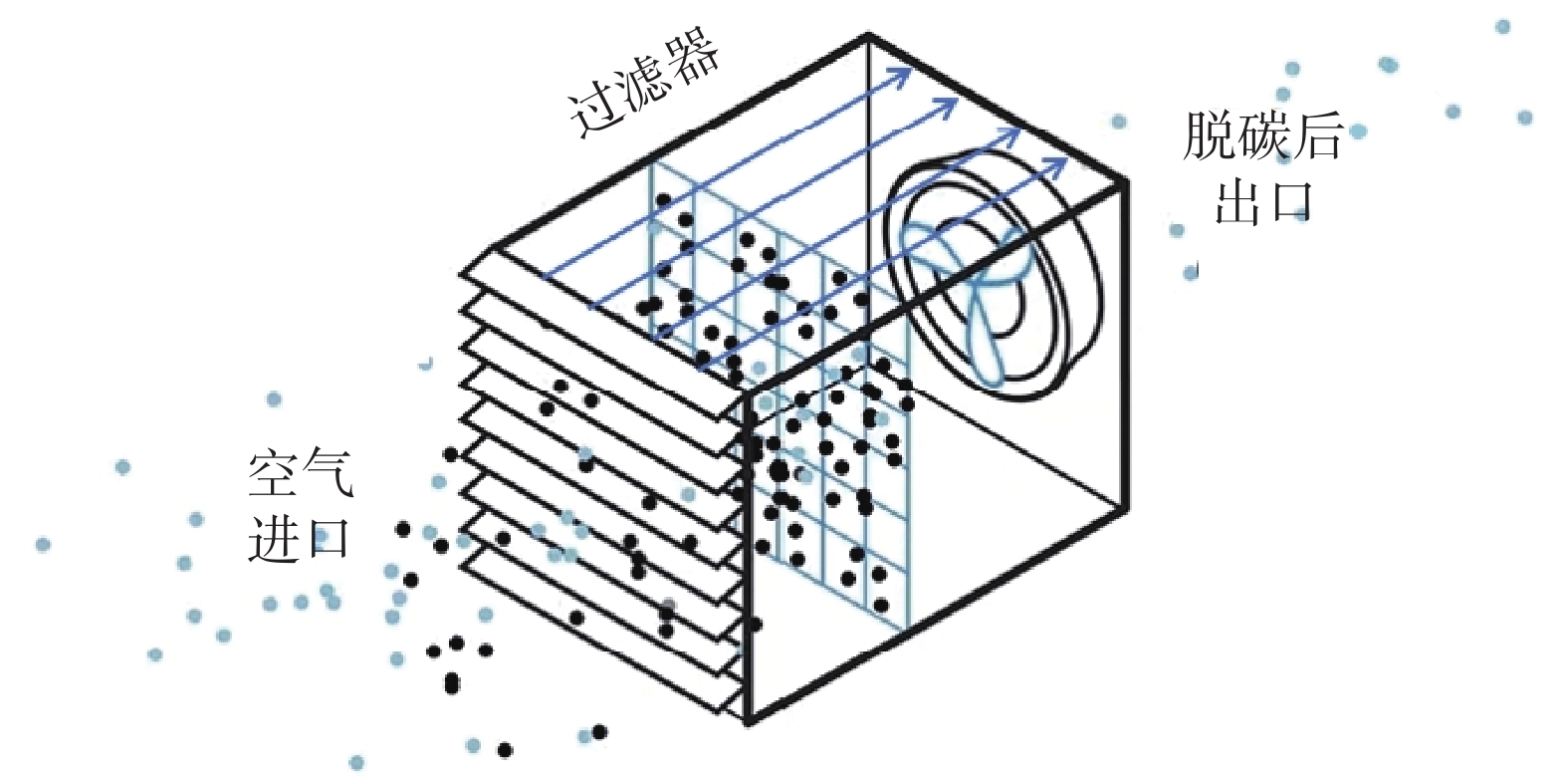
-
摘要:目的 旨在探讨面向碳中和背景下直接空气捕碳(Direct Air Capture,DAC)技术的发展现状、应用案例及其经济性评估,以期为我国实现碳减排目标提供参考。方法 文章综述了DAC技术的工作原理、类型、运用案例,并分析了其在国内外的发展情况。通过比较不同研究中的成本数据,评估了DAC技术的经济性,并讨论了当前面临的挑战与可能的解决措施。结果 研究发现,DAC技术能有效从空气中捕集CO2,具有布置灵活、可与可再生能源结合等优点。但其商业化应用仍受到高成本、高能耗和大规模部署的技术挑战的限制。国内外的案例分析揭示DAC技术在实际应用中的效率和成本问题亟待解决,同时也显示了通过技术改进和政策支持可能实现的优化潜力。结论 尽管存在挑战,DAC技术仍是实现碳中和目标的潜在储备技术,尤其对中国等面临严峻碳减排压力的国家具有重要意义。需要集中研究力量开发更高效、低成本的吸收/吸附剂,改进系统设计,降低能源消耗,并积极探索与可再生能源的结合使用。政府的政策支持和社会的广泛认可也是实现DAC技术商业化的关键因素。通过这些措施可以推动DAC技术的发展和应用,助力实现碳减排和环境保护的双重目标。Abstract:Introduction This paper aims to explore the development status, application cases, and economic evaluation of direct air capture (DAC) technology in the context of carbon neutrality, thus providing references for achieving carbon emission reduction targets in China.Method This paper reviewed the working principles, types, and application cases of DAC technology and analyzed its development status both at home and abroad. By comparing cost data from different studies, it assessed the economy of DAC technology and discussed current challenges and potential solutions.Result The study finds that DAC technology effectively captures CO2 from the air and offers advantages such as flexibility in deployment and compatibility with renewable energy. However, its commercialization is still constrained by high costs, high energy consumption, and technical challenges related to large-scale deployment. Case analysis at home and abroad reveal the urgent need to address the efficiency and cost issues in practical applications, while also showing potential for optimization through technological improvements and policy support.Conclusion Despite the existing challenges, DAC technology remains a potential reserve technology for achieving carbon neutrality goals, especially for countries facing severe carbon reduction pressures like China. Research efforts should focus on developing more efficient and low-cost absorbents and adsorbents, improving system design, reducing energy consumption, and exploring combination with renewable energy sources. Government policy support and broad social acceptance are also key factors for the commercialization of DAC technology. These measures can drive the development and application of DAC technology, contributing to both carbon emission reduction and environmental protection goals.
-
表 1 固体DAC技术对比
Table 1 Comparison of solid DAC technologies
表 2 DAC技术对比
Table 2 Comparison DAC technologies
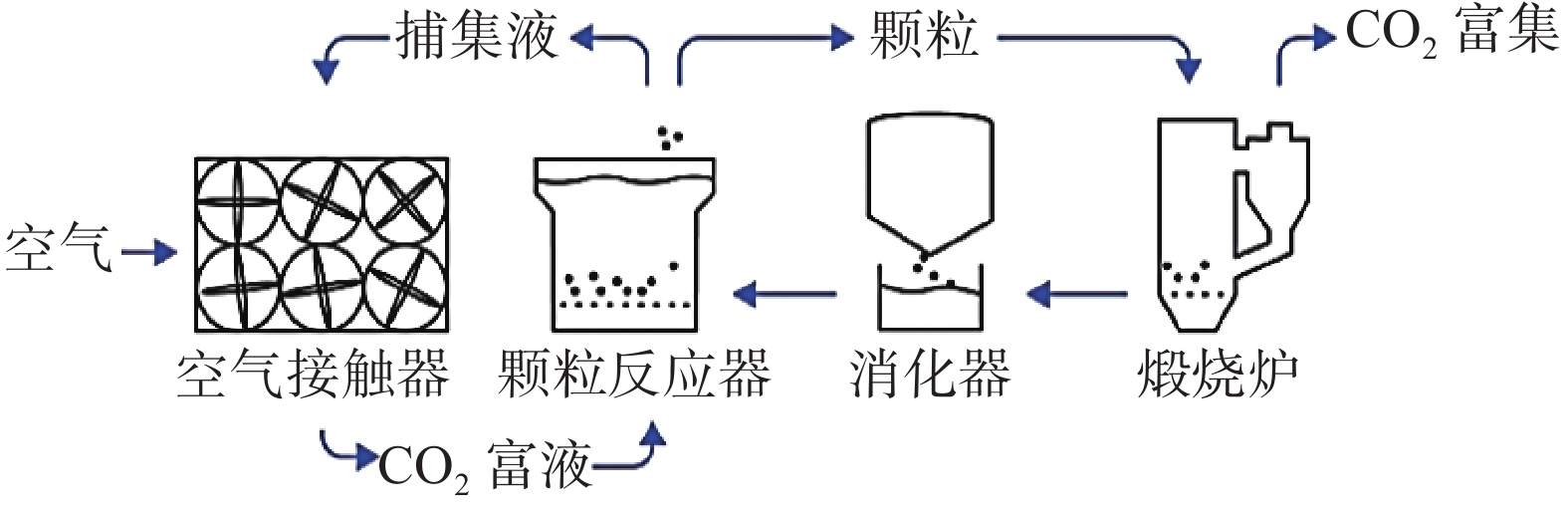
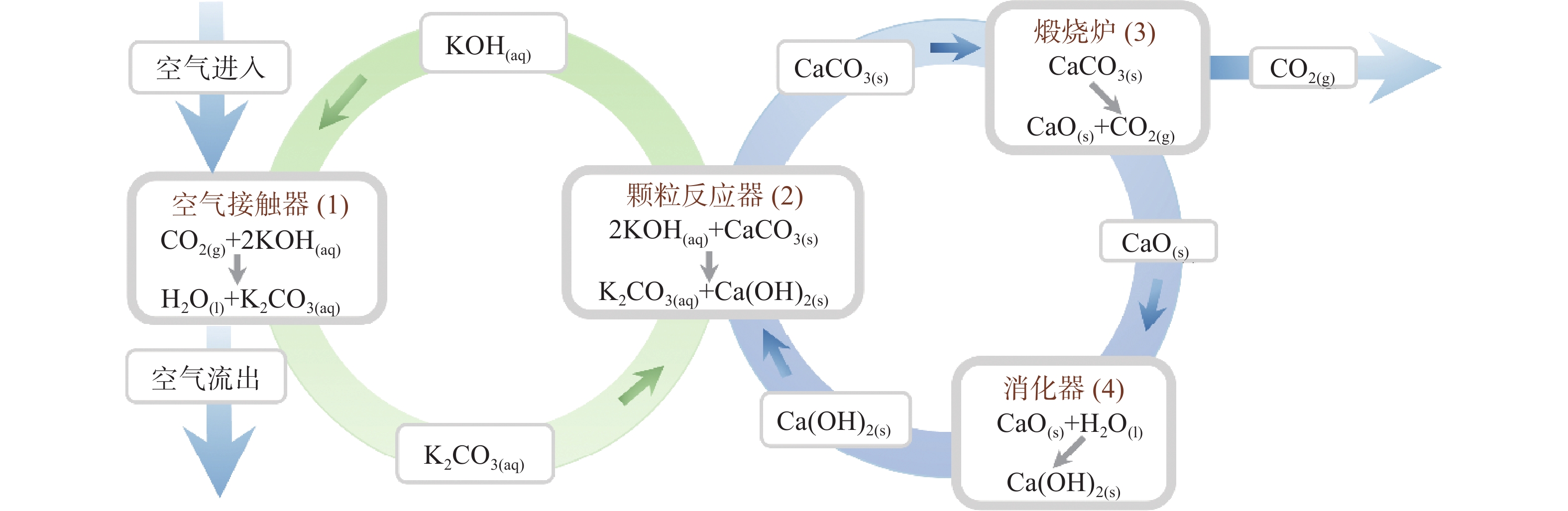
分类 原理 优点 缺点 技术发展建议方向 液体DAC
技术CO2与碱性氢氧化物反应生成碳酸盐 技术成熟、吸收速率高、溶剂损失少 设备和运营成本较高, 能耗和维护难度大 研究可以充分发挥捕集材料性能的空气接触器 固体DAC
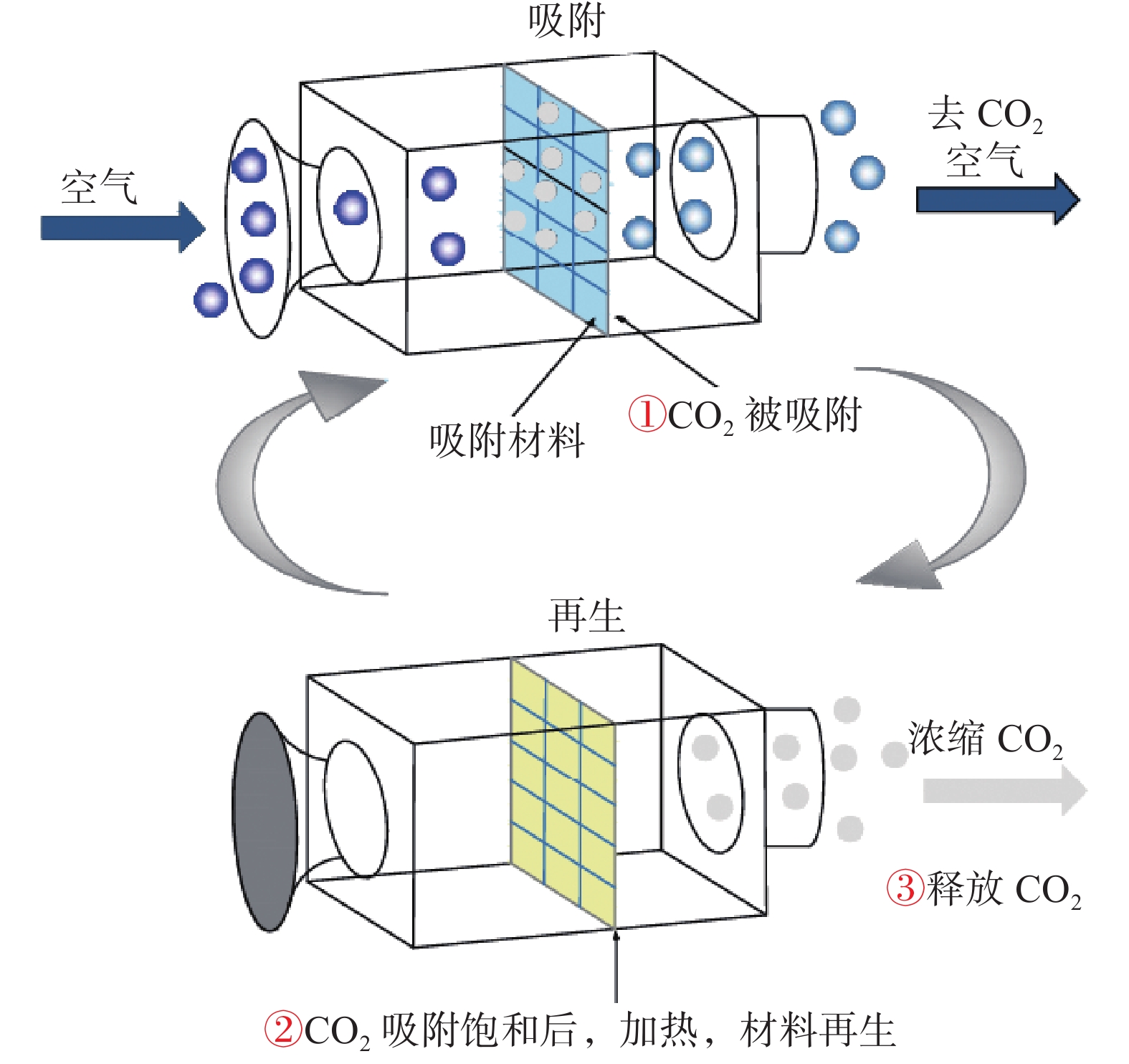
技术低温下固体吸附剂捕获CO2 吸附效率较高、再生稳定性较好、技术成熟、吸附速率快、再生温度低 成本较高, 长期稳定性差, 吸附剂的回收和再生过程复杂 多种载体或有效成分的复合研究 变湿吸附
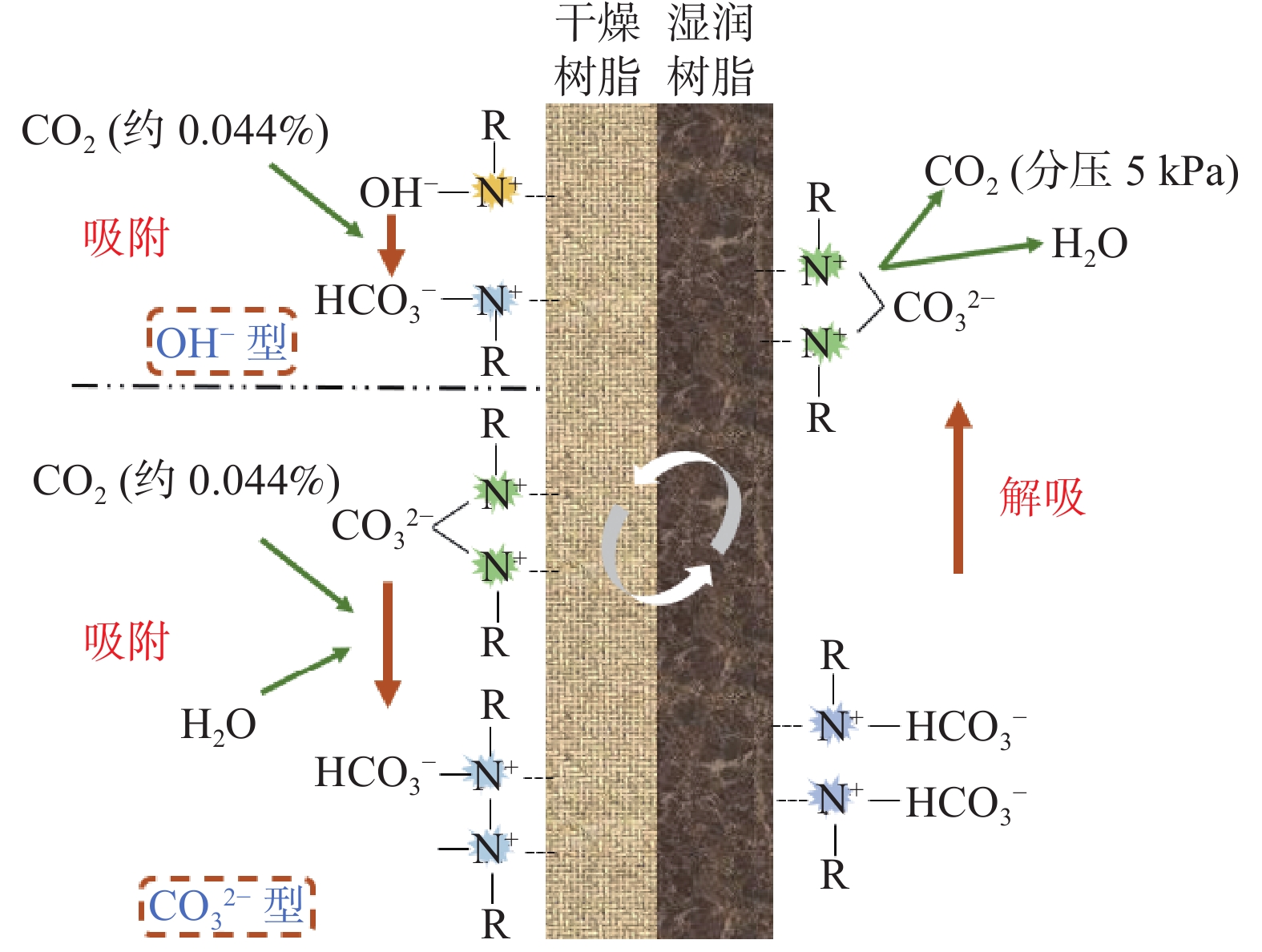
工艺变湿吸附剂在湿度发生变化时对CO2吸脱附 吸脱附动力学速率快,再生能耗低 捕获后CO2浓度较低,水分消耗大 开发出安全、可规模化量产的整体型功能化材料 表 3 DAC技术成本比较
Table 3 Cost comparison of DAC technologies
研究 方法/技术 成本范围/ [$·(t CO2)−1] 说明 美国物理学会 2011年报告[45] KOH吸收 不低于705 采用KOH吸收的空气捕集成本评估 Keith等[32] KOH 溶液吸收 97~238 基于中试数据的KOH溶液吸收成本测算 Kulkarni等[47] 蒸汽辅助再生 TVSA流程 ~ 108 采用天然气与低品位热实现的蒸汽辅助再生 Sinha等[48] 胺基MOFs
吸附剂63~200 投资成本波动大,受MOFs材料生产成本影响 Climeworks 公司[46] 商业示范装置 300~600 根据600 ~900 t CO2/a规模示范装置的成本报告 Lackner等[12] 变湿吸附 50~100 实验室研究的技术成本预测 -
[1] 王林. 第28届联合国气候变化大会在迪拜开幕 [N]. 2023-12-04(01). DOI: 10.28693/n.cnki.nshca.2023.001934. WANG L. The 28th United Nations climate change conference opens in Dubai [N]. 2023-12-04(01). DOI: 10.28693/n.cnki.nshca.2023.001934.
[2] 蔡绍宽. 双碳目标的挑战与电力结构调整趋势展望 [J]. 南方能源建设, 2021, 8(3): 8-17. DOI: 10.16516/j.gedi.issn2095-8676.2021.03.002. CAI S K. Challenges and prospects for the trends of power structure adjustment under the goal of carbon peak and neutrality [J]. Southern energy construction, 2021, 8(3): 8-17. DOI: 10.16516/j.gedi.issn2095-8676.2021.03.002.
[3] DJALANTE R. Key assessments from the IPCC special report on global warming of 1.5 °C and the implications for the Sendai framework for disaster risk reduction [J]. Progress in disaster science, 2019, 1: 100001. DOI: 10.1016/j.pdisas.2019.100001.
[4] 胡鞍钢. 中国实现2030年前碳达峰目标及主要途径 [J]. 北京工业大学学报(社会科学版), 2021, 21(3): 1-15. DOI: 10.12120/bjutskxb202103001. HU A G. China's goal of achieving carbon peak by 2030 and its main approaches [J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology (social sciences edition), 2021, 21(3): 1-15. DOI: 10.12120/bjutskxb202103001.
[5] 邢伟, 徐汝隆, 高贺同, 等. 专利视角下空气中直接捕集CO2技术发展分析 [J]. 洁净煤技术, 2023, 29(4): 86-97. DOI: 10.13226/j.issn.1006-6772.RM23041801. XING W, XU R L, GAO H T, et al. Analysis of the development of direct capture of carbon dioxide in the air from patent perspective [J]. Clean coal technology, 2023, 29(4): 86-97. DOI: 10.13226/j.issn.1006-6772.RM23041801.
[6] STEVENSON R. Negative emissions technologies and reliable sequestration: a research agenda [J]. Integrated environmental assessment and management, 2021, 17(2): 488-489.
[7] TIAN Y X, WANG R H, DENG S M, et al. Coupling direct atmospheric CO2 capture with photocatalytic CO2 reduction for highly efficient C2H6 production [J]. Nano letters, 2023, 23(23): 10914-10921. DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.3c03167.
[8] ZHU X C, XIE W W, WU J Y, et al. Recent advances in direct air capture by adsorption [J]. Chemical society reviews, 2022, 51(15): 6574-6651. DOI: 10.1039/D1CS00970B.
[9] 曹成, 侯正猛, 熊鹰, 等. 云南省碳中和技术路线与行动方案 [J]. 工程科学与技术, 2022, 54(1): 37-46. DOI: 10.15961/j.jsuese.202100919. CAO C, HOU Z M, XIONG Y, et al. Technical routes and action plan for carbon neutral for Yunnan Province [J]. Advanced engineering sciences, 2022, 54(1): 37-46. DOI: 10.15961/j.jsuese.202100919.
[10] 侯正猛, 熊鹰, 刘建华, 等. 河南省碳达峰与碳中和战略、技术路线和行动方案 [J]. 工程科学与技术, 2022, 54(1): 23-36. DOI: 10.15961/j.jsuese.202100627. HOU Z M, XIONG Y, LIU J H, et al. Strategy, technical route and action plan towards carbon peak and carbon neutrality in Henan Province [J]. Advanced engineering sciences, 2022, 54(1): 23-36. DOI: 10.15961/j.jsuese.202100627.
[11] 陈彬, 谢和平, 刘涛, 等. 碳中和背景下先进制氢原理与技术研究进展 [J]. 工程科学与技术, 2022, 54(1): 106-116. DOI: 10.15961/j.jsuese.202100686. CHEN B, XIE H P, LIU T, et al. Principles and progress of advanced hydrogen production technologies in the context of carbon neutrality [J]. Advanced engineering sciences, 2022, 54(1): 106-116. DOI: 10.15961/j.jsuese.202100686.
[12] LACKNER K S. Capture of carbon dioxide from ambient air [J]. The European physical journal special topics, 2009, 176(1): 93-106. DOI: 10.1140/epjst/e2009-01150-3.
[13] SUTHERLAND B R. Pricing CO2 direct air capture [J]. Joule, 2019, 3(7): 1571-1573. DOI: 10.1016/j.joule.2019.06.025.
[14] BRETHOME F M, WILLIAMS N J, SEIPP C A, et al. Direct air capture of CO2 via aqueous-phase absorption and crystalline-phase release using concentrated solar power [J]. Nature energy, 2018, 3(7): 553-559. DOI: 10.1038/s41560-018-0150-z.
[15] LACKNER K S, BRENNAN S, MATTER J M, et al. The urgency of the development of CO2 capture from ambient air [J]. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(33): 13156-13162. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1108765109.
[16] 王涛, 董昊, 侯成龙, 等. 直接空气捕碳CO2吸附剂综述 [J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2022, 56(3): 462-475. DOI: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2022.03.005. WANG T, DONG H, HOU C L, et al. Review of CO2 direct air capture adsorbents [J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (engineering science), 2022, 56(3): 462-475. DOI: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2022.03.005.
[17] 廖昌建, 张可伟, 王晶, 等. 直接空气捕碳二氧化碳技术研究进展 [J]. 化工进展, 2024, 43(4): 2031-2048. DOI: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2023-0606. LIAO C J, ZHANG K W, WANG J, et al. Progress on direct air capture of carbon dioxide [J]. Chemical industry and engineering progress, 2024, 43(4): 2031-2048. DOI: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2023-0606.
[18] ZEMAN F. Energy and material balance of CO2 capture from ambient air [J]. Environmental science & technology, 2007, 41(21): 7558-7563. DOI: 10.1021/es070874m.
[19] KEITH D W, HA-DUONG M, STOLAROFF J K. Climate strategy with CO2 capture from the air [J]. Climatic change, 2006, 74(1/3): 17-45. DOI: 10.1007/s10584-005-9026-x.
[20] MAHMOUDKHANI M, HEIDEL K R, FERREIRA J C, et al. Low energy packed tower and caustic recovery for direct capture of CO2 from air [C]//Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Greenhouse Gas Control Technologies, Washington, USA, November 16-20, 2008. 2009.
[21] 王献红. 二氧化碳捕集和利用 [M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2016. WANG X H. CO2 capture and utilization [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2016.
[22] HODDENBAGH J M A, WILFING K, MILLER K, et al. Borate autocausticizing: a cost effective technology [C]//Paper Presented at the 2001 Intl. Chemical Recovery Conference, Whistler, Canada, June 11, 2001. 2002.
[23] STOLAROFF J K, KEITH D W, LOWRY G V. Carbon dioxide capture from atmospheric air using sodium hydroxide spray [J]. Environmental science & technology, 2008, 42(8): 2728-2735. DOI: 10.1021/es702607w.
[24] SEIPP C A, WILLIAMS N J, KIDDER M K, et al. CO2 capture from ambient air by crystallization with a guanidine sorbent [J]. Angewandte chemie international edition, 2017, 56(4): 1042-1045. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201610916.
[25] CAMPER D, BARA J E, GIN D L, et al. Room-temperature ionic liquid−amine solutions: tunable solvents for efficient and reversible capture of CO2 [J]. Industrial & engineering chemistry research, 2008, 47(21): 8496-8498. DOI: 10.1021/ie801002m.
[26] 翁小涵, 韩涛, 冯玮, 等. 负碳排放技术研究现状及进展 [J/OL]. 洁净煤技术, 2024: 1-19 (2024-07-30) [2024-08-27]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3676.TD.20240729.1729.010.html. WENG X H, HAN T, FENG W, et al. Current status and progress of negative carbon emission technologies [J/OL]. Clean coal technology, 2024: 1-19 (2024-07-30) [2024-08-27]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3676.TD.20240729.1729.010.html.
[27] ZHAO M, XIAO J, GAO W, et al. Defect-rich Mg-Al MMOs supported TEPA with enhanced charge transfer for highly efficient and stable direct air capture [J]. Journal of energy chemistry, 2022, 68: 401-410. DOI: 10.1016/j.jechem.2021.12.031.
[28] ZHANG Z Q, DING Q, CUI J Y, et al. High and selective capture of low-concentration CO2 with an anion-functionalized ultramicroporous metal-organic framework [J]. Science China materials, 2021, 64(3): 691-697. DOI: 10.1007/s40843-020-1471-0.
[29] BHATT P M, BELMABKHOUT Y, CADIAU A, et al. A fine-tuned fluorinated MOF addresses the needs for trace CO2 removal and air capture using physisorption [J]. Journal of the American chemical society, 2016, 138(29): 9301-9307. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.6b05345.
[30] WANG T, WANG X R, HOU C L, et al. Quaternary functionalized mesoporous adsorbents for ultra-high kinetics of CO2 capture from air [J]. Scientific reports, 2020, 10(1): 21429. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-77477-1.
[31] UNIVERSITY Z, CHINA H Z, UNIVERSITY A S, et al. Characterization of kinetic limitations to atmospheric CO2 capture by solid sorbent [J]. Greenhouse gases: science and technology, 2015.
[32] KEITH D W, HOLMES G, ANGELO D S, et al. A process for capturing CO2 from the atmosphere [J]. Joule, 2018, 2(8): 1573-1594. DOI: 10.1016/j.joule.2018.05.006.
[33] 克里斯托夫·格巴尔, 尼古拉斯·皮亚考斯基, 托拜厄斯·吕埃施, 等. 用于吸附气体分离过程的颗粒吸附床的低压降结构: CN105163830A [P]. 2018-01-09. CHRISTOPH GEBAHR, NICOLAS PIAKOWSKI, TOBIAS LUEESCH, et al. Low-pressure drop structure of particle adsorbent bed for adsorption gas separation process: CN105163830A [P]. 2018-01-09.
[34] 彼得·艾森伯格尔. 捕集和封存二氧化碳的系统和方法: CN103079671A [P]. 2013-05-01. EISENBERGER P. System and method for carbon dioxide capture and sequestration: CN103079671A [P]. 2013-05-01.
[35] 彼得·艾森伯格尔. 用于二氧化碳捕集和储存的系统和方法: CN104380021B [P]. 2016-11-30. EISENBERGER P. System and method for carbon dioxide capture and sequestration: CN104380021B [P]. 2016-11-30.
[36] 彼得·艾森伯格尔, 格雷谢拉·奇奇尔尼斯基. 从大气中除去二氧化碳和全球恒温器: CN106268183A [P]. 2017-01-04. EISENBERGER P, CHICHILNISKY G. Removing carbon dioxide from atmosphere and global thermostat: CN106268183A [P]. 2017-01-04.
[37] 王焕君, 郭东方, 汪世清, 等. 一种利用二氧化碳和水合成甲醇的装置及方法: CN113511955A [P]. 2021-10-19. WANG H J, GUO D F, WANG S Q, et al. Device and method for synthesizing methanol by using carbon dioxide and water: CN113511955A [P]. 2021-10-19.
[38] 王焕君, 郭东方, 刘蓉, 等. 一种捕碳调峰耦合装置及方法: CN113521967A [P]. 2021-10-22. WANG H J, GUO D F, LIU R, et al. Carbon capture peak regulation coupling device and method: CN113521967A [P]. 2021-10-22.
[39] 邓帅, 孙鹏, 黄耀炜. 一种双极膜电渗析空气碳捕集系统: CN114307567A [P]. 2022-04-12. DENG S, SUN P, HUANG Y W. Bipolar membrane electrodialysis air carbon capture system: CN114307567A [P]. 2022-04-12.
[40] 王涛, 刘卫山, 夏芝香, 等. 具有精准离子控制的直接空气捕碳二氧化碳节能系统和方法: CN114515494B [P]. 2022-11-25. WANG T, LIU W S, XIA Z X, et al. Direct air capture carbon dioxide energy saving system and method with precise ion control: CN114515494B [P]. 2022-11-25.
[41] 冯俊婷, 李殿卿, 岳晓雪, 等. 一种CO2捕获转化耦合生物质氧化用光催化剂及其制备方法和应用: CN114471567B [P]. 2023-04-28. FENG J T, LI D Q, YUE X X, et al. Photocatalyst for CO2 capture and conversion coupled biomass oxidation as well as preparation method and application of photocatalyst: CN114471567B [P]. 2023-04-28.
[42] 周爱国, 郑家乐, 杨川箬, 等. 直接空气二氧化碳捕集技术工业化进展 [J]. 化工进展, 2024, 43(6): 2928-2939. DOI: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2023-2211. ZHOU A G, ZHENG J L, YANG C R, et al. Industrial progress in direct air CO2 capture technology [J]. Chemical industry and engineering progress, 2024, 43(6): 2928-2939. DOI: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2023-2211.
[43] 王焕君, 刘蓉, 郭东方, 等. 一种可再生能源驱动的二氧化碳加氢合成甲酸的系统及方法: CN113620798A [P]. 2021-11-09. WANG H J, LIU R, GUO D F, et al. Renewable energy driven system and method for synthesizing formic acid through carbon dioxide hydrogenation: CN113620798A [P]. 2021-11-09.
[44] IEA bioenergy - update 74 [J]. Biomass and bioenergy, 2024, 184: 107023. DOI: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2023.107023.
[45] SOCOLOW R, DESMOND M, AINES R, et al. Direct air capture of CO2 with chemicals: a technology assessment for the APS panel on public affairs [J]. American physical society, 2011.
[46] DEUTZ S, BARDOW A. Life-cycle assessment of an industrial direct air capture process based on temperature-vacuum swing adsorption [J]. Nature energy, 2021, 6(2): 203-213. DOI: 10.1038/s41560-020-00771-9.
[47] KULKARNI A R, SHOLL D S. Analysis of equilibrium-based TSA processes for direct capture of CO2 from air [J]. Industrial & engineering chemistry research, 2012, 51(25): 8631-8645. DOI: 10.1021/ie300691c.
[48] SINHA A, DARUNTE L A, JONES C W, et al. Systems design and economic analysis of direct air capture of CO2 through temperature vacuum swing adsorption using MIL-101(Cr)-PEI-800 and mmen-Mg2(dobpdc) MOF adsorbents (vol 56, pg 750, 2017) [J]. Industrial & engineering chemistry research, 2020, 59(1): 503-505. DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.9b06779.
[49] AZARABADI H, LACKNER K S. A sorbent-focused techno-economic analysis of direct air capture [J]. Applied energy, 2019, 250: 959-975.




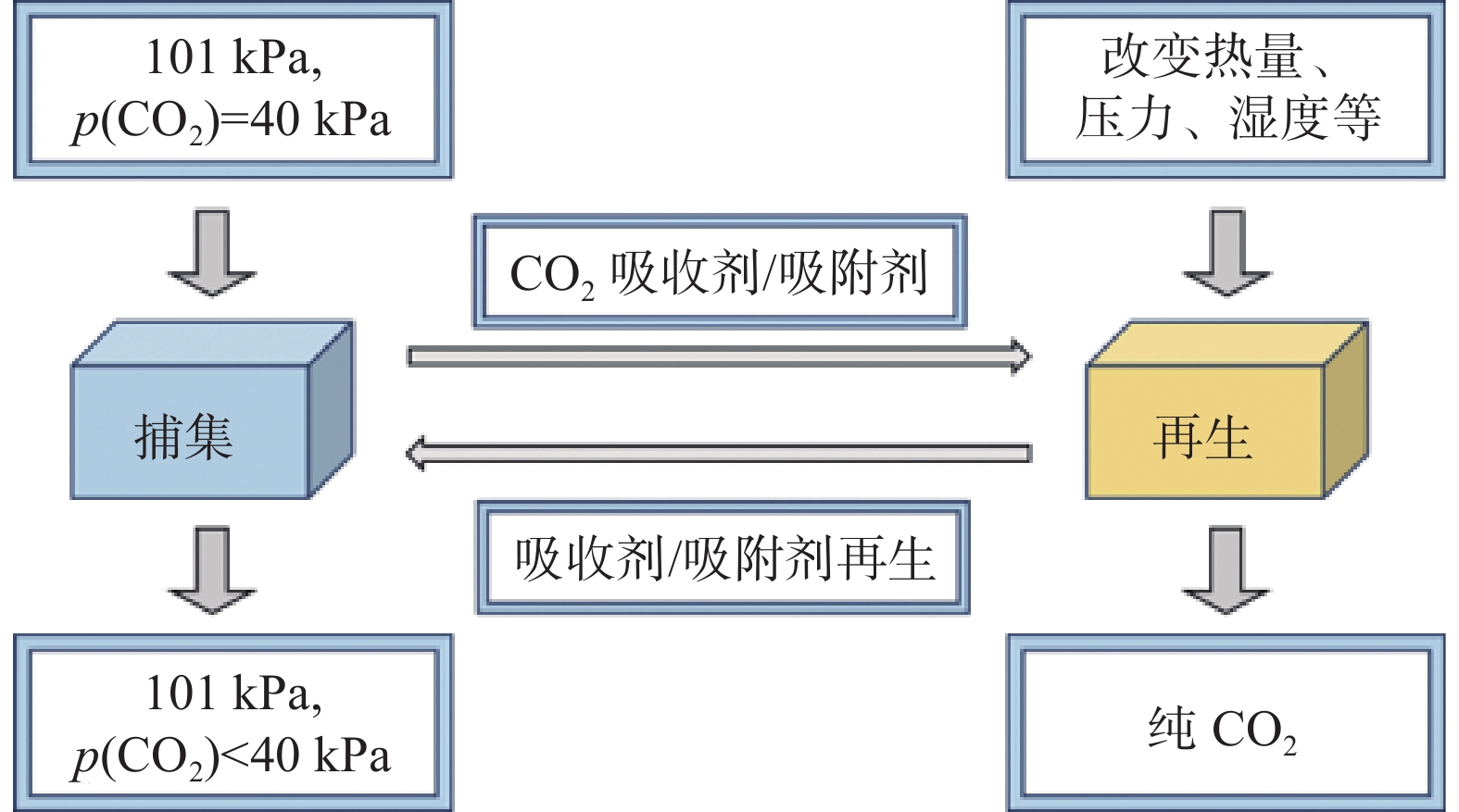
 下载:
下载: