-
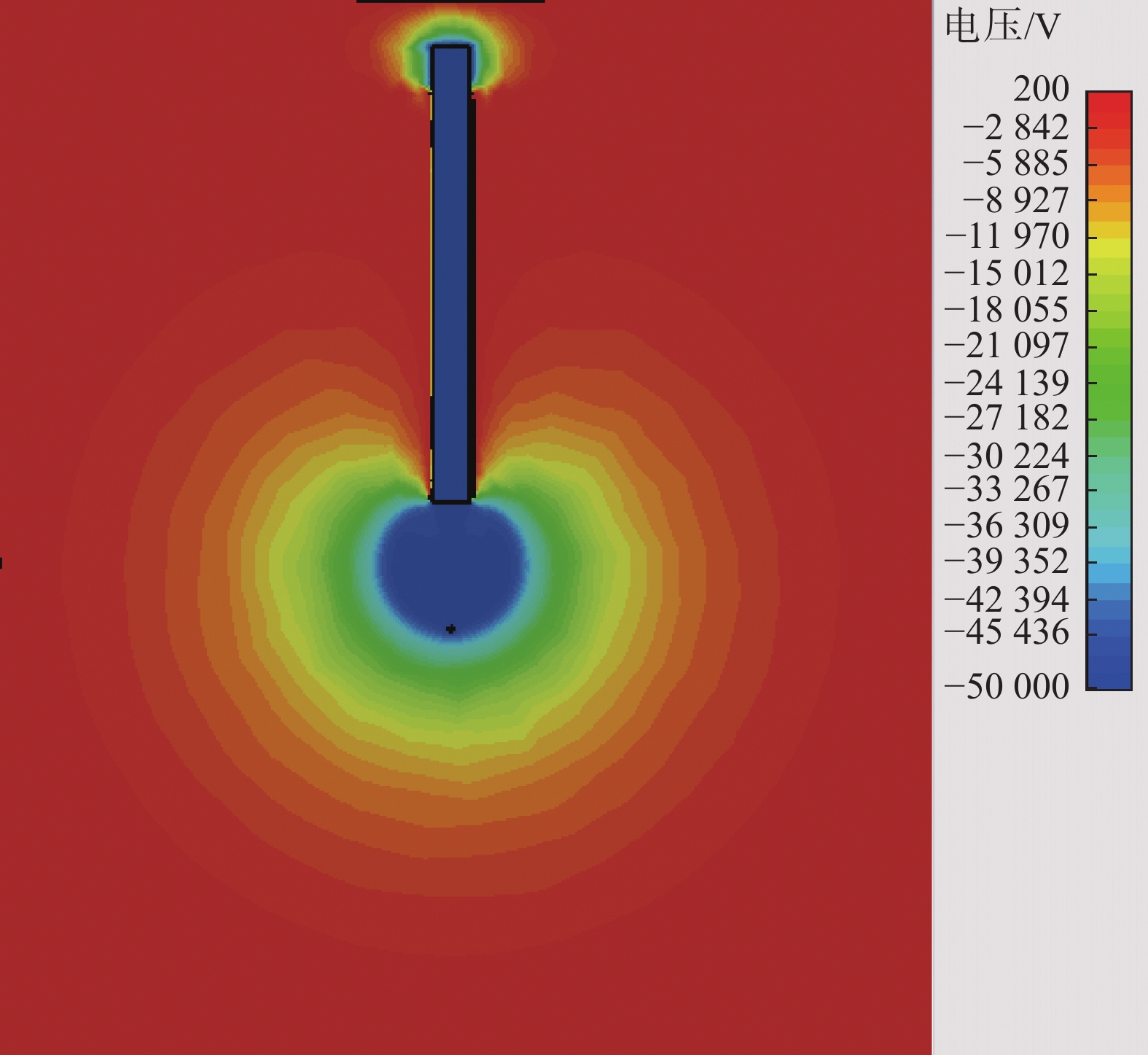
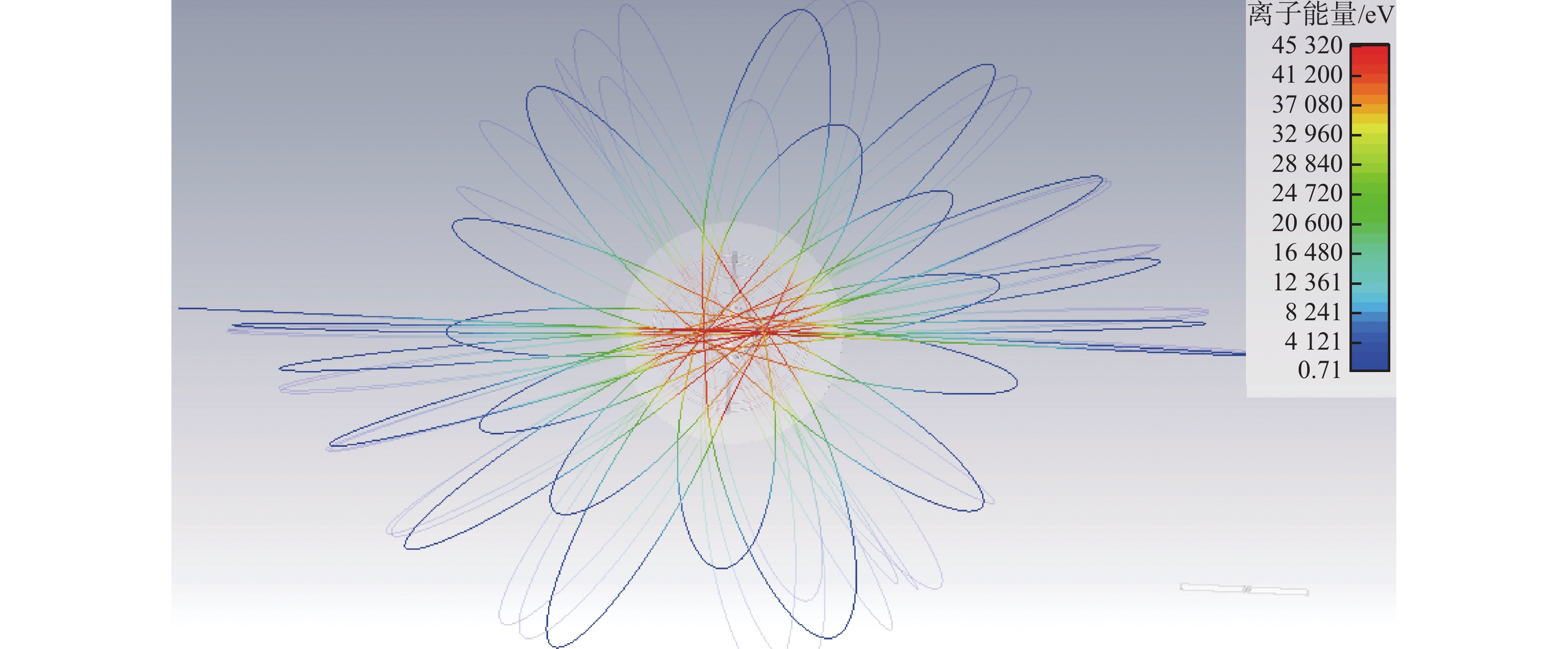
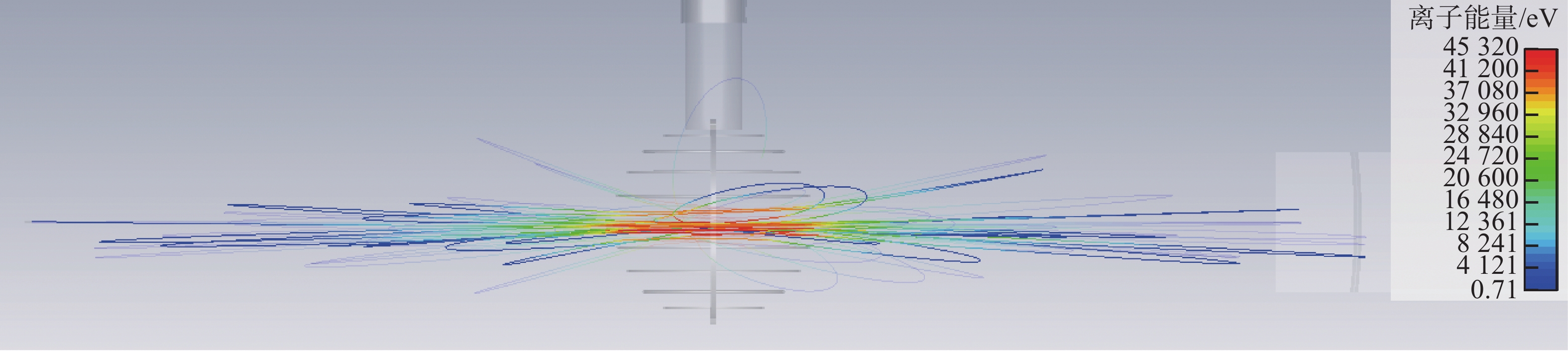
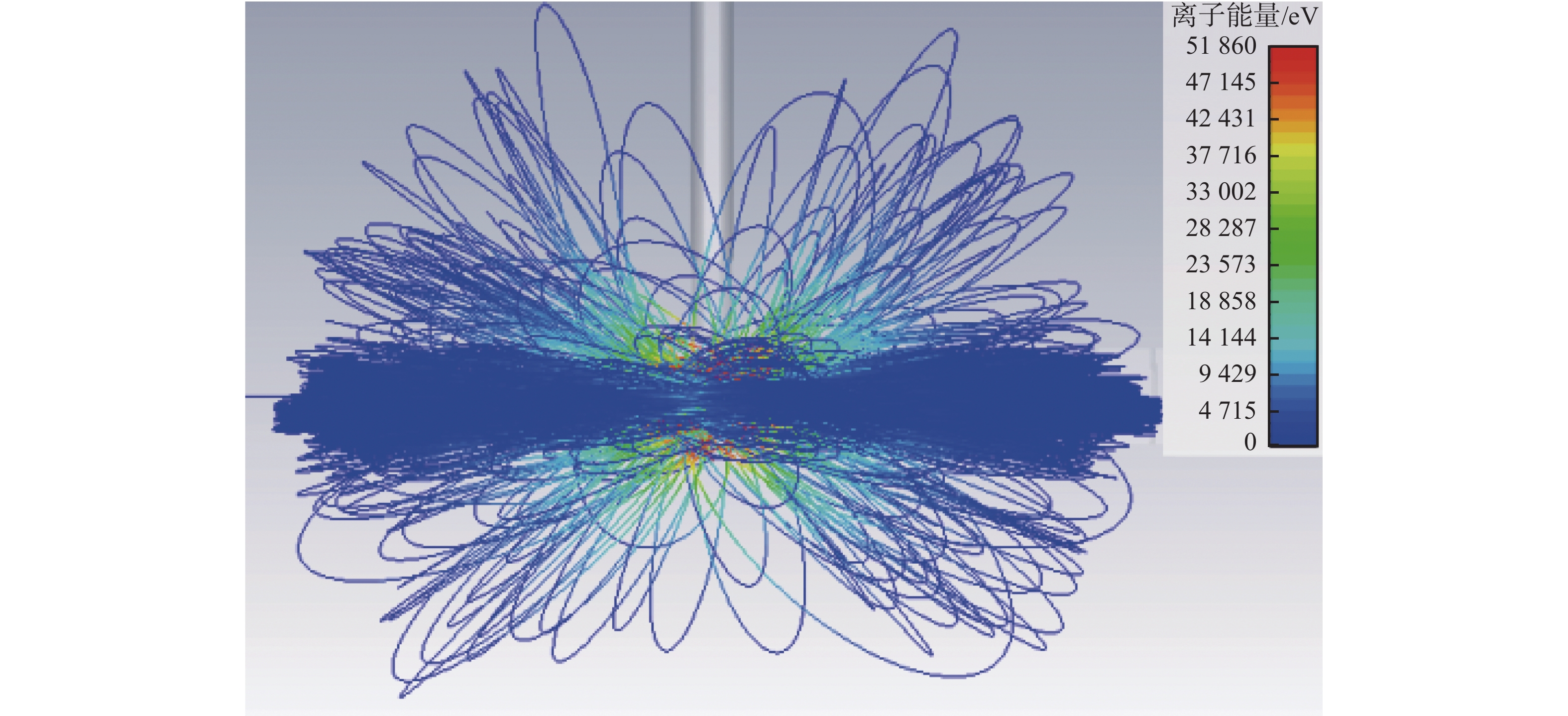
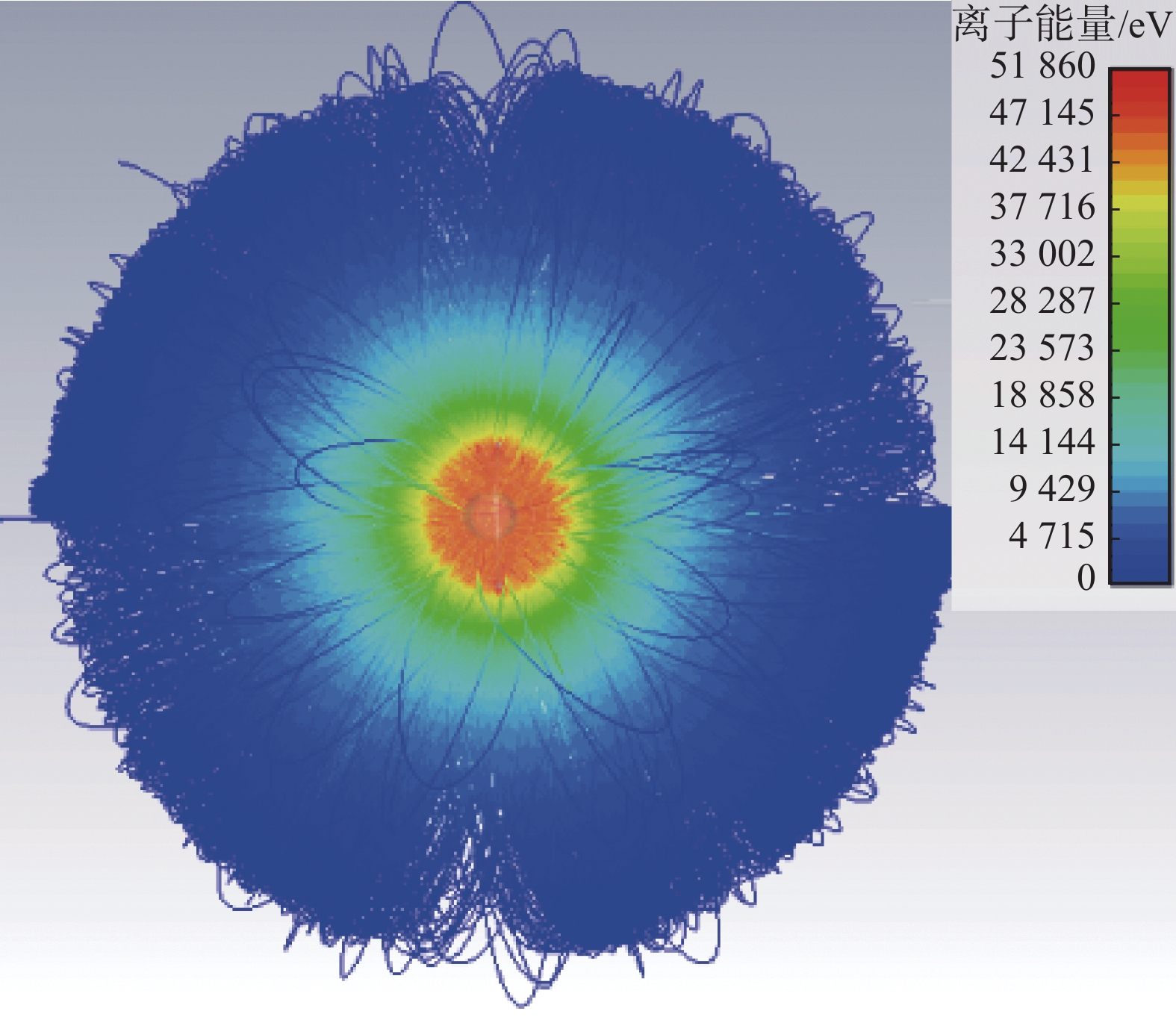
摘要:目的 惯性静电约束聚变是一种小型聚变装置。文章目的是要解决惯性静电约束聚变装置目前存在阴极熔化和Q值低等问题。方法 首先分析了产生这些问题的原因,然后提出一种内离子源惯性静电约束聚变技术,以便降低离子在约束过程中的损失,解决阴极熔化问题,同时提高装置内的真空度,以及提高装置的Q值。结果 最后通过估算的方法定性分析了中子产额的提高,并通过数值仿真模拟计算,模拟了内离子源惯性静电约束聚变装置内的非常复杂的离子运动情况,得到了各向异性的离子运动轨迹。结论 根据估算和数值模拟计算结果,确证了内离子源惯性静电约束聚变技术的可行性,可以解决阴极熔化和Q值低的问题。Abstract:Introduction The inertial electrostatic confinement (IEC) fusion facility is a small fusion device. This paper aims to solve the problems of IEC fusion devices, such as the cathode melting, the very low Q value, and so on.Method This paper first analyzed the reasons for these problems, and then a new type of inner ion source IEC fusion was proposed to decrease the ion loss during the confinement process, solve the cathode melting, and increase the vacuum in the device and the Q value.Result At last, the improvement of neutron yield is qualitatively analyzed through the estimation, the very complex ion motion inside the fusion device is simulated through numerical simulation calculation, and anisotropic ion motion trajectories are obtained.Conclusion Based on estimation and numerical simulation results, the feasibility of the IEC with an inner ion source is confirmed, which can solve the problems of cathode melting and low Q value.
-
Keywords:
- Q value /
- inertial electrostatic confinement /
- fusion /
- neutron source /
- inner ion source /
- simulation
-
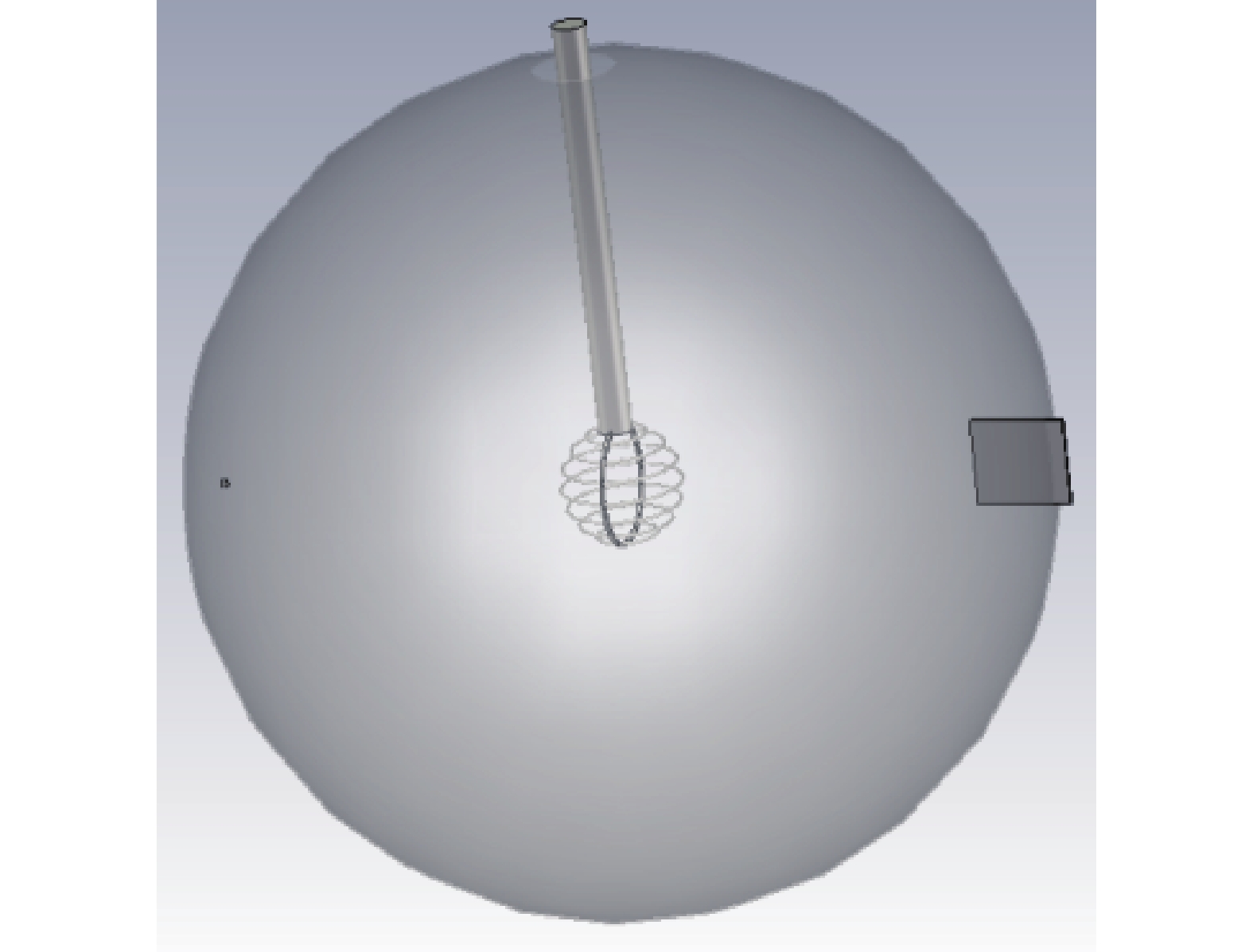
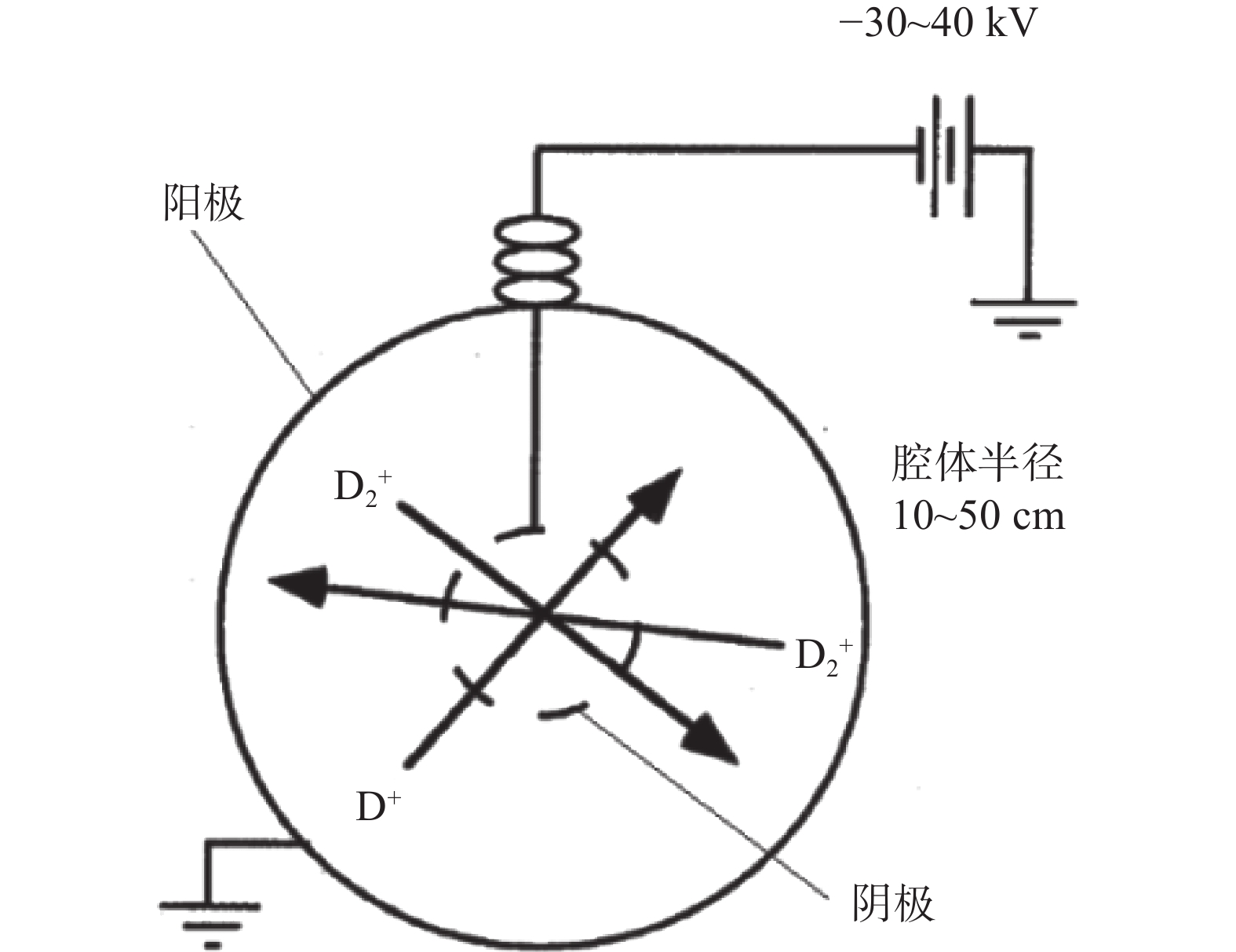
表 1 内离子源IEC模拟计算参数
Table 1 The simulation calculation parameters of inner ion source IEC
参数 数值 阴极高压/kV 50 离子流强/mA 0.1 阳极直径/m 0.5 阴极直径/m 0.01 离子枪直径/mm 1 -
[1] 胡星光, 宋执权, 高格, 等. ITER聚变装置及其电源系统 [J]. 南方能源建设, 2022, 9(2): 19-25. DOI: 10.16516/j.gedi.issn2095-8676.2022.02.002. HU X G, SONG Z Q, GAO G, et al. ITER fusion device and its power supply system [J]. Southern energy construction, 2022, 9(2): 19-25. DOI: 10.16516/j.gedi.issn2095-8676.2022.02.002.
[2] MILEY H G, MURALI S K. Inertial electrostatic confinement (IEC) fusion: fundamentals and applications [M]. New York: Springer, 2014. DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4614-9338-9.
[3] KULCINSKI G L, SANTARIUS J F. Non-electric applications of the inertial electrostatic confinement fusion concept [J]. Fusion science and technology, 2013, 64(2): 365-372. DOI: 10.13182/FST13-A18104.
[4] KULCINSKI G L. Non-electric applications of fusion energy - an important precursor to commercial electric power [J]. Fusion technology, 1998, 34(3P2): 477-783. DOI: 10.13182/FST98-A11963658.
[5] KULCINSKI G L, SANTARIUS J F. New opportunities for fusion in the 21st century - advanced fuels [J]. Fusion technology, 2001, 39(2P2): 480-485. DOI: 10.13182/FST01-A11963282.
[6] MCCARTHY K, BAKER C, CHENG E, et al. Nonelectric applications of fusion [J]. Journal of fusion energy, 2002, 21(3/4): 121-153. DOI: 10.1023/A:1026281007353.
[7] HIRSCH R L. Inertial-electrostatic confinement of ionized fusion gases [J]. Journal of applied physics, 1967, 38(11): 4522-4534. DOI: 10.1063/1.1709162.
[8] SANTARIUS J F, EMMERT G A. Atomic physics effects on convergent, spherically symmetric ion flow [C]//Presented at the 8th US–Japan IEC Workshop, May 10-12, 2006. Osaka, 2006.
[9] DOBSON C C, HRBUD I. Electron density and two-channel neutron emission measurements in steady-state spherical inertial-electrostatically confined plasmas, with review of the one-dimensional kinetic model [J]. Journal of applied physics, 2004, 96(1): 94-108. DOI: 10.1063/1.1755854.
[10] FARNSWORTH P T. Electric discharge device for producing interactions between nuclei: 3258402 [P]. 1966-06-28.
[11] LAVRENTYEV O A. Investigation of plasma containment by a magnetic field layer [J]. Ukr. Fiz. Zh. , 1963, 8: 446.
[12] BUSSARD R W. Method and apparatus for controlling charged particles: 4826646 [P]. 1989-05-02.
[13] BUSSARD R W. Some physics considerations of magnetic inertial-electrostatic confinement: a new concept for spherical converging-flow fusion [J]. Fusion technology, 1991, 19(2): 273-293. DOI: 10.13182/FST91-A29364.
[14] BARNES D C, NEBEL R A, TURNER L. Production and application of dense Penning trap plasmas [J]. Physics of fluids B:plasma physics, 1993, 5(10): 3651-3660. DOI: 10.1063/1.860837.
[15] BARNES D C, MITCHELL T B, SCHAUER M M. Beyond the Brillouin limit with the Penning fusion experiment [J]. Physics of plasmas, 1997, 4(5): 1745-1751. DOI: 10.1063/1.872276.
[16] RIDER T H. A general critique of inertial-electrostatic confinement fusion systems [J]. Physics of plasmas, 1995, 2(6): 1853-1872. DOI: 10.1063/1.871273.
[17] BAKR M, WULFKÜHLER J P, MUKAI K, et al. Evaluation of 3D printed buckyball-shaped cathodes of titanium and stainless-steel for IEC fusion system [J]. Physics of plasmas, 2021, 28(1): 012706. DOI: 10.1063/5.0033342.
[18] TOLEDO G E B. Analysis of fast neutral particles in inertial electrostatic confinement fusion devices [D]. Madison: University of Wisconsin-Madison, 2014.
[19] KIPRITIDIS J, KHACHAN J, FITZGERALD M, et al. Absolute densities of energetic hydrogen ion species in an abnormal hollow cathode discharge [J]. Physical review E, 2008, 77(6): 066405. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.77.066405.
[20] 李金海, 刘丹. 一种内离子源惯性静电约束聚变装置: 202010138339.3 [P]. 2020-06-05. LI J H, LIU D. One kind of IEC with inner ion source: 202010138339.3 [P]. 2020-06-05.
[21] GHAMMAS H, NASRABADI M N. Investigating the effect of changing parameters in the IEC device in comparative study [J]. Nuclear engineering and technology, 2024, 56(1): 292-300. DOI: 10.1016/j.net.2023.09.038.
[22] BAKR M, SAKABE T, WULFKÜHLER J P, et al. Influence of electrodes' geometrical properties on the neutron production rate of a discharge fusion neutron source [J]. Physical of plasmas, 2023, 30(3): 032701. DOI: 10.1063/5.0134631.
[23] MILEY G H. A portable neutron/tunable X-ray source based on inertial electrostatic confinement [J]. Nuclear instruments and methods in physics research section A: accelerators, spectrometers, detectors and associated equipment, 1999, 422(1/3): 16-20. DOI: 10.1016/S0168-9002(98)01108-5.
[24] GU Y B, MILEY G H. Experimental study of potential structure in a spherical IEC fusion device [J]. IEEE transactions on plasma science, 2000, 28(1): 331-346. DOI: 10.1109/27.842929.
[25] MURALI S K, SANTARIUS J F, KULCINSKI G L. Effects of the cathode grid wires on fusion proton measurements in inertial-electrostatic confinement devices [J]. IEEE transactions on plasma science, 2011, 39(2): 749-755. DOI: 10.1109/TPS.2010.2090542.




 下载:
下载: