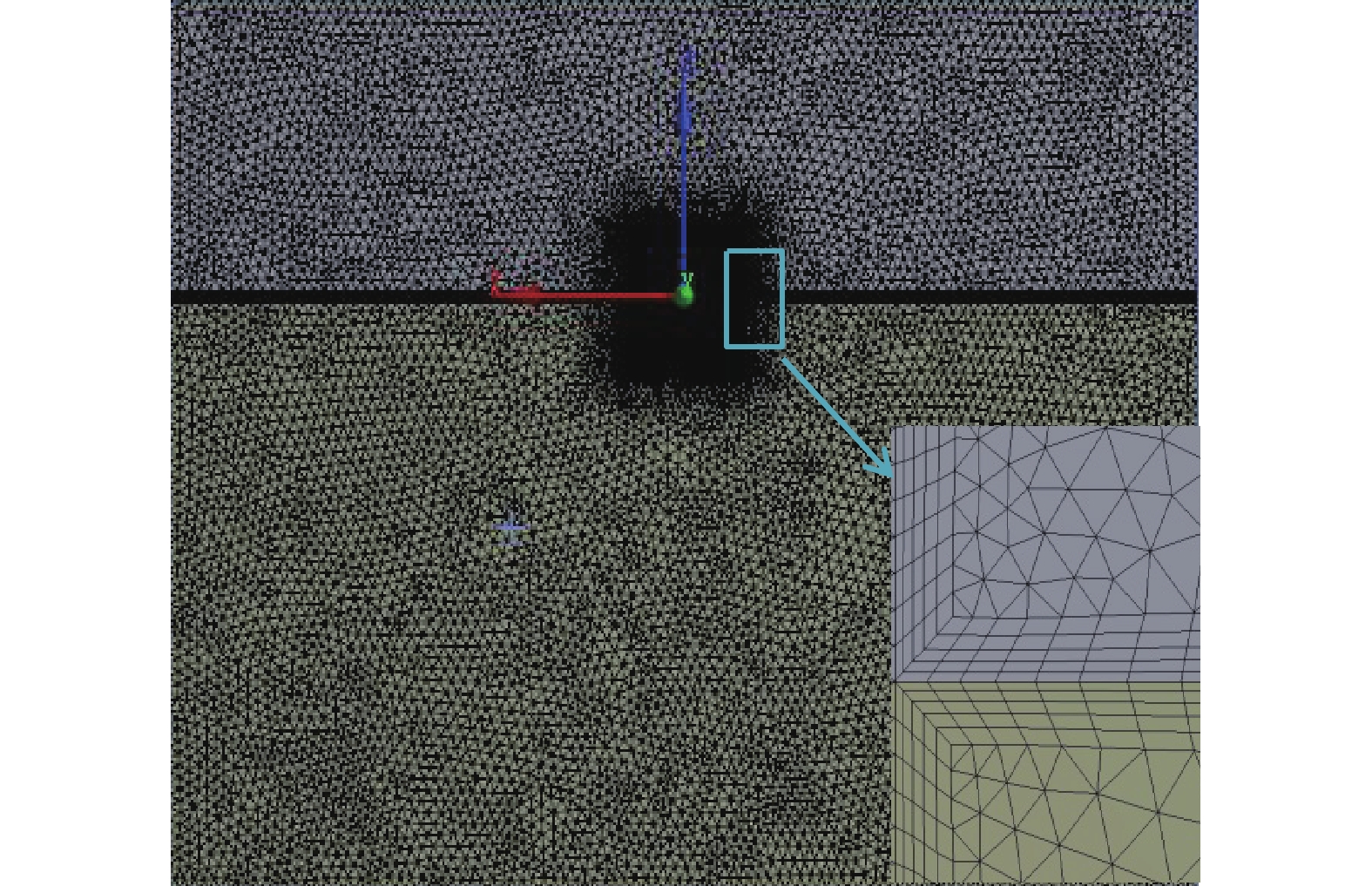
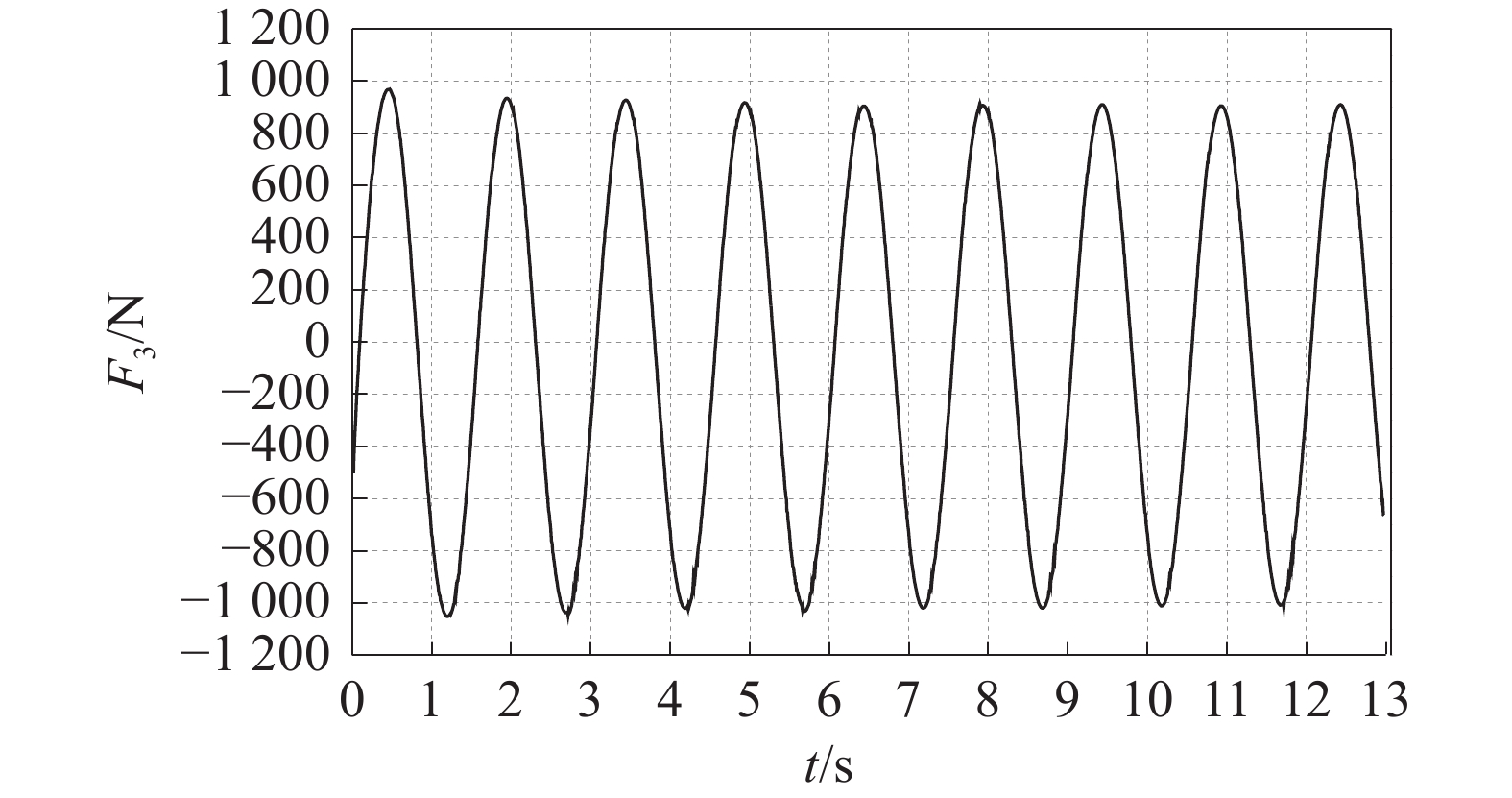
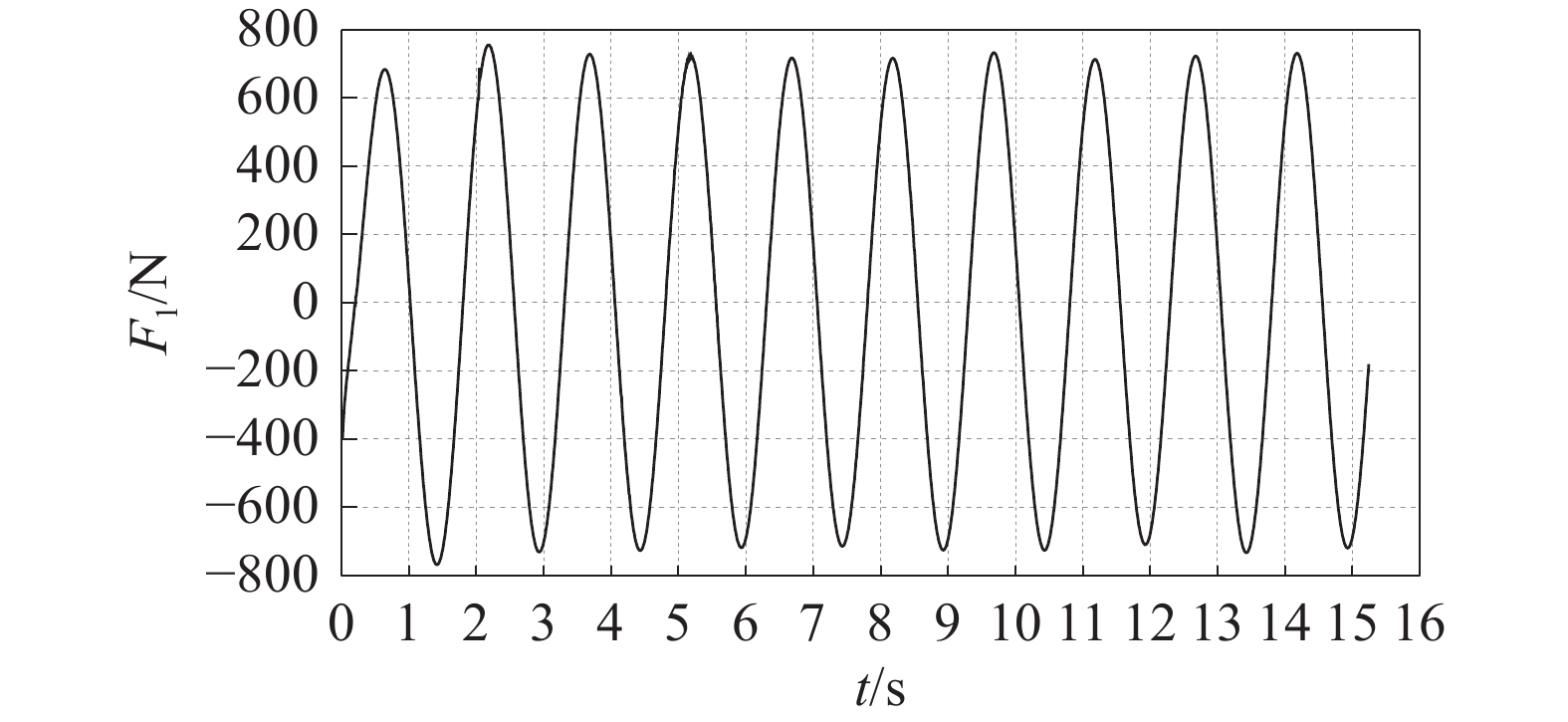
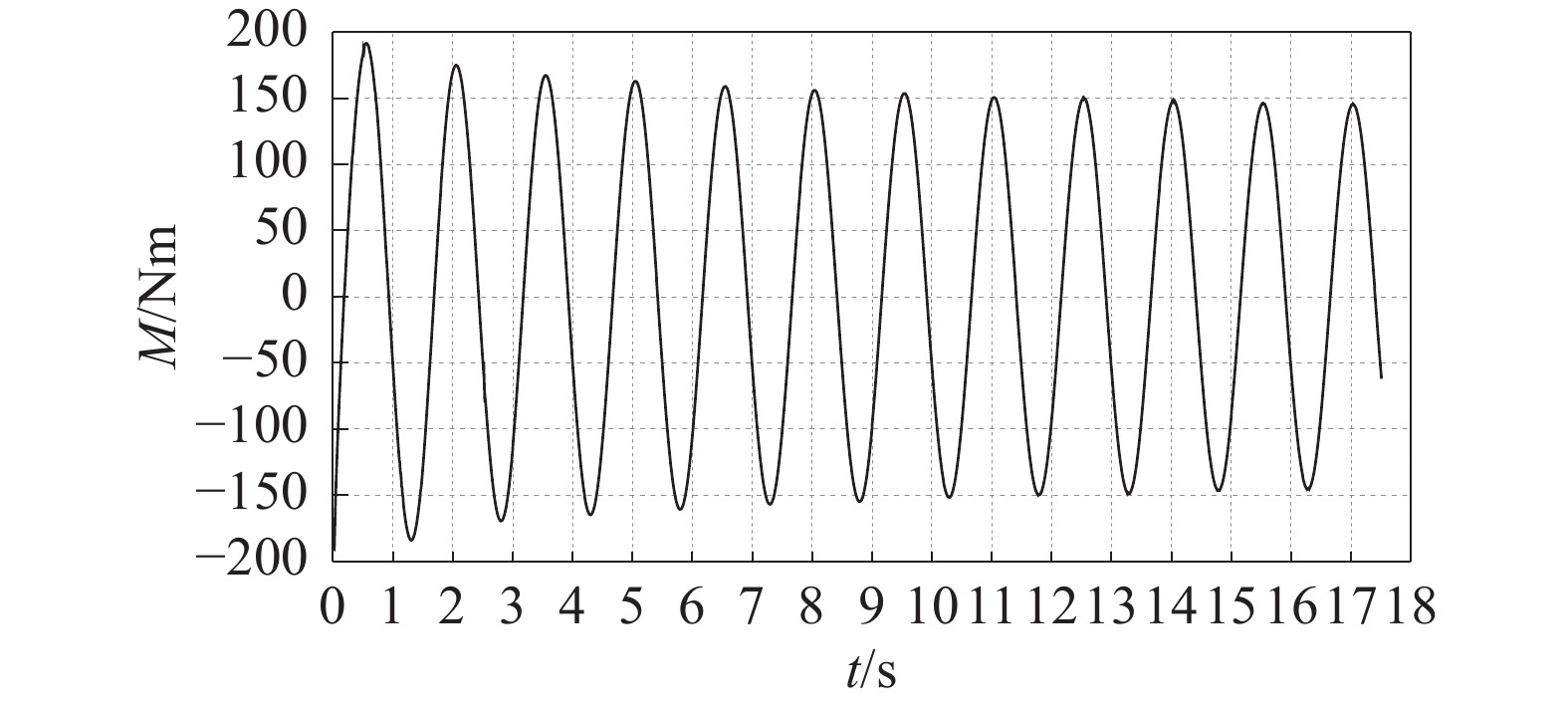
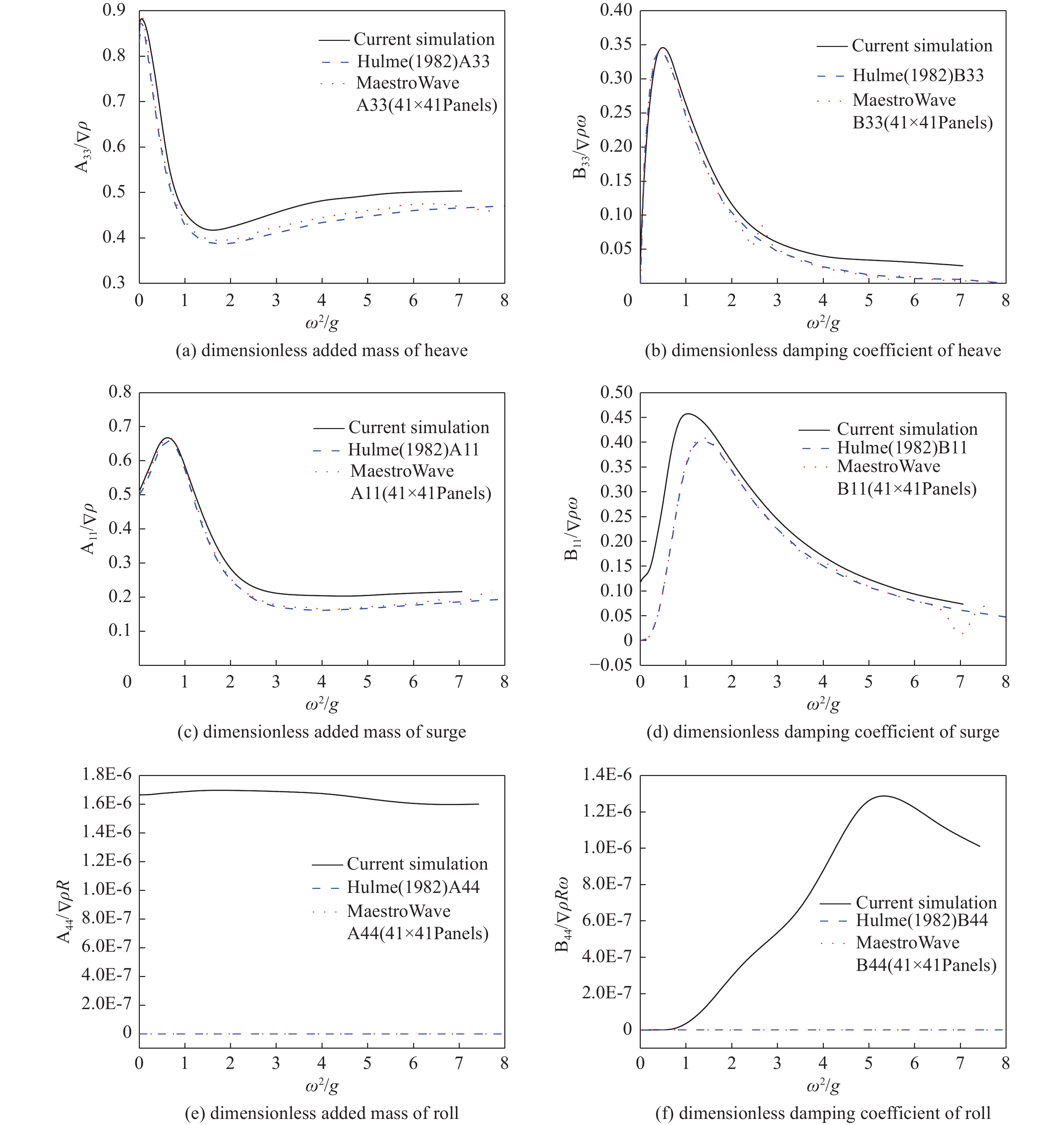
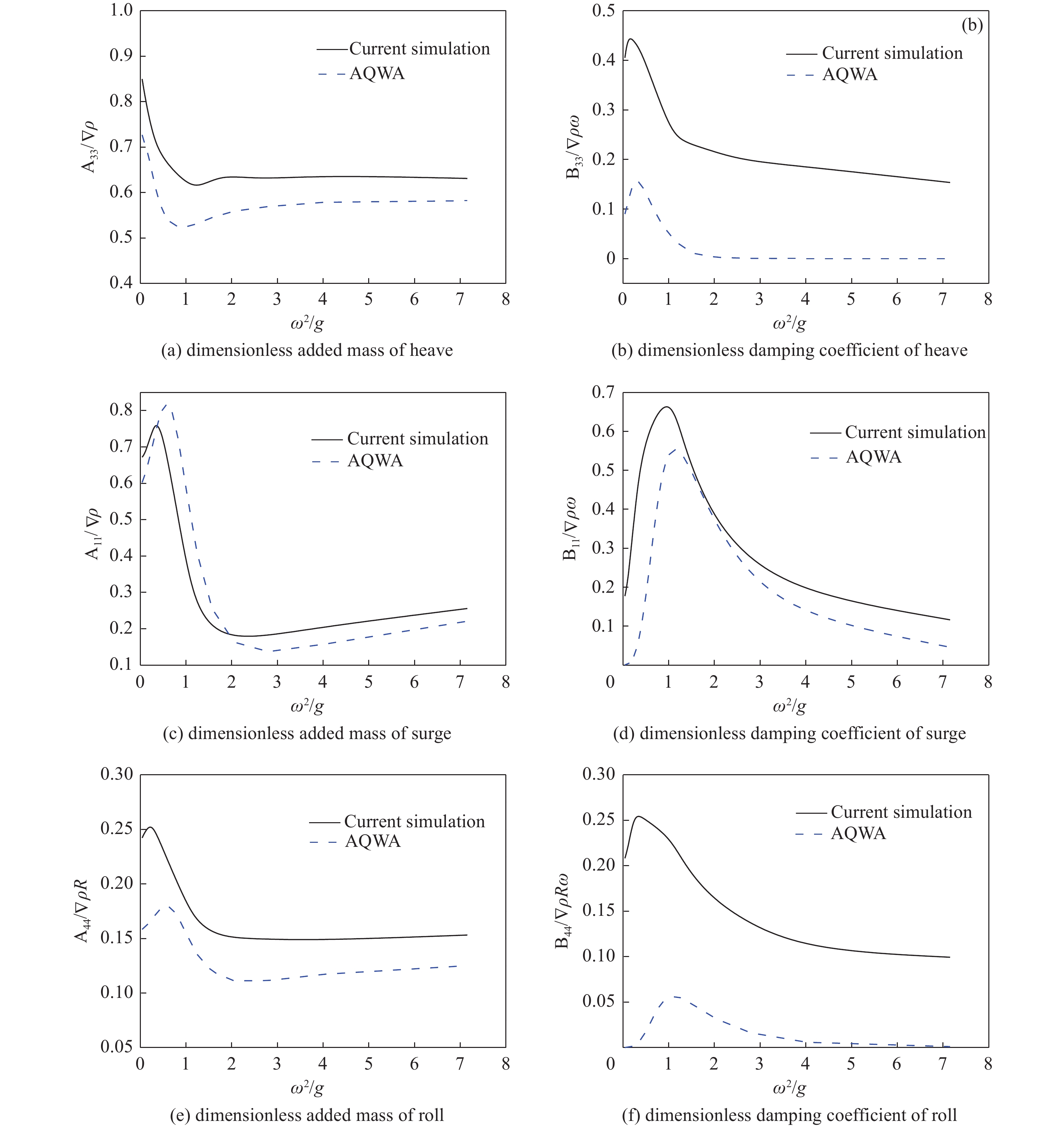
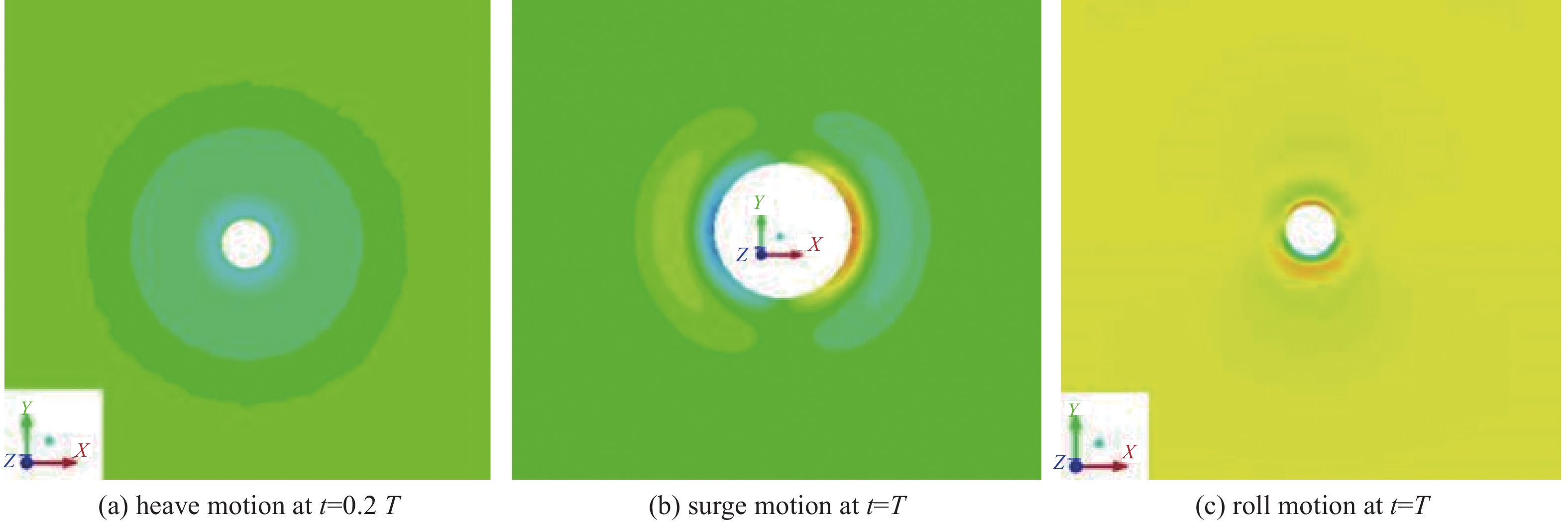
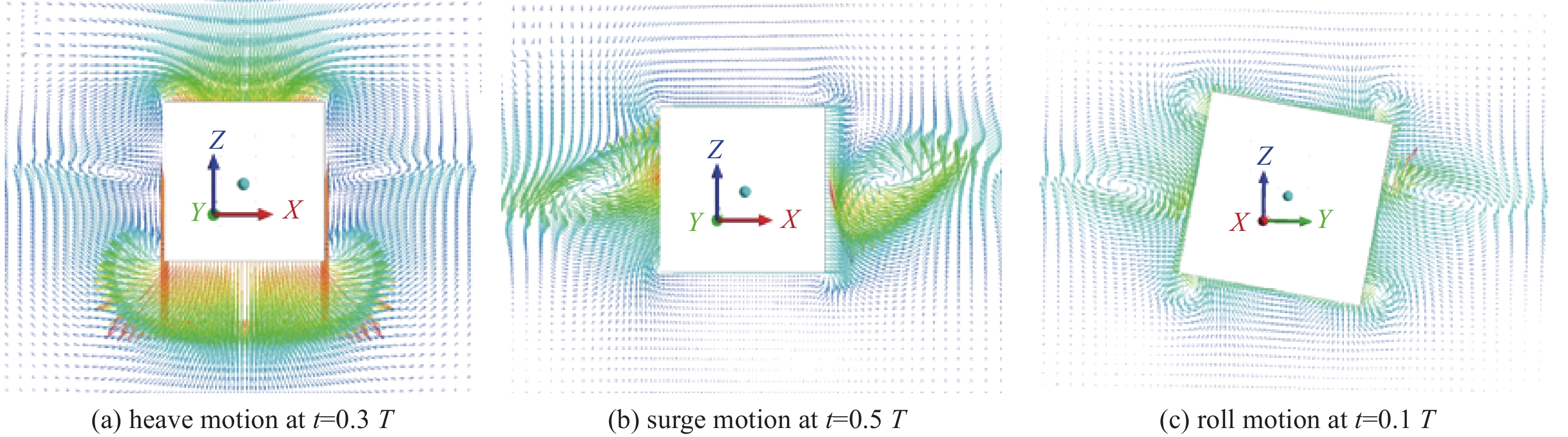
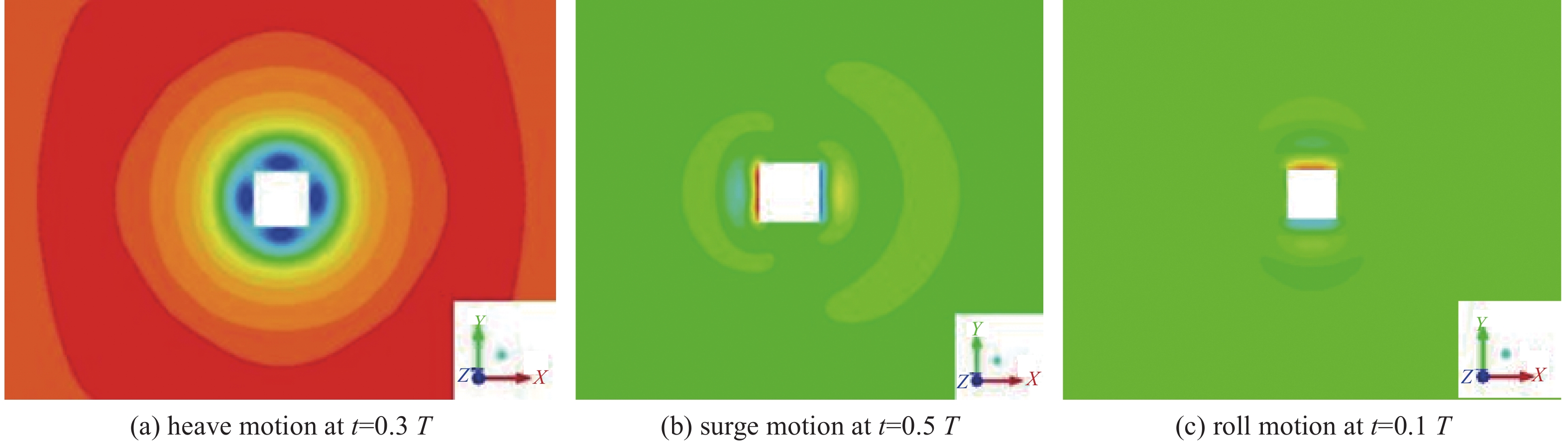
-
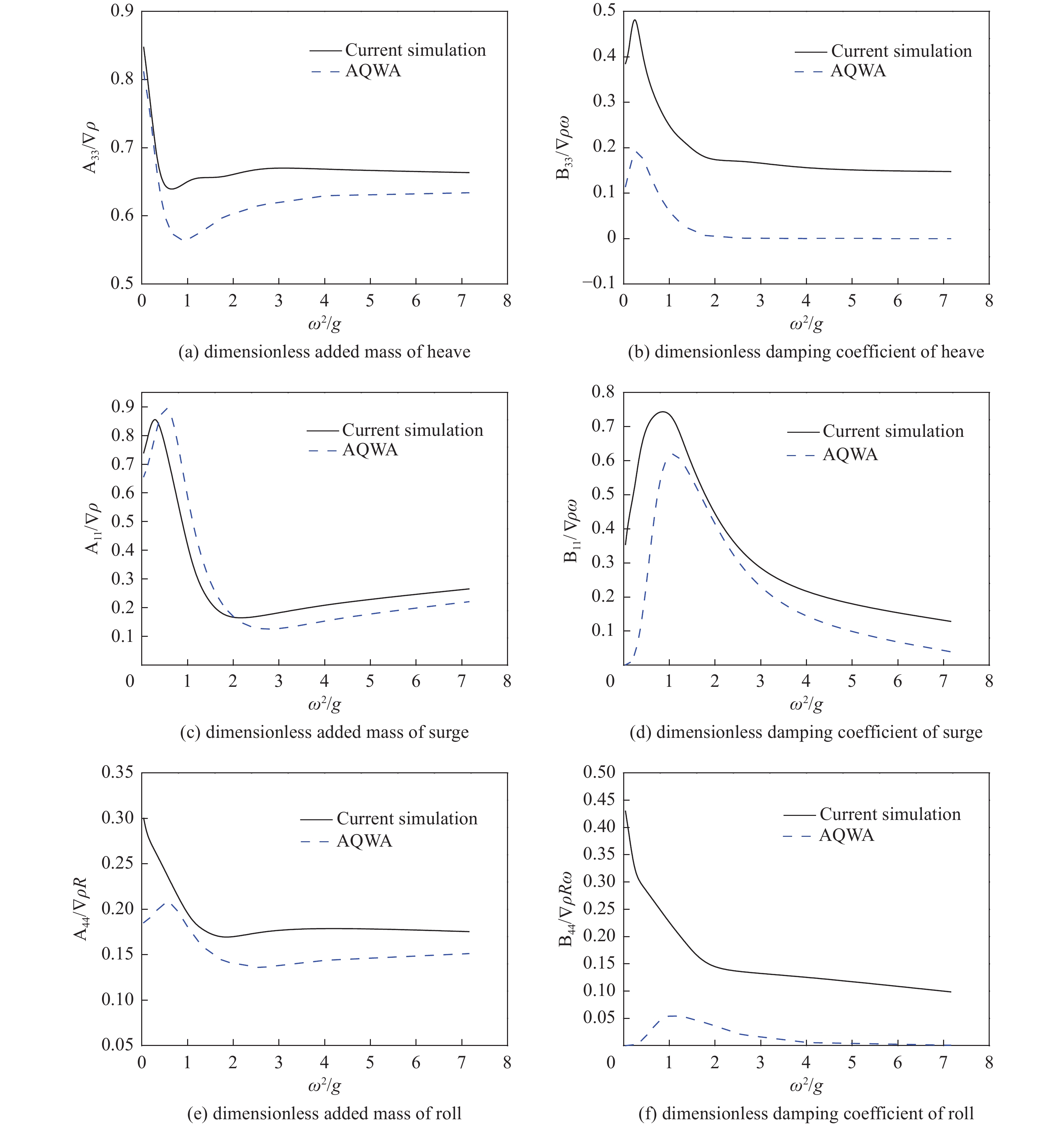
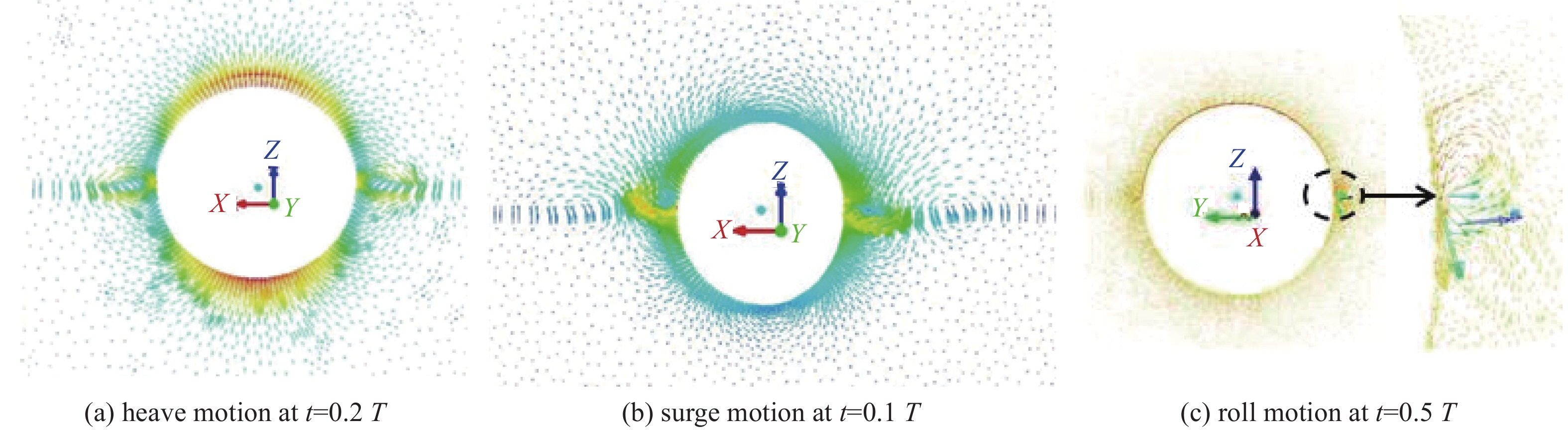
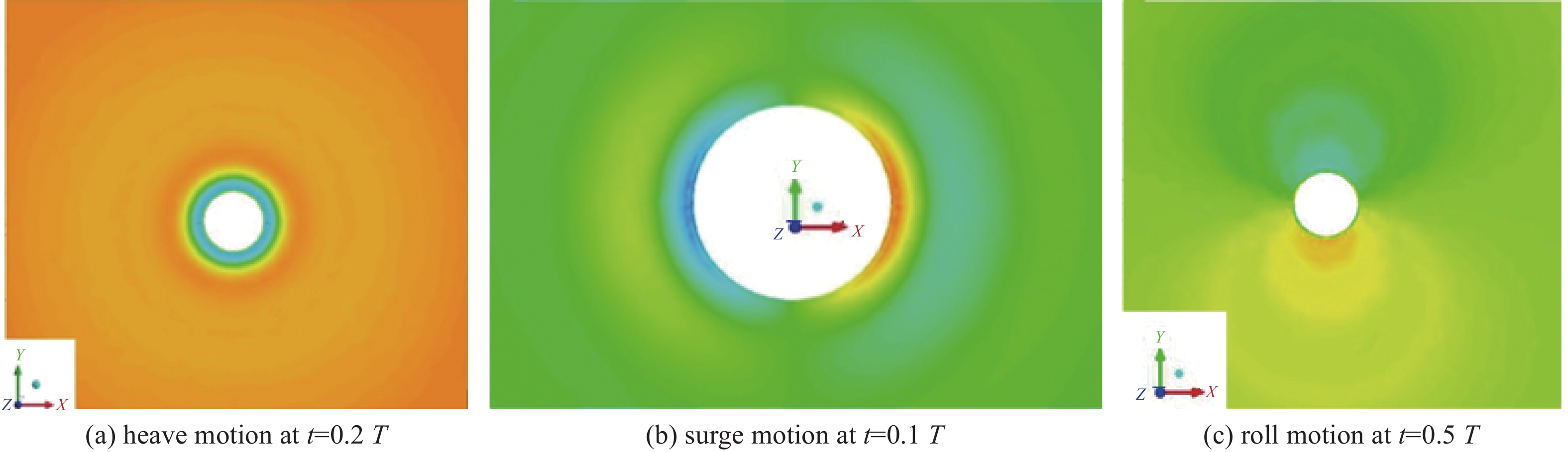
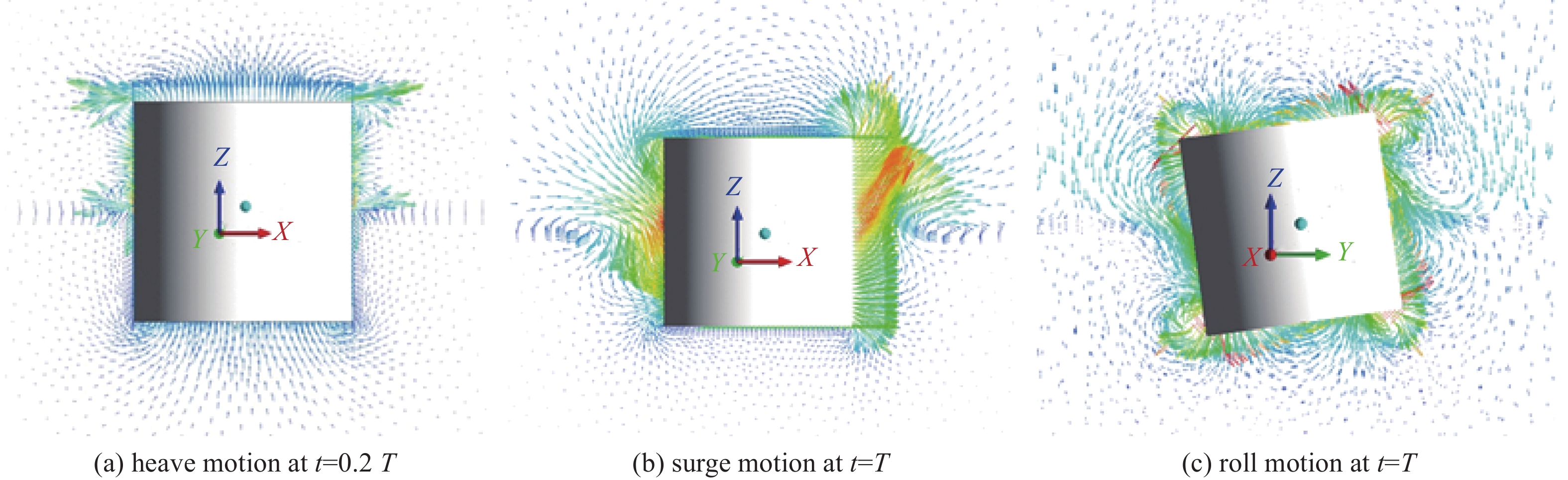
Abstract:Introduction Accurate calculation of the hydrodynamic coefficients for floating structures and the investigation of the flow field distribution around floating bodies on the marine free surface are essential for improving the engineering design and application of marine structures.Method This study utilized the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) approach and the Reynolds Averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) method and considered the effects of viscosity and free surface interactions on the hydrodynamic behavior of floating structures. By employing the dynamic mesh technique, this study simulated the periodic movements of simplified three-dimensional (3D) shapes: spheres, cylinders, and cubes, which were representative of complex marine structures. The volume of fluid (VOF) method was leveraged to accurately track the nonlinear behavior of the free surface. In this analysis, the added mass and damping coefficients for the fundamental modes of motion (surge, heave, and roll) were calculated across a spectrum of frequencies, facilitating the fast determination of hydrodynamic forces and moments exerted on floating structures.Result The results of this study are not only consistent with the results of the 3D potential flow theory but also further reflect the role of viscosity. This method can be used for precise calculation of the hydrodynamic coefficients of floating structures and for describing the flow field of such structures in motion on a free surface.Conclusion The methodology presented goes beyond the traditional potential flow approach.摘要:目的 精确计算海洋浮体结构物的流体力学系数和研究浮体在海洋自由表面上的流场分布对于增强海洋结构物工程设计应用至关重要。方法 本研究利用计算流体动力学(CFD)方法,采用雷诺平均纳维-斯托克斯(RANS)方法,考虑了粘度和自由表面相互作用对浮体结构水动力的影响。通过采用动态网格技术,文章模拟了简化三维(3D)形状(球体、圆柱体和立方体)的周期性运动,这些形状用来简化代表复杂的海洋结构。利用流体体积(VOF)方法来精确跟踪自由表面的非线性行为。在该分析中,计算了各种频率的基本运动模式(纵荡、垂荡和横摇)的附加质量和阻尼系数,从而有助于快速确定在浮体结构上的流体作用力和力矩。结果 这项研究的结果不仅与三维势流理论的结果基本吻合,还进一步反映了粘度的作用。该方法可用于精准计算浮体结构物的水动力系数和描述此类结构在自由表面运动的流场。结论 所提出的方法超越了传统的势流方法。
-
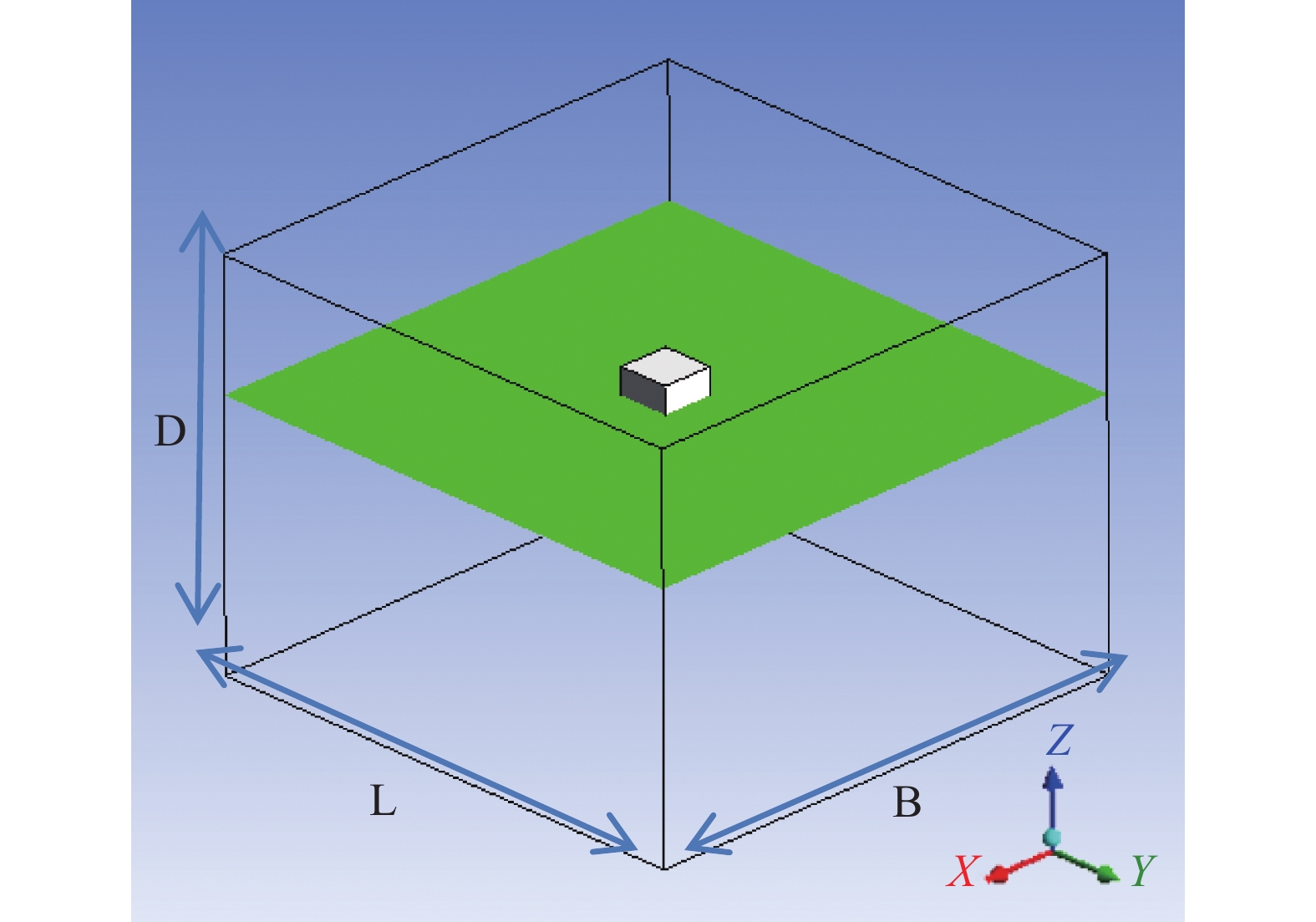
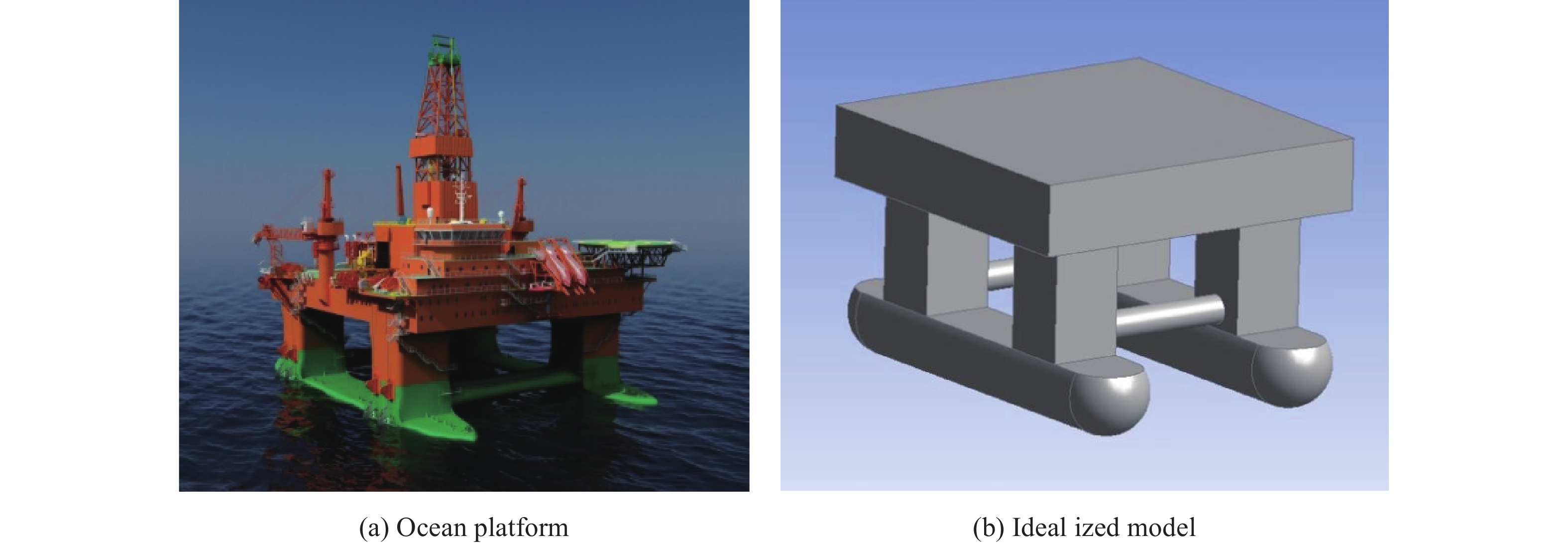
Table 1 Computational domain and principal dimensions of models
Cases L×B×D/m×m×m Radius/m Length/m Center of gravity Draft/m Sphere 20×20×15 1 — Centroid 1 Cylinder 20×20×15 1 2 Centroid 1 Cube 20×20×15 — 2 Centroid 1 -
[1] ISAACSON M, MATHAI T. High frequency hydrodynamic coefficients of vertical cylinders [J]. Canadian journal of civil engineering, 1992, 19(4): 606-615. DOI: 10.1139/l92-070.
[2] ISAACSON M, MATHAI T, MIHELCIC C. Hydrodynamic coefficients of a vertical circular cylinder [J]. Canadian journal of civil engineering, 1990, 17(3): 302-310. DOI: 10.1139/l90-037.
[3] KIM Y G, KIM S Y, KIM H T, et al. Prediction of the maneuverability of a large container ship with twin propellers and twin rudders [J]. Journal of marine science and technology, 2007, 12(3): 130-138. DOI: 10.1007/s00773-007-0246-9.
[4] LI G, DUAN W Y. Experimental study on the hydrodynamic property of a complex submersible [J]. Journal of ship mechanics, 2011, 15(1): 58-65. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2011.01.008.
[5] OBREJA D, NABERGOJ R, CRUDU L, et al. Identification of hydrodynamic coefficients for manoeuvring simulation model of a fishing vessel [J]. Ocean engineering, 2010, 37(8/9): 678-687. DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2010.01.009.
[6] FAN S B, LIAN L, REN P, et al. Oblique towing test and maneuver simulation at low speed and large drift angle for deep sea open-framed remotely operated vehicle [J]. Journal of hydrodynamics, 2012, 24(2): 280-286. DOI: 10.1016/S1001-6058(11)60245-X.
[7] YEUNG R W, LIAO S W, RODDIER D. Hydrodynamic coefficients of rolling rectangular cylinders [J]. International journal of offshore and polar engineering, 1998, 8(4): 242-250.
[8] SABUNCU T, CALISAL S. Hydrodynamic coefficients for vertical circular cylinders at finite depth [J]. Ocean engineering, 1981, 8(1): 25-63. DOI: 10.1016/0029-8018(81)90004-4.
[9] YEUNG R W. Added mass and damping of a vertical cylinder in finite-depth waters [J]. Applied ocean research, 1981, 3(3): 119-133. DOI: 10.1016/0141-1187(81)90101-2.
[10] CHAKRABARTI S K. Hydrodynamics of offshore structures [M]. Southampton: Computational Mechanics Publication, 1987.
[11] WILLIAMS A N, DEMIRBILEK Z. Hydrodynamic interactions in floating cylinder arrays-I. Wave scattering [J]. Ocean engineering, 1988, 15(6): 549-583. DOI: 10.1016/0029-8018(88)90002-9.
[12] MCIVER P, LINTON C M. The added mass of bodies heaving at low frequency in water of finite depth [J]. Applied ocean research, 1991, 13(1): 12-17. DOI: 10.1016/S0141-1187(05)80036-7.
[13] RAHMAN M, BHATTA D D. Evaluation of added mass and damping coefficient of an oscillating circular cylinder [J]. Applied mathematical modelling, 1993, 17(2): 70-79. DOI: 10.1016/0307-904X(93)90095-X.
[14] DEBNATH L. Nonlinear water waves [M]. Boston: Academic Press, 1994.
[15] BLACK J L, MEI C C, BRAY M C G. Radiation and scattering of water waves by rigid bodies [J]. Journal of fluid mechanics, 1971, 46(1): 151-164. DOI: 10.1017/S0022112071000454.
[16] BHATTA D D, RAHMAN M. On scattering and radiation problem for a circular cylinder in water of finite depth [J]. International journal of engineering science, 2003, 41(9): 931-967. DOI: 10.1016/S0020-7225(02)00381-6.
[17] LEE J F. On the heave radiation of a rectangular structure [J]. Ocean engineering, 1995, 22(1): 19-34. DOI: 10.1016/0029-8018(93)E0009-H.
[18] ANDERSEN P, HE W Z. On the calculation of two-dimensional added mass and damping coefficients by simple green's function technique [J]. Ocean engineering, 1985, 12(5): 425-451. DOI: 10.1016/0029-8018(85)90003-4.
[19] HSU H H, WU Y C. The hydrodynamic coefficients for an oscillating rectangular structure on a free surface with sidewall [J]. Ocean engineering, 1997, 24(2): 177-199. DOI: 10.1016/0029-8018(96)00009-1.
[20] HSU H H, WU Y C. Scattering of water wave by a submerged horizontal plate and a submerged permeable breakwater [J]. Ocean engineering, 1998, 26(4): 325-341. DOI: 10.1016/S0029-8018(97)10032-4.
[21] SANNASIRAJ S A, SUNDAR V, SUNDARAVADIVELU R. The hydrodynamic behaviour of long floating structures in directional seas [J]. Applied ocean research, 1995, 17(4): 233-243. DOI: 10.1016/0141-1187(95)00011-9.
[22] CHEN X M, ZHANG C, TANG Y H, et al. An immersed boundary method with an approximate projection on nonstaggered grids to solve unsteady fluid flow with a submerged moving rigid object [J]. Proceedings of the institution of mechanical engineers, part M: journal of engineering for the maritime environment, 2014, 228(3): 272-283. DOI: 10.1177/1475090212463498.
[23] ZHANG C, ZHANG W, LIN N S, et al. A two-phase flow model coupling with volume of fluid and immersed boundary methods for free surface and moving structure problems [J]. Ocean engineering, 2013, 74: 107-124. DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2013.09.010.
[24] ZHANG C, LIN N S, TANG Y H, et al. A sharp interface immersed boundary/VOF model coupled with wave generating and absorbing options for wave-structure interaction [J]. Computers & fluids, 2014, 89: 214-231. DOI: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2013.11.004.
[25] WU B S, XING F, KUANG X F, et al. Investigation of hydrodynamic characteristics of submarine moving close to the sea bottom with CFD methods [J]. Journal of ship mechanics, 2005, 9(3): 19-28.
[26] TYAGI A, SEN D. Calculation of transverse hydrodynamic coefficients using computational fluid dynamic approach [J]. Ocean engineering, 2006, 33(5/6): 798-809. DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2005.06.004.
[27] PAN Y C, ZHANG H X, ZHOU Q D. Numerical prediction of submarine hydrodynamic coefficients using CFD simulation [J]. Journal of hydrodynamics, ser. B, 2012, 24(6): 840-847. DOI: 10.1016/S1001-6058(11)60311-9.
[28] PHILLIPS A B, TURNOCK S R, FURLONG M. Influence of turbulence closure models on the vortical flow field around a submarine body undergoing steady drift [J]. Journal of marine science and technology, 2010, 15(3): 201-217. DOI: 10.1007/s00773-010-0090-1.
[29] LIN P Z. A fixed-grid model for simulation of a moving body in free surface flows [J]. Computers & fluids, 2007, 36(3): 549-561. DOI: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2006.03.004.
[30] HULME A. The wave forces acting on a floating hemisphere undergoing forced periodic oscillations [J]. Journal of fluid mechanics, 1982, 121: 443-463. DOI: 10.1017/S0022112082001980.
[31] VUGTS J H. The hydrodynamic coefficients for swaying, heaving and rolling cylinders in a free surface [J]. International shipbuilding progress, 1968, 15(167): 251-276. DOI: 10.3233/ISP-1968-1516702.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 张孝宇. 海浪发电机能量转换效率提升策略探究. 船舶物资与市场. 2025(05): 124-126 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: