. WANG X, WU J C, PU L. Consideration of the development situation of nuclear power under the goal of carbon peaking and carbon neutraulity [J]. Nuclear Science and Engineering, 2022, 42(2): 241-245. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0918.2022.02.001.
[5] 蒋祖跃. 秦山核电厂反应堆保护系统及其相关设备数字化改造规划和实施策略 [J]. 原子能科学技术, 2010, 44(1): 65-69. DOI: 10.7538/yzk.2010.44.01.0065. JIANG Z Y. Upgrading planning and executive strategy for reactor protection system and relative equipment in Qinshan nuclear power plant [J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2010, 44(1): 65-69. DOI: 10.7538/yzk.2010.44.01.0065.
[6] 高麒瀚, 江德正. 智能化工艺系统设计平台技术在核电工程设计的应用探讨 [J]. 核科学与工程, 2014, 34(1): 125-133+141. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0918.2014.01.020. GAO Q H, JIANG D Z. Study on application of intelligent process system design platform technology in nuclear engineering [J]. Nuclear Science and Engineering, 2014, 34(1): 125-133+141. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0918.2014.01.020.
[7] AGRAWAL R, SRIKANT R. Fast algorithms for mining association rules in large databases [C]// Anon. Proceedings of the 20th international conference on very large data bases, Santiago de Chile, Chile, September 12-15, 1994. Santiago de Chile: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc, 1994: 487-499.
[8] 程路明, 楼平, 诸骏豪, 等. 基于APRIORI-贝叶斯优化XGBoost的电力通信网根告警预测 [J]. 电力建设, 2022, 43(1): 113-121. DOI: 10.12204/j.issn.1000-7229.2022.01.013. CHENG L M, LOU P, ZHU J H, et al. Root alarm prediction of power communication network applying APRIORI-Bayesian optimization XGBoost [J]. Electric Power Construction, 2022, 43(1): 113-121. DOI: 10.12204/j.issn.1000-7229.2022.01.013.
[9] 廖孟柯, 樊冰, 李忠政, 等. 基于改进Apriori算法的配电网设备退役信息挖掘 [J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021, 21(24): 10381-10386. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.24.039. LIAO M K, FAN B, LI Z Z, et al. Mining of distribution network equipment decommissioning factors based on improved Apriori algorithm [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(24): 10381-10386. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.24.039.
[10] HAN J W, PEI J, YIN Y W. Mining frequent patterns without candidate generation [J]. ACM SIGMOD Record, 2000, 29(2): 1-12. DOI: 10.1145/335191.335372.
[11] 肖永立, 刘松, 见伟, 等. 一种基于FP-growth算法的变电站二次设备缺陷分析方法 [J]. 电测与仪表, 2020, 57(12): 83-90. DOI: 10.19753/j.issn1001-1390.2020.12.013. XIAO Y L, LIU S, JIAN W, et al. A kind of defects analysis method for secondary device of substation based on FP-growth algorithm [J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2020, 57(12): 83-90. DOI: 10.19753/j.issn1001-1390.2020.12.013.
[12] 张斌, 滕俊杰, 满毅. 改进的并行fp-growth算法在工业设备故障诊断中的应用研究 [J]. 计算机科学, 2018, 45(增刊1): 508-512. ZHANG B, TENG J J, MAN Y. Application research of improved parallel fp-growth algorithm in fault diagnosis of industrial equipment [J]. Computer Science, 2018, 45(Supp. 1): 508-512.
[13] 方晓洁, 黄伟琼, 叶东华, 等. 分布式并行FP-growth算法在二次设备缺陷监测中的应用 [J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(8): 160-167. DOI: 10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.200715. FANG X J, HUANG W Q, YE D H, et al. Application of a distributed parallel FP-growth algorithm in secondary device defects monitoring [J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(8): 160-167. DOI: 10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.200715.
[14] 何望, 林果园. 基于FP-Growth改进算法的云服务器故障数据分析 [J]. 计算机工程与科学, 2020, 42(5): 770-775. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2020.05.002. HE W, LIN G Y. Analysis of cloud server fault data based on improved FP-Growth algorithm [J]. Computer Engineering & Science, 2020, 42(5): 770-775. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2020.05.002.
[15] 纪德洋, 金锋, 冬雷, 等. 基于皮尔逊相关系数的光伏电站数据修复 [J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42(4): 1514-1522. DOI: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.211172. JI D Y, JIN F, DONG L, et al. Data repairing of photovoltaic power plant based on Pearson correlation coefficient [J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42(4): 1514-1522. DOI: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.211172.
[16] 张婧, 任刚. 城市道路交通拥堵状态时空相关性分析 [J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2015, 15(2): 175-181. DOI: 10.16097/j.cnki.1009-6744.2015.02.027. ZHANG J, REN G. Spatio-temporal correlation analysis of urban traffic congestion diffusion [J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2015, 15(2): 175-181. DOI: 10.16097/j.cnki.1009-6744.2015.02.027.
[17] 张华, 龙呈, 胡思洋, 等. 基于层次聚类法与皮尔逊相关系数的配电网拓扑校验方法 [J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(21): 88-96. DOI: 10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.210075. ZHANG H, LONG C, HU S Y, et al. Topology verification method of a distribution network based on hierarchical clustering and the Pearson correlation coefficient [J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(21): 88-96. DOI: 10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.210075.
[18] 刘永阔, 谢春丽, 成守宇, 等. 核电站分布式智能故障诊断系统研究与设计 [J]. 原子能科学技术, 2011, 45(6): 688-694. LIU Y K, XIE C L, CHENG S Y, et al. Research and design of distributed intelligence fault diagnosis system in nuclear power plant [J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2011, 45(6): 688-694.
[19] JUSTUSSON B J. Median filtering: statistical properties [M]//HUANG T S. Two-dimensional digital signal prcessing II: transform and median filters. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 1981. DOI: 10.1007/BFB0057597.
[20] 叶林, 滕景竹, 蓝海波, 等. 变尺度时间窗口和波动特征提取的短期风电功率组合预测 [J]. 电力系统自动化, 2017, 41(17): 29-36. DOI: 10.7500/AEPS20161201016. YE L, TENG J Z, LAN H B, et al. Combined prediction for short-term wind power based on variable time window and feature extraction [J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2017, 41(17): 29-36. DOI: 10.7500/AEPS20161201016.




 下载:
下载: