-
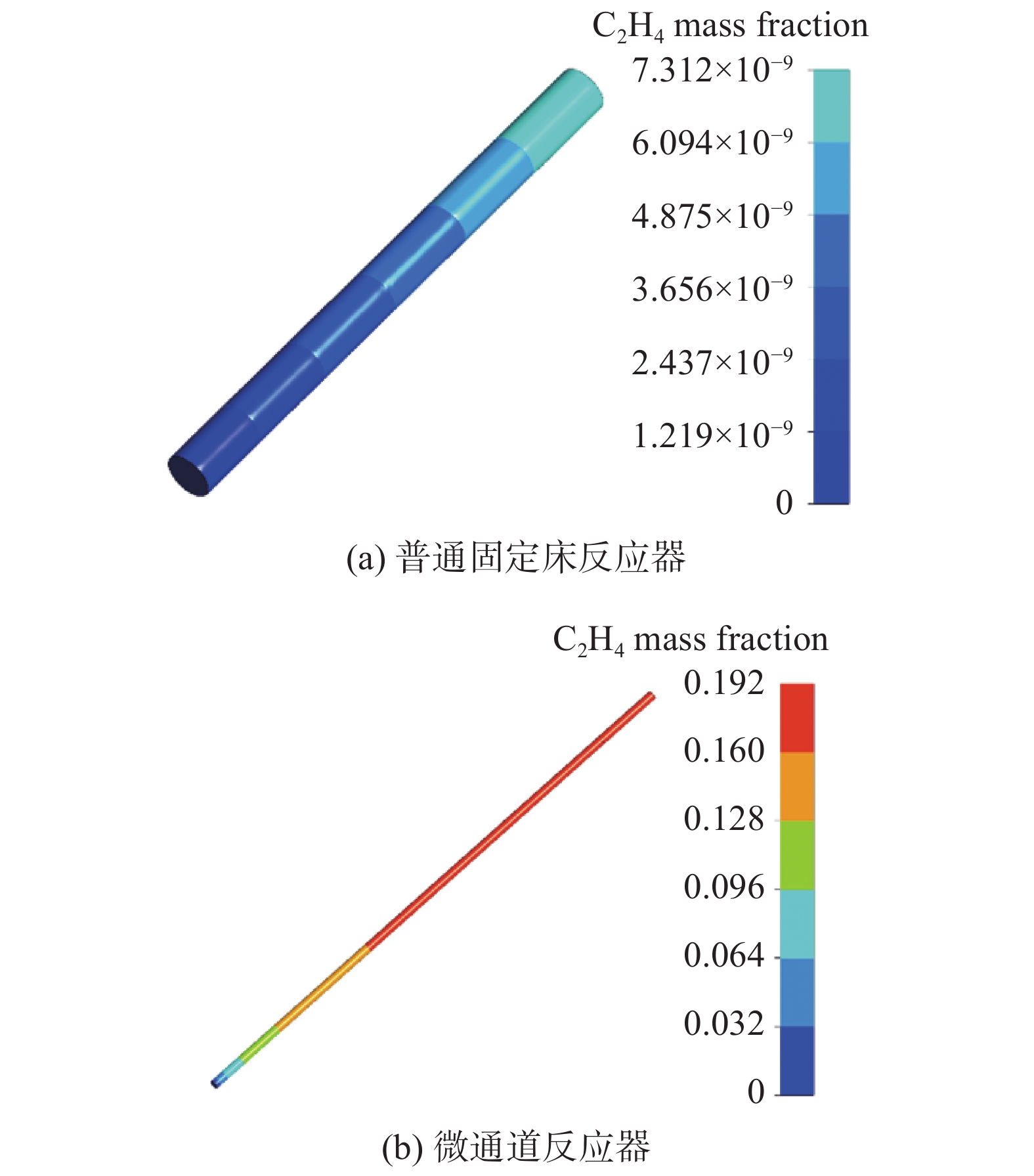
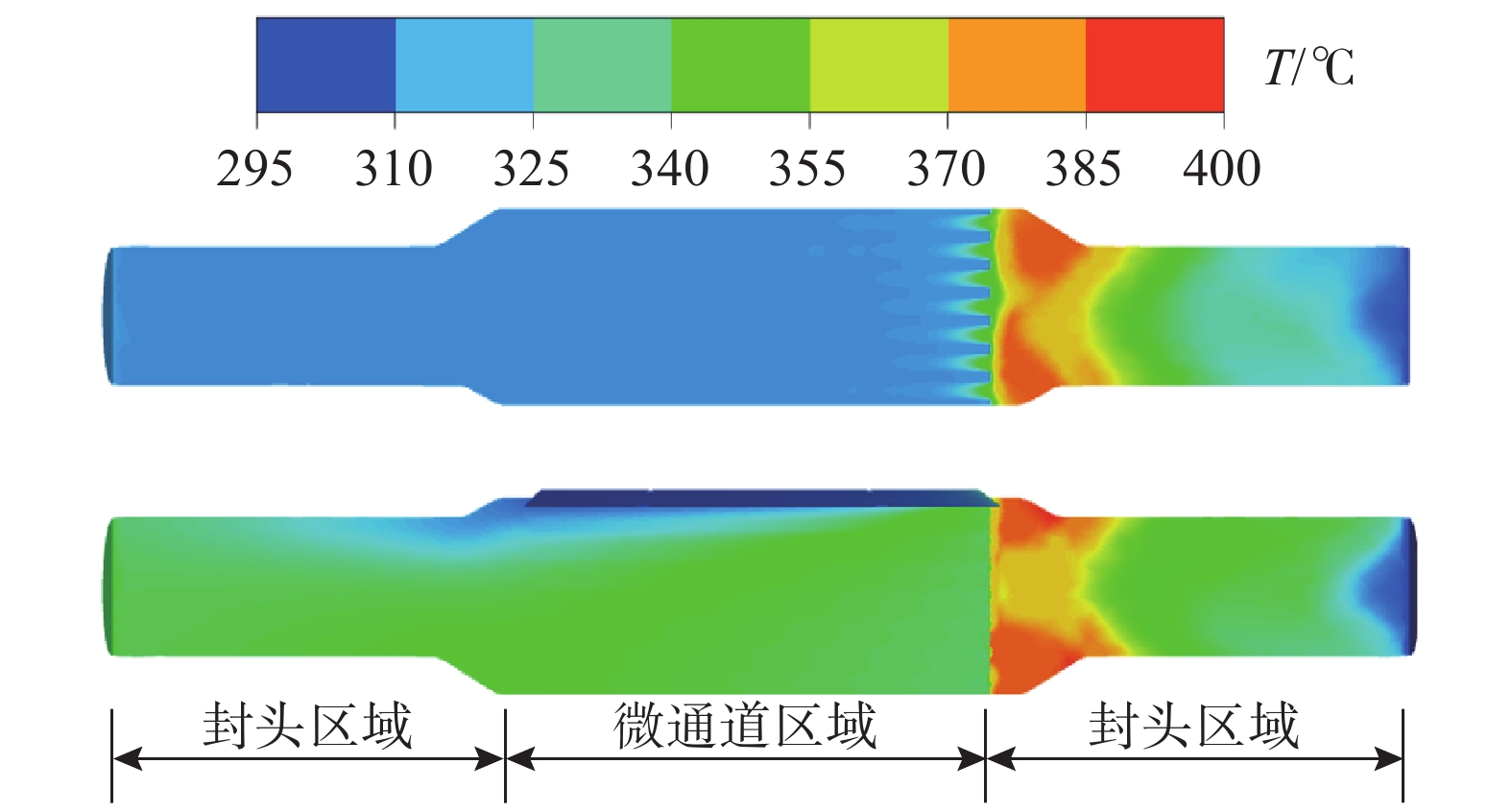
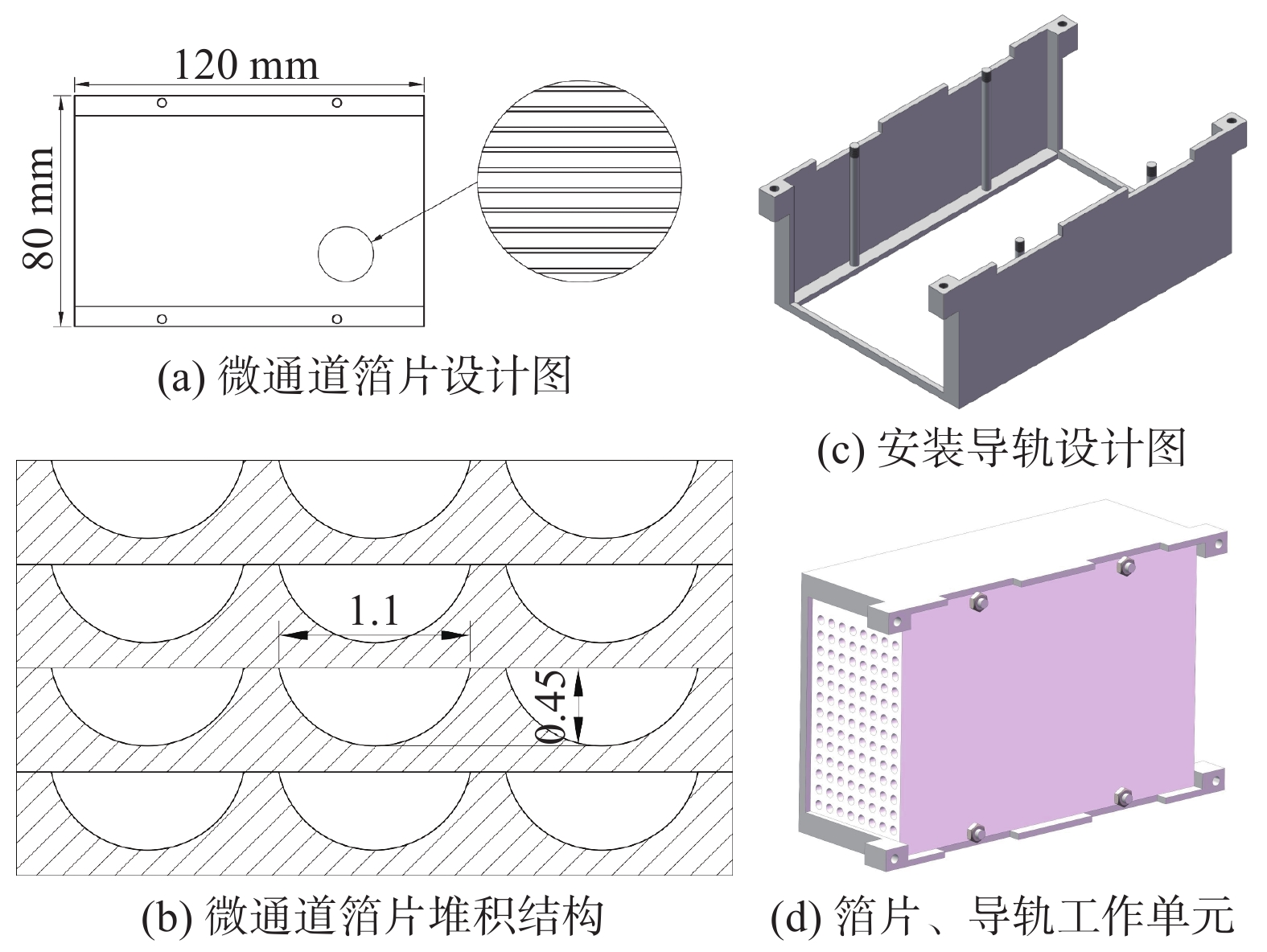
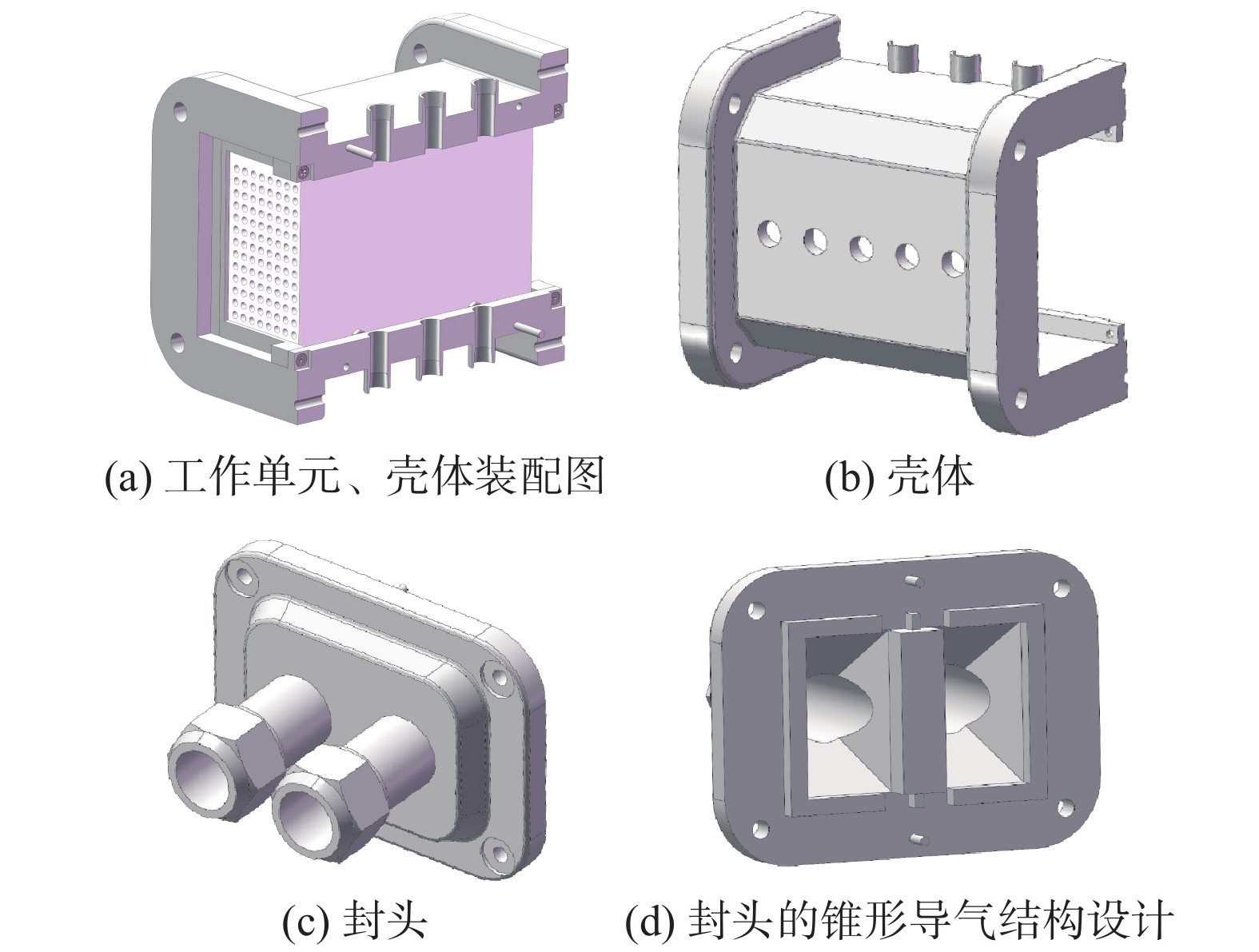
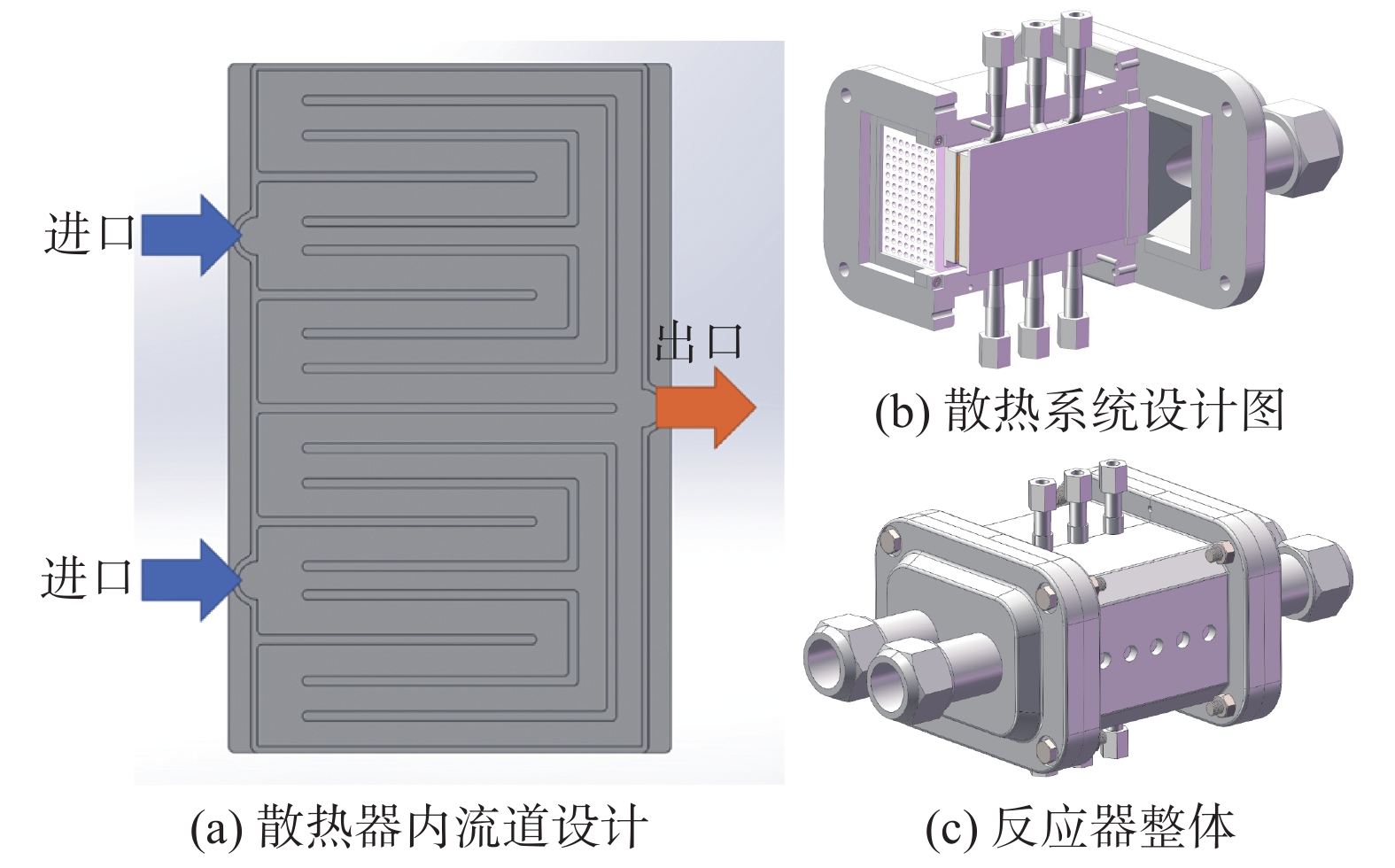
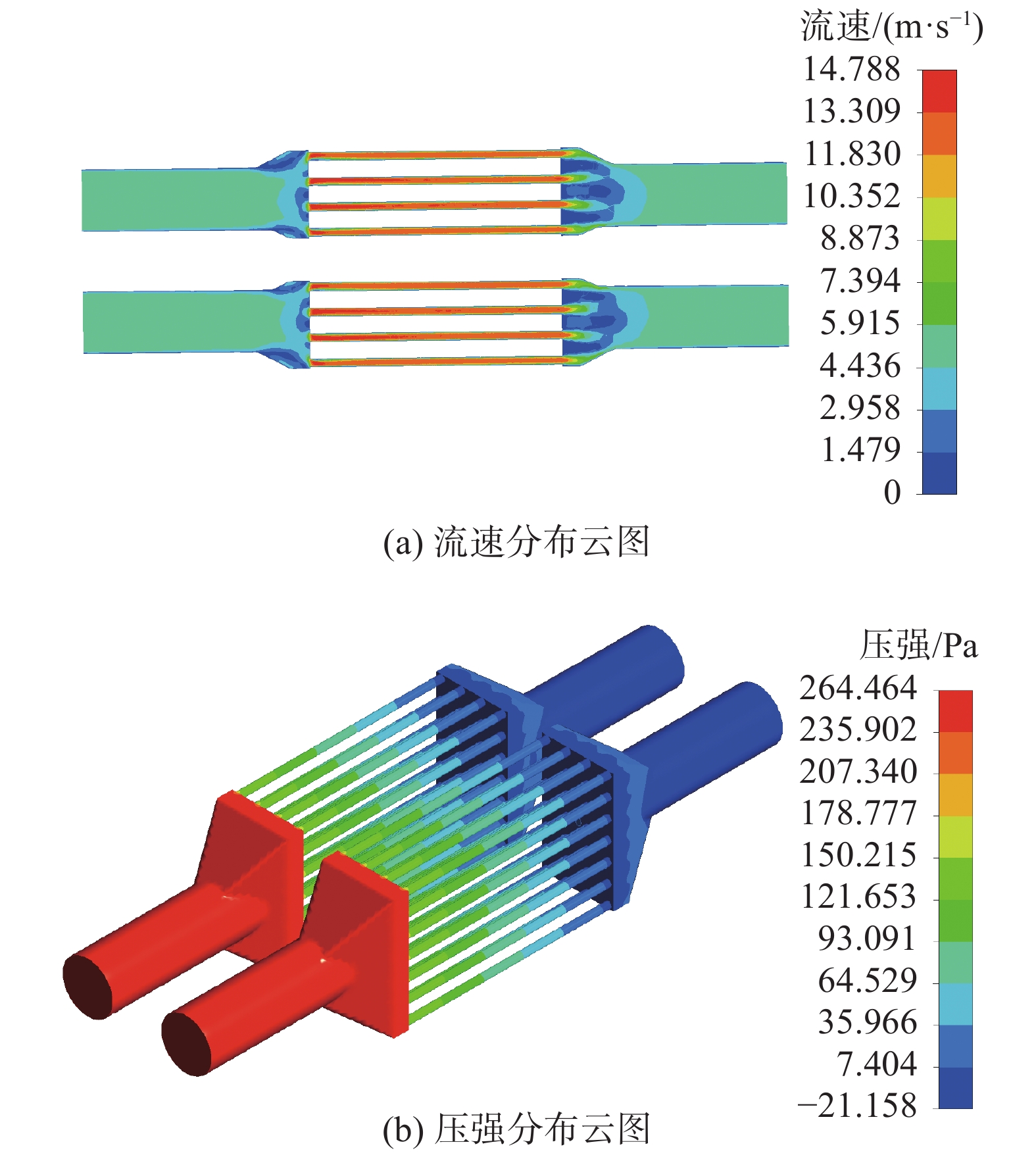
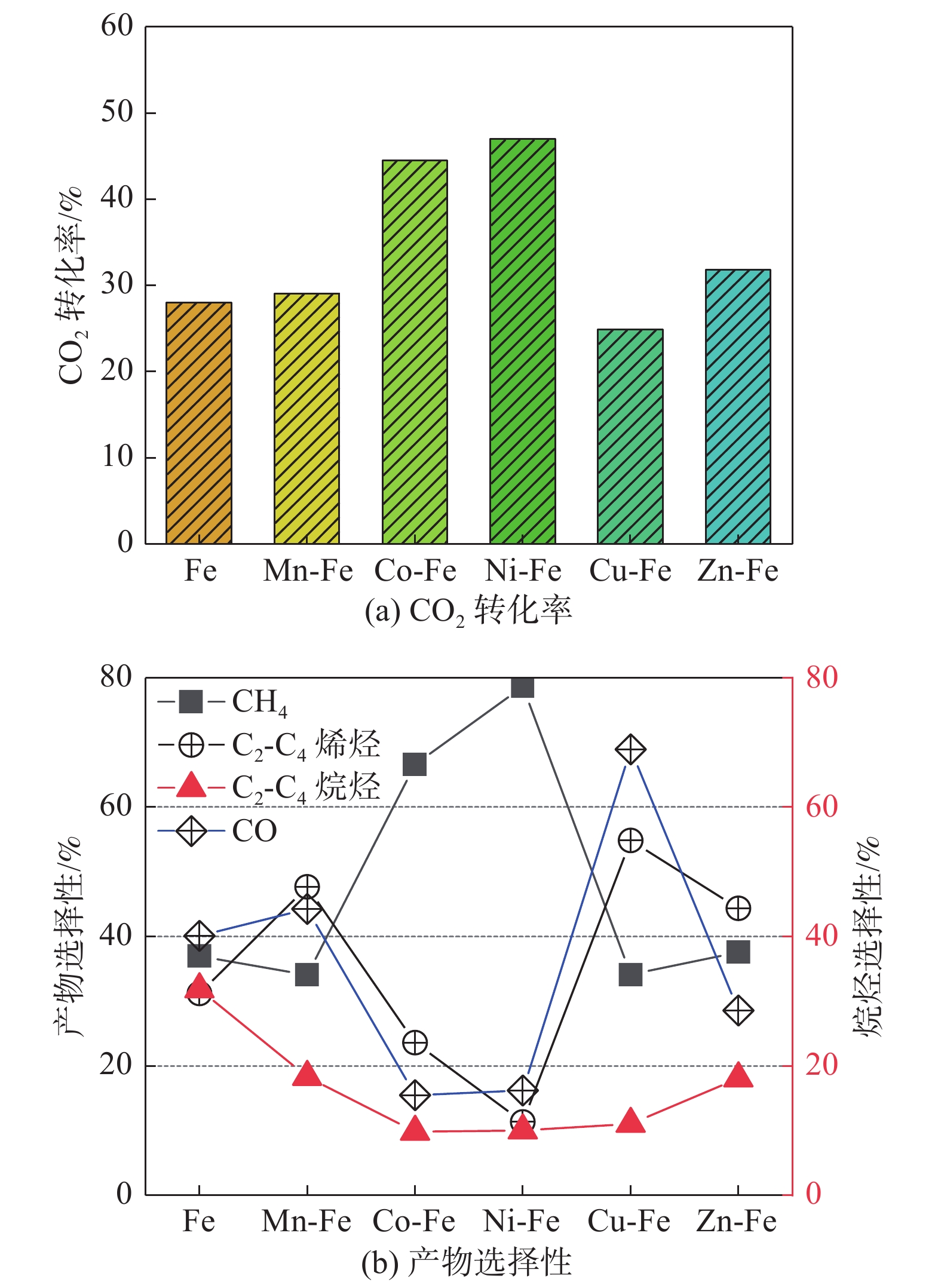
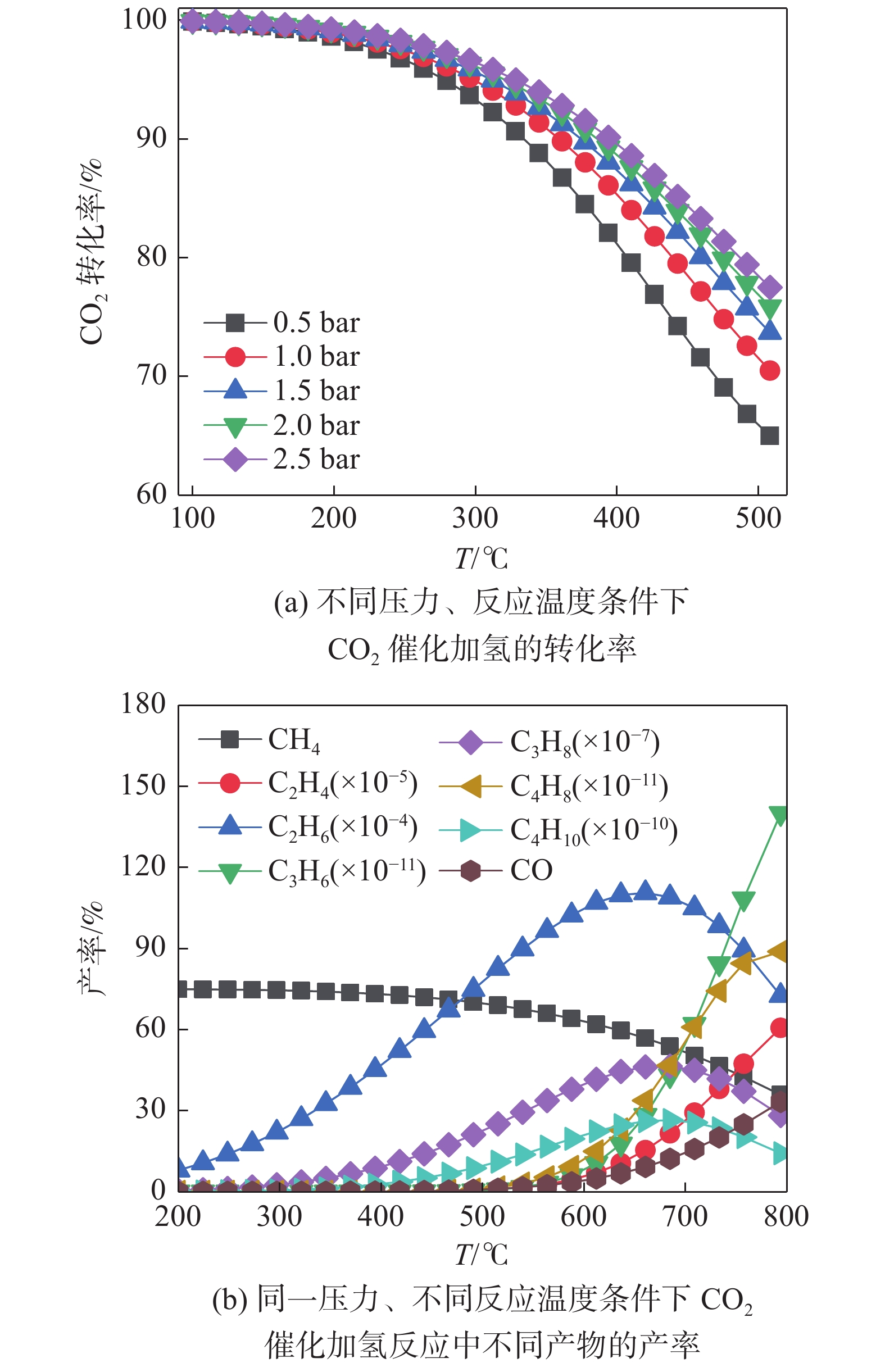
摘要:目的 CO2催化加氢合成燃料是一种经济可行、可大规模实施的CO2利用技术,能够解决环境和资源短缺的问题,近年来获得了国内外广泛的关注。文章旨在研究开发1种CO2催化加氢合成碳氢燃料的微通道反应器。方法 通过采用热力学计算-催化剂制备-反应器设计-结构优化-性能测试的设计思路进行分析。结果 热力学理论分析表明:CO2催化加氢可以形成碳氢燃料;开发了6种铁基催化剂,从而提高碳氢燃料合成的反应速率;基于流体数值模拟,设计并优化了微通道反应器的结构,该反应器具有结构简单紧凑、传热传质能力强等优点。实验结果表明:Zn-Fe催化剂表现出最好的CO2催化加氢合成低碳烯烃性能,CO2转化率和低碳烯烃选择性分别为32%和44%。结论 设计的微通道反应器具备CO2资源化利用合成碳氢燃料的功能,对我国应对气候变化、双碳目标实现以及碳氢燃料产业发展具有重要的意义。Abstract:Introduction CO2 catalytic hydrogenation for fuel synthesis is an economically feasible and large-scale implementable technology for CO2 utilization, which can solve the problems of environment and resource shortage, and has gained wide attention in recent years. In this work, a microchannel reactor for CO2 catalytic hydrogenation to synthesize hydrocarbon fuels is developed.Method Based on the design concept of thermodynamic calculation, catalyst preparation, reactor design, structure optimization and performance testing, an anlysis was carried out.Result The thermodynamic analysis shows that hydrocarbon fuels can be produced from CO2 catalytic hydrogenation. Six iron-based catalysts are developed to improve the reaction rate of hydrocarbon fuel synthesis. Based on the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation, the structure of the microchannel reactor is designed and optimized. The microchannel reactor has the advantages of simple-compact structure and strong heat-mass transfer capability. The experimental results show that the Zn-Fe catalyst exhibits the best performance of CO2 catalytic hydrogenation for the synthesis of low-carbon olefins. CO2 conversion and low-carbon olefins selectivity are 32% and 44% respectively.Conclusion The microchannel reactor designed in this work has the dual functions of CO2 utilization for hydrocarbon fuel synthesis, which is of great significance to China's response to climate change, the realization of the dual-carbon target and the development of hydrocarbon fuel industry.
-
[1] 罗海中, 吴大卫, 范永春, 等. 碳中和背景下CCUS技术发展及广东离岸封存潜力评估 [J]. 南方能源建设, 2023, 10(6): 1-13. DOI: 10.16516/j.gedi.issn2095-8676.2023.06.001. LUO H Z, WU D W, FAN Y C, et al. Development of CCUS technology in the context of carbon neutrality and assessment of the potential for offshore storage in Guangdong province [J]. Southern energy construction, 2023, 10(6): 1-13. DOI: 10.16516/j.gedi.issn2095-8676.2023.06.001.
[2] SAEIDI S, NAJARI S, HESSEL V, et al. Recent advances in CO2 hydrogenation to value-added products: current challenges and future directions [J]. Progress in energy and combustion science, 2021, 85: 100905. DOI: 10.1016/j.pecs.2021.100905.
[3] YANG Y J, ZHANG J C, LIU J, et al. Nickel nanoparticles encapsulated in SSZ-13 cage for highly efficient CO2 hydrogenation [J]. Energy & fuels, 2021, 35(16): 13240-13248. DOI: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.1c01881.
[4] HUA Z X, YANG Y J, LIU J. Direct hydrogenation of carbon dioxide to value-added aromatics [J]. Coordination chemistry reviews, 2023, 478: 214982. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2022.214982.
[5] KARAKAYA C, PARKS J. Thermochemical processes for CO2 hydrogenation to fuels and chemicals: challenges and opportunities [J]. Applications in energy and combustion science, 2023, 15: 100171. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaecs.2023.100171.
[6] JIANG X, NIE X W, GUO X W, et al. Recent advances in carbon dioxide hydrogenation to methanol via heterogeneous catalysis [J]. Chemical reviews, 2020, 120(15): 7984-8034. DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00723.
[7] JIANG Y J, WANG K Z, WANG Y, et al. Recent advances in thermocatalytic hydrogenation of carbon dioxide to light olefins and liquid fuels via modified fischer-tropsch pathway [J]. Journal of CO2 utilization, 2023, 67: 102321. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2022.102321.
[8] GAO X H, ATCHIMARUNGSRI T, MA Q X, et al. Realizing efficient carbon dioxide hydrogenation to liquid hydrocarbons by tandem catalysis design [J]. EnergyChem, 2020, 2(4): 100038. DOI: 10.1016/j.enchem.2020.100038.
[9] FRANCO F, RETTENMAIER C, JEON H S, et al. Transition metal-based catalysts for the electrochemical CO2 reduction: from atoms and molecules to nanostructured materials [J]. Chemical society reviews, 2020, 49(19): 6884-6946. DOI: 10.1039/D0CS00 835D.
[10] ARTZ J, MÜLLER T E, THENERT K, et al. Sustainable conversion of carbon dioxide: an integrated review of catalysis and life cycle assessment [J]. Chemical reviews, 2018, 118(2): 434-504. DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00435.
[11] QIAO J L, LIU Y Y, HONG F, et al. A review of catalysts for the electroreduction of carbon dioxide to produce low-carbon fuels [J]. Chemical society reviews, 2014, 43(2): 631-675. DOI: 10.1039/C3CS60323G.
[12] YANG Z Y, QI Y, WANG F L, et al. State-of-the-art advancements in photo-assisted CO2 hydrogenation: recent progress in catalyst development and reaction mechanisms [J]. Journal of materials chemistry A, 2020, 8(47): 24868-24894. DOI: 10.1039/D0TA08781E.
[13] YANG S Y, ZHANG L, WANG Z J. Advances in the preparation of light alkene from carbon dioxide by hydrogenation [J]. Fuel, 2022, 324: 124503. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.124503.
[14] ZHONG J W, YANG X F, WU Z L, et al. State of the art and perspectives in heterogeneous catalysis of CO2 hydrogenation to methanol [J]. Chemical society reviews, 2020, 49(5): 1385-1413. DOI: 10.1039/C9CS00614A.
[15] ASHOK J, PATI S, HONGMANOROM P, et al. A review of recent catalyst advances in CO2 methanation processes [J]. Catalysis today, 2020, 356: 471-489. DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2020.07.023.
[16] WEI J, YAO R W, HAN Y, et al. Towards the development of the emerging process of CO2 heterogenous hydrogenation into high-value unsaturated heavy hydrocarbons [J]. Chemical society reviews, 2021, 50(19): 10764-10805. DOI: 10.1039/D1CS00260K.
[17] BAILERA M, LISBONA P, ROMEO L M, et al. Power to gas projects review: lab, pilot and demo plants for storing renewable energy and CO2 [J]. Renewable and sustainable energy reviews, 2017, 69: 292-312. DOI: 10.1016/j.rser.2016.11.130.
[18] WULF C, LINBEN J, ZAPP P. Review of power-to-gas projects in Europe [J]. Energy procedia, 2018, 155: 367-378. DOI: 10.1016/j.egypro.2018.11.041.
[19] THEMA M, BAUER F, STERNER M. Power-to-gas: electrolysis and methanation status review [J]. Renewable and sustainable energy reviews, 2019, 112: 775-787. DOI: 10.1016/j.rser.2019.06.030.
[20] 郭嘉懿, 何育荣, 马晶晶, 等. 二氧化碳催化加氢制甲醇研究进展 [J]. 洁净煤技术, 2023, 29(4): 49-64. DOI: 10.13226/j.issn.1006-6772.RM22092601. GUO J Y, HE Y R, MA J J, et al. Research progress on catalytic hydrogenation of carbon dioxide to methanol [J]. Clean coal technology, 2023, 29(4): 49-64. DOI: 10.13226/j.issn.1006-6772.RM22092601.
[21] 云梁, 李国峰. CO2催化加氢制甲醇技术研究进展 [J]. 工业催化, 2022, 30(4): 13-17. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1143.2022.04.003. YUN L, LI G F. Research progress on catalytic hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol [J]. Industrial catalysis, 2022, 30(4): 13-17. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1143.2022.04.003.
[22] WANG D, XIE Z H, POROSOFF M D, et al. Recent advances in carbon dioxide hydrogenation to produce olefins and aromatics [J]. Chem, 2021, 7(9): 2277-2311. DOI: 10.1016/j.chempr.2021.02.024.
[23] MARQUES MOTA F, KIM D H. From CO2 methanation to ambitious long-chain hydrocarbons: alternative fuels paving the path to sustainability [J]. Chemical society reviews, 2019, 48(1): 205-259. DOI: 10.1039/C8CS00527C.
[24] POROSOFF M D, YAN B H, CHEN J G. Catalytic reduction of CO2 by H2 for synthesis of CO, methanol and hydrocarbons: challenges and opportunities [J]. Energy & environmental science, 2016, 9(1): 62-73. DOI: 10.1039/C5EE02657A.




 下载:
下载: