-
随着人们对清洁能源的需求不断增长,全球范围内建设的光伏电站不断增加。尤其是海上漂浮光伏电站,能够利用海洋资源,不占用陆地资源,其发展前景广阔[1-2]。然而,在海上漂浮的光伏电站面临着多种恶劣气候条件,如雷击、大风浪等自然灾害,容易受到损毁和安全问题的困扰。海上漂浮光伏电站的防雷设计方法是一项非常重要的工作,直接关系到电站的安全和稳定运行。海洋环境的复杂性,加之雷电活动的不可预测性,使得防雷设计具有一定的技术难度。下面,我将从海洋环境、光伏电站结构和雷电特征等方面介绍海上漂浮光伏电站的防雷设计方法。因此,进行有效的防雷设计至关重要。文章将从海上漂浮光伏电站的防雷设计原理、防雷设计的方法和技术选取以及具体的防雷措施实施等方面探讨防雷设计的有效性。
-
海上漂浮光伏电站建设在开阔而复杂的海洋环境中,防雷材料在海水中的腐蚀形式分为均匀腐蚀和局部腐蚀2大类,局部腐蚀又包括点蚀、缝隙腐蚀、电偶腐蚀、应力腐蚀、腐蚀疲劳、磨蚀、气蚀等不同形式。如表1所示,根据腐蚀条件不同,把海洋环境分为海洋大气区、飞溅区、潮汐区、浅海区、大陆架区、深海区和海泥区。这些区域的海洋环境条件各异,对防雷设计也有不同的要求。比如,在深海区域,由于电站距离陆地远、海水深,晴天时的静电场强度较强,需要更加完善的避雷系统。而在受潮带,电站洗涤作用较强,设备老化、腐蚀等损伤对防雷系统形成威胁的可能性也较大。因此,在防雷设计中需要充分考虑海洋环境条件,全面科学地制定各项措施。
海洋区域 环境条件 腐蚀特点 大气区 海风盐粒,影响因素:高度、风速、雨量、温度 海盐粒子加速腐蚀,随离海岸距离而不同 飞溅区 潮湿,充分充气的表面,无海生物
玷污海水飞溅,干湿交替,腐蚀刺烈 潮汐区 周期沉泡,供养
充分氧浓差电池使用本区收到保护 浸泡区浅水
海水饱和,影响因素:流速、水温、
污染、海生物、细菌等腐蚀随着温度变化,浅水区腐蚀较重,阴极区形成石灰质垢,生物因素影响大 大陆架 生物污染减少,氧含量降低,温度
降低深度增加,腐蚀减轻,但不易生成水垢保护层 深海 含氧量比表层高,温度接近0 ℃,水流速低,pH低 镀铜的腐蚀通常较轻 海泥区 常有细菌
(如硫酸盐还原菌)泥浆有腐蚀性,现场泥浆与海水间的腐蚀电池有微生物腐蚀产物 Table 1. Comparative analysis of corrosion characteristics in different marine environments
在受潮带区域,可以考虑采用防雷接地、避雷针等措施来保护海上漂浮光伏电站和设施;在浅海区,可以采取屏蔽、滤波、接地等措施来降低雷电电磁脉冲干扰的影响;在深海区,可以采取建立漂浮散流接地网方法来进行防雷保护。
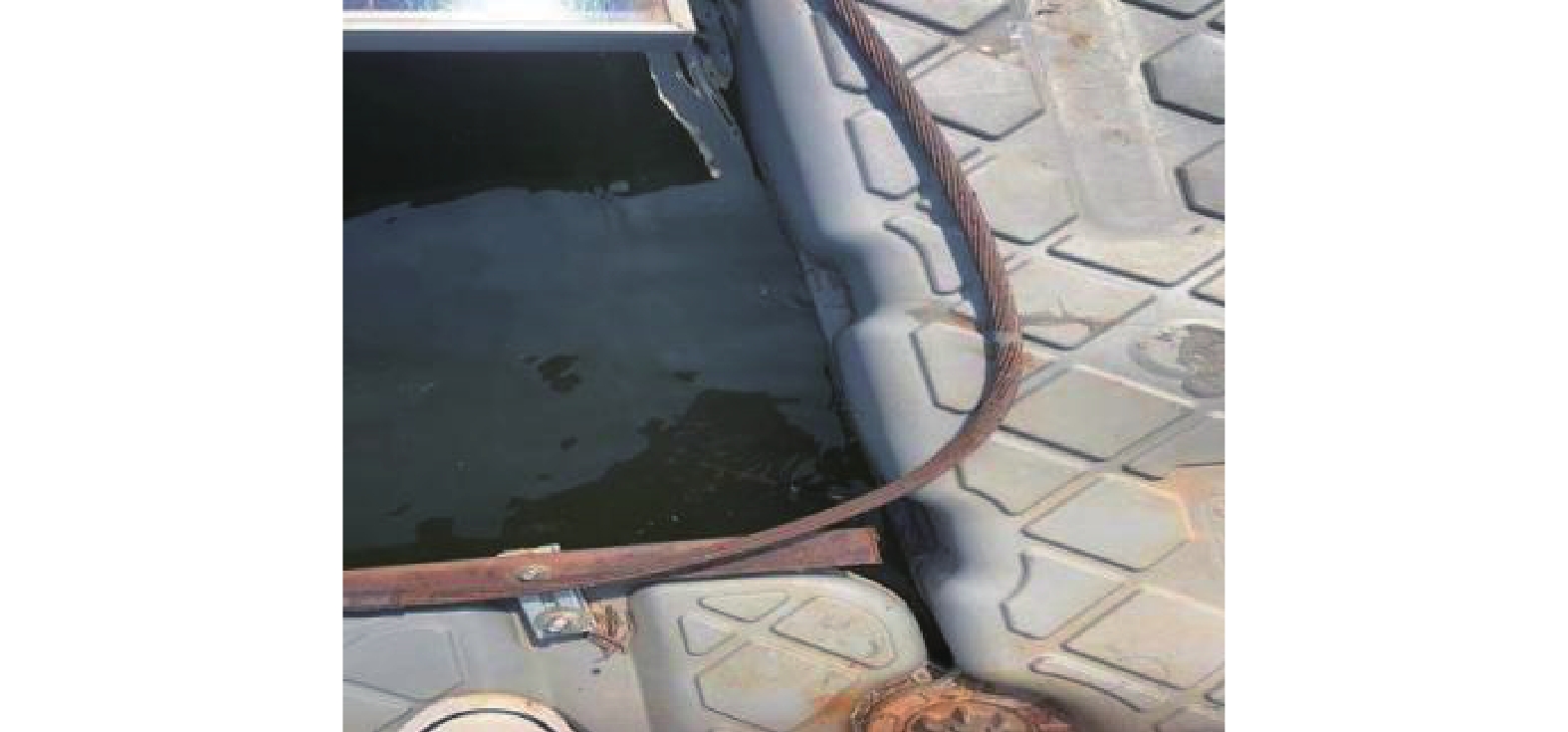
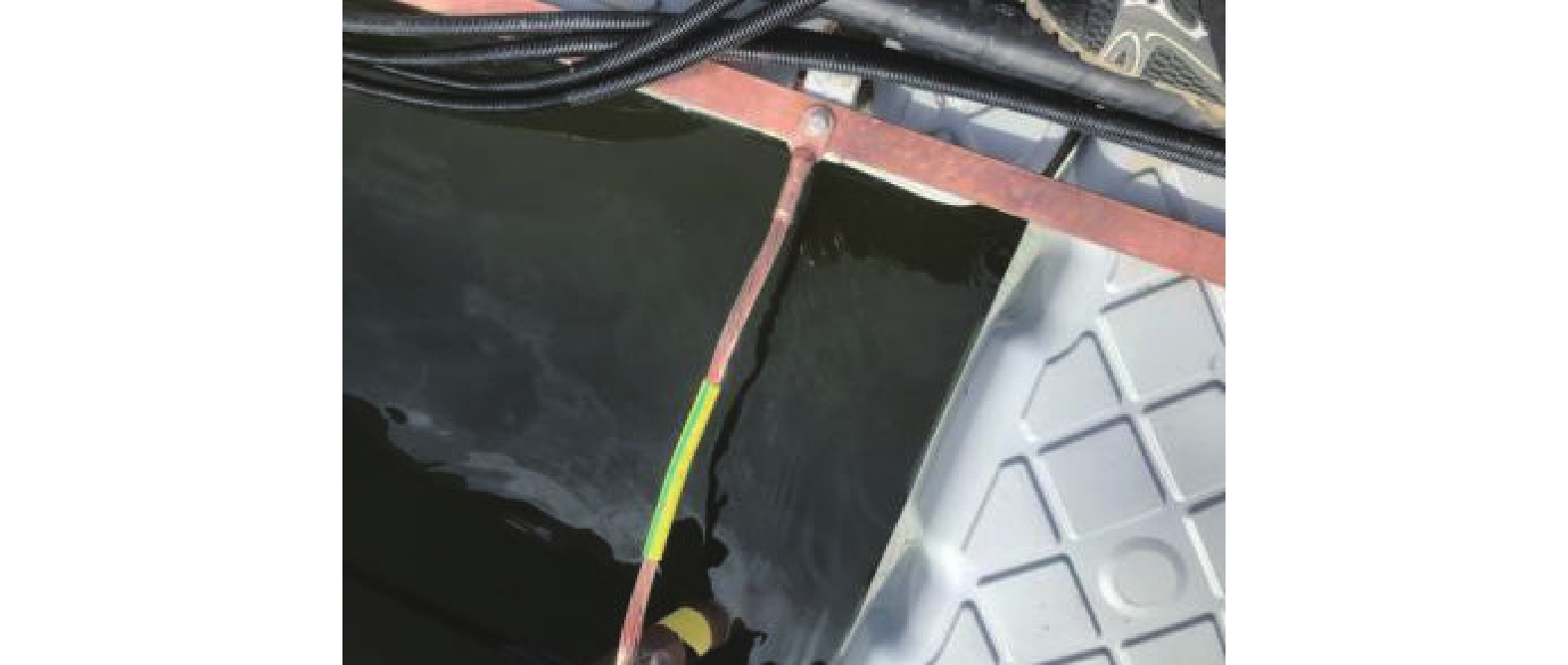
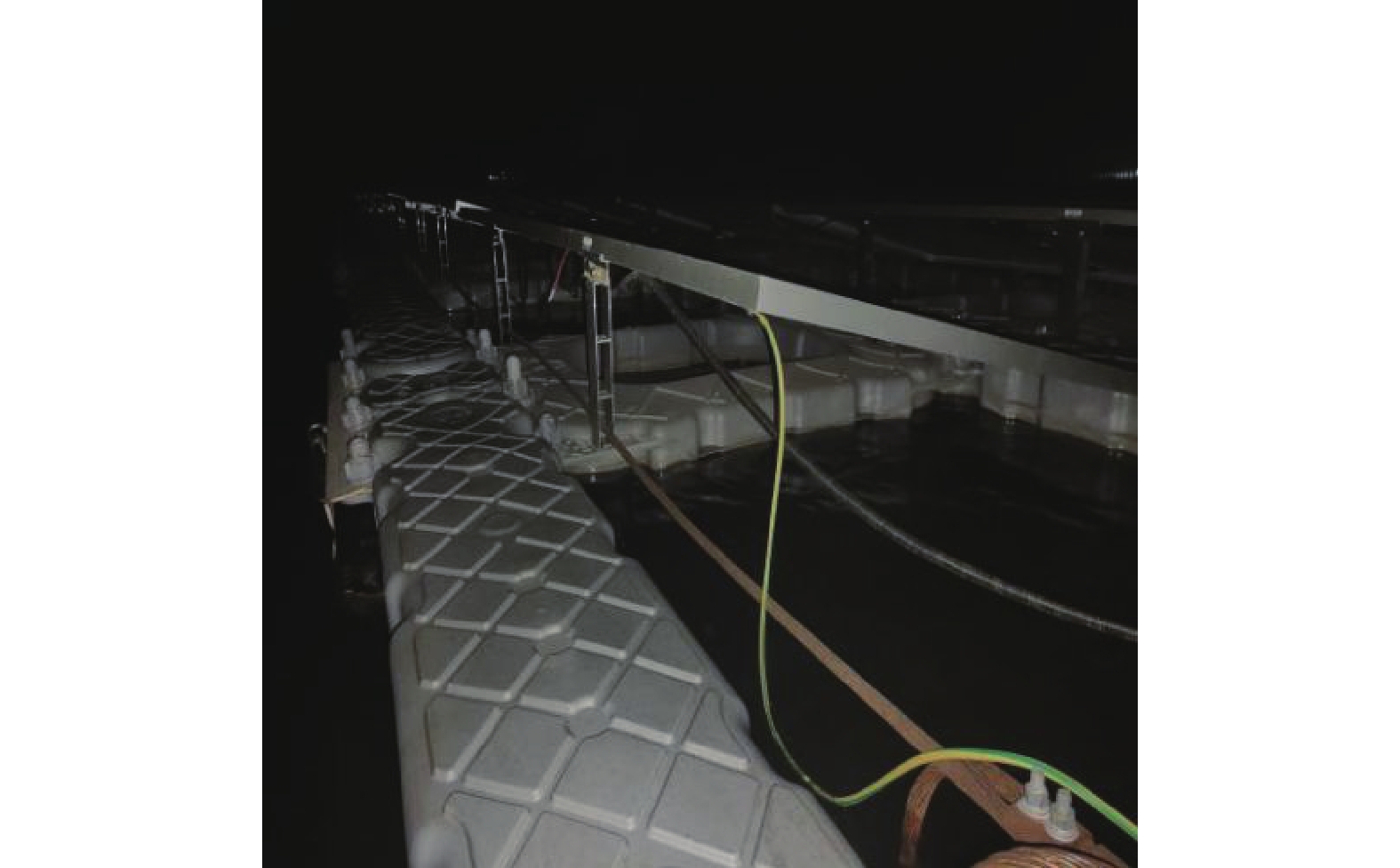
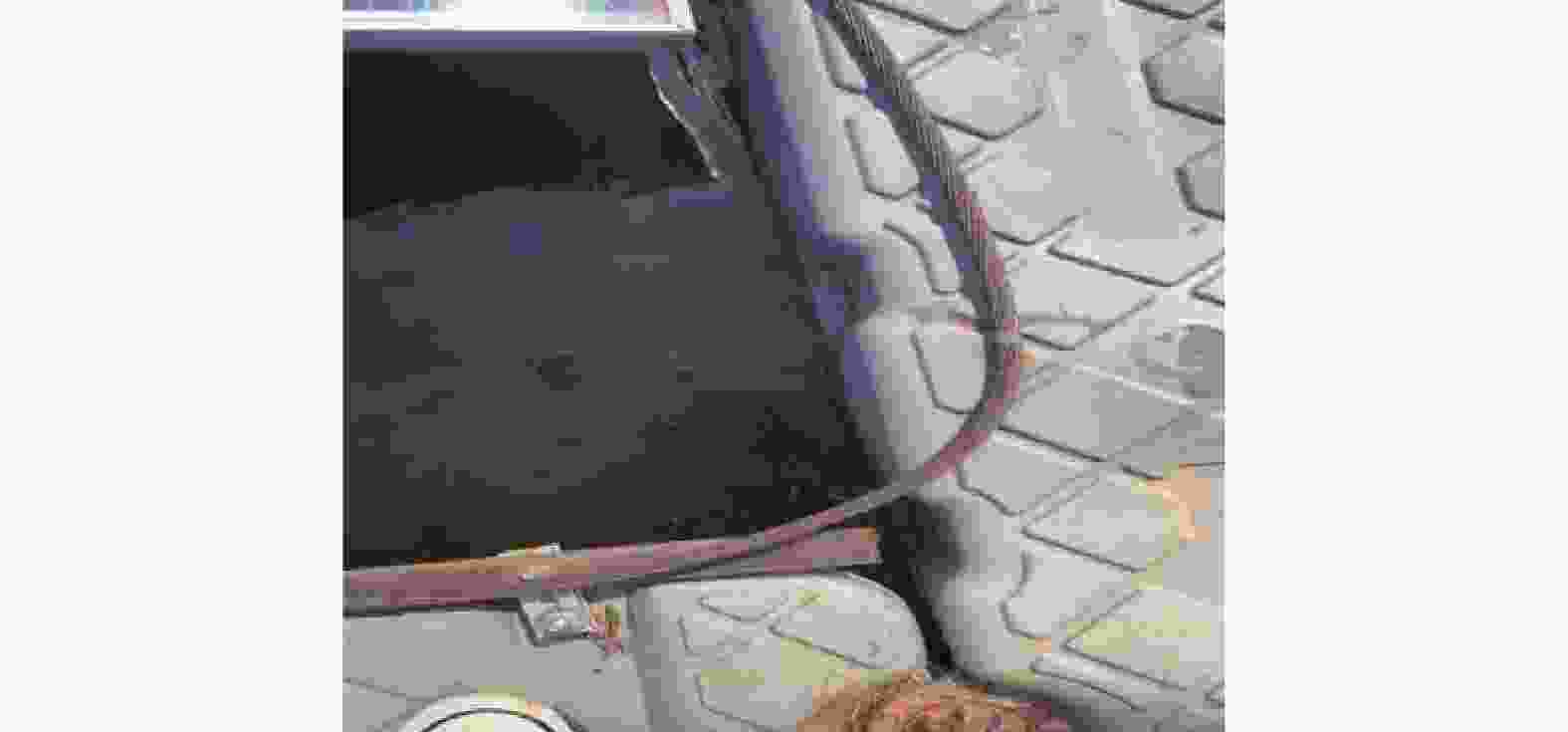
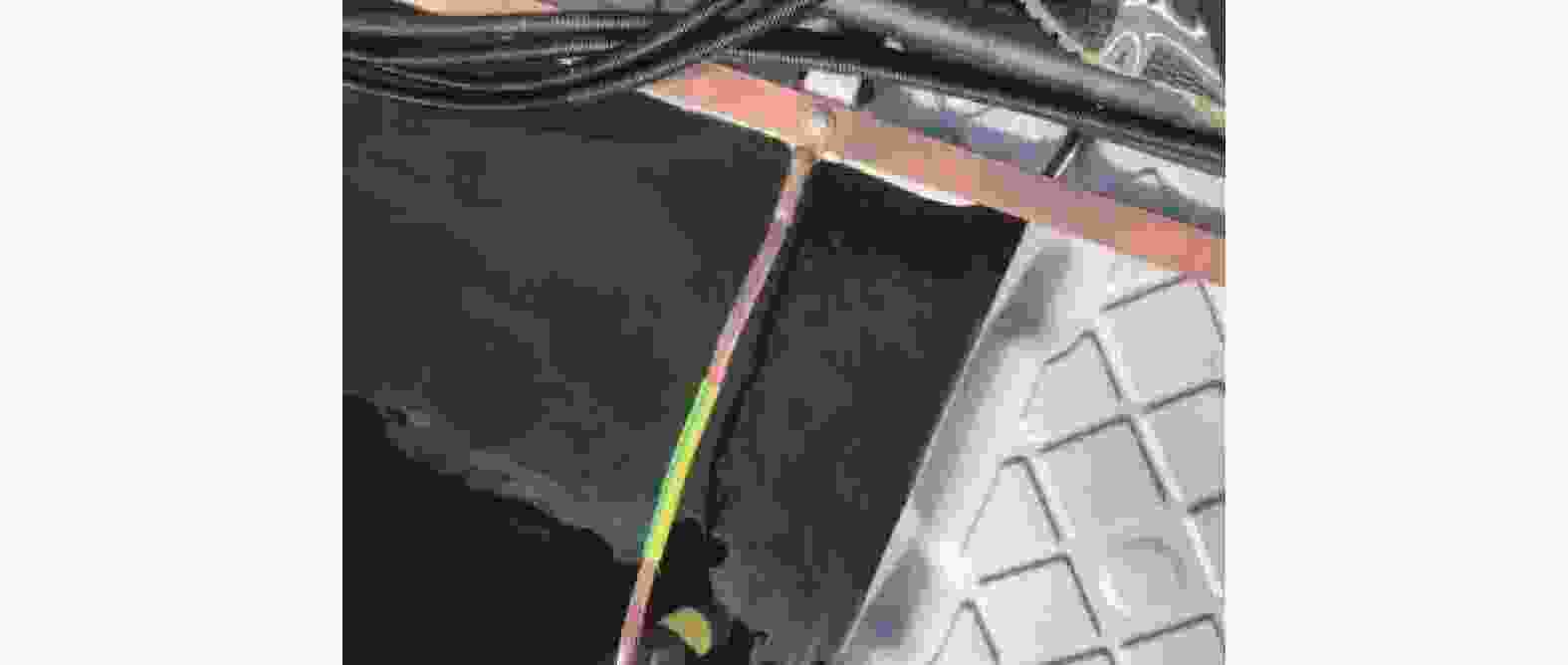
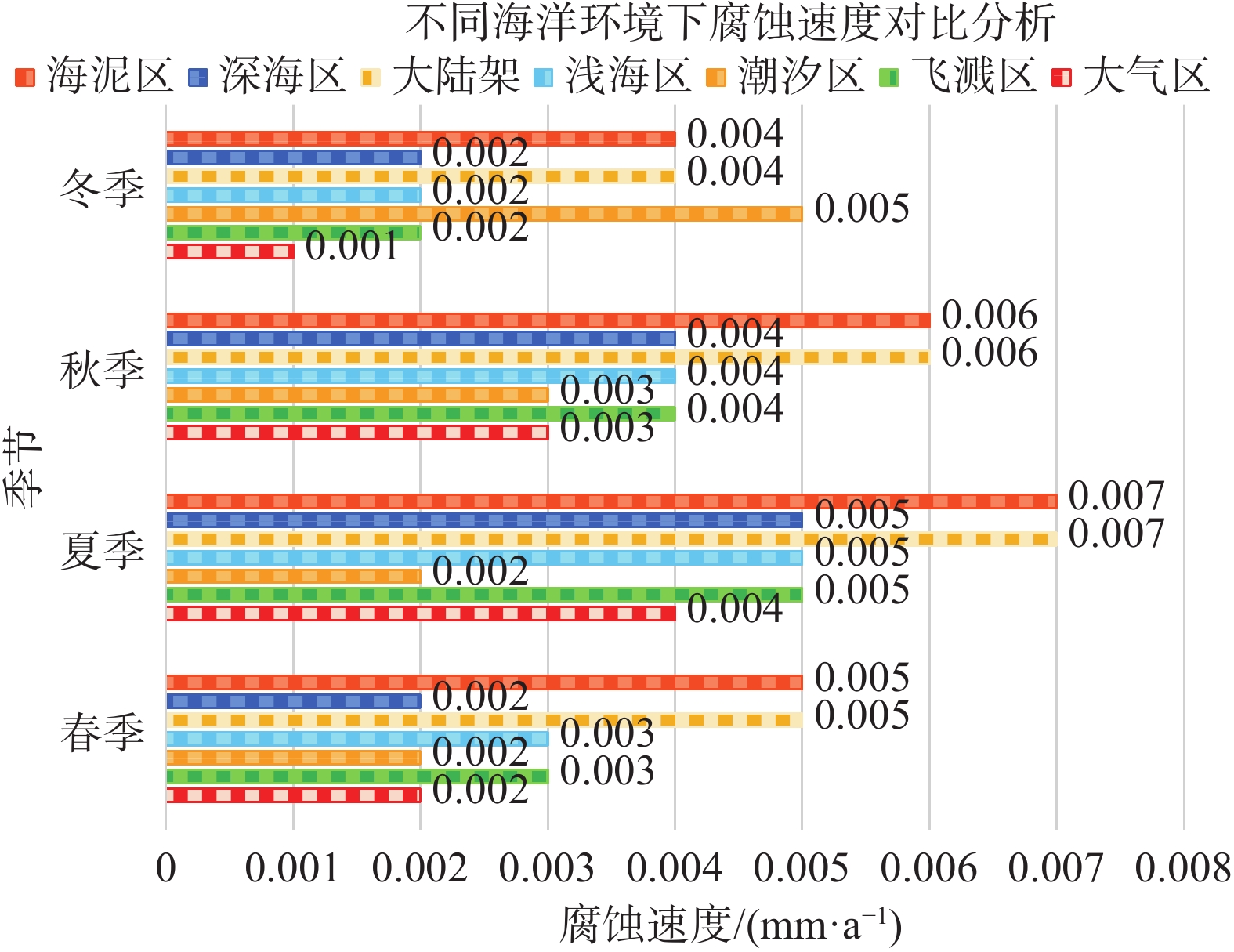
如图1所示,在不同海洋环境下,海上漂浮光伏电站防雷材料选择至关重要。以天津某浅海漂浮为例,选择了镀铜、包塑镀铜2种接地材料进行对比使用情况,如图2和图3所示。
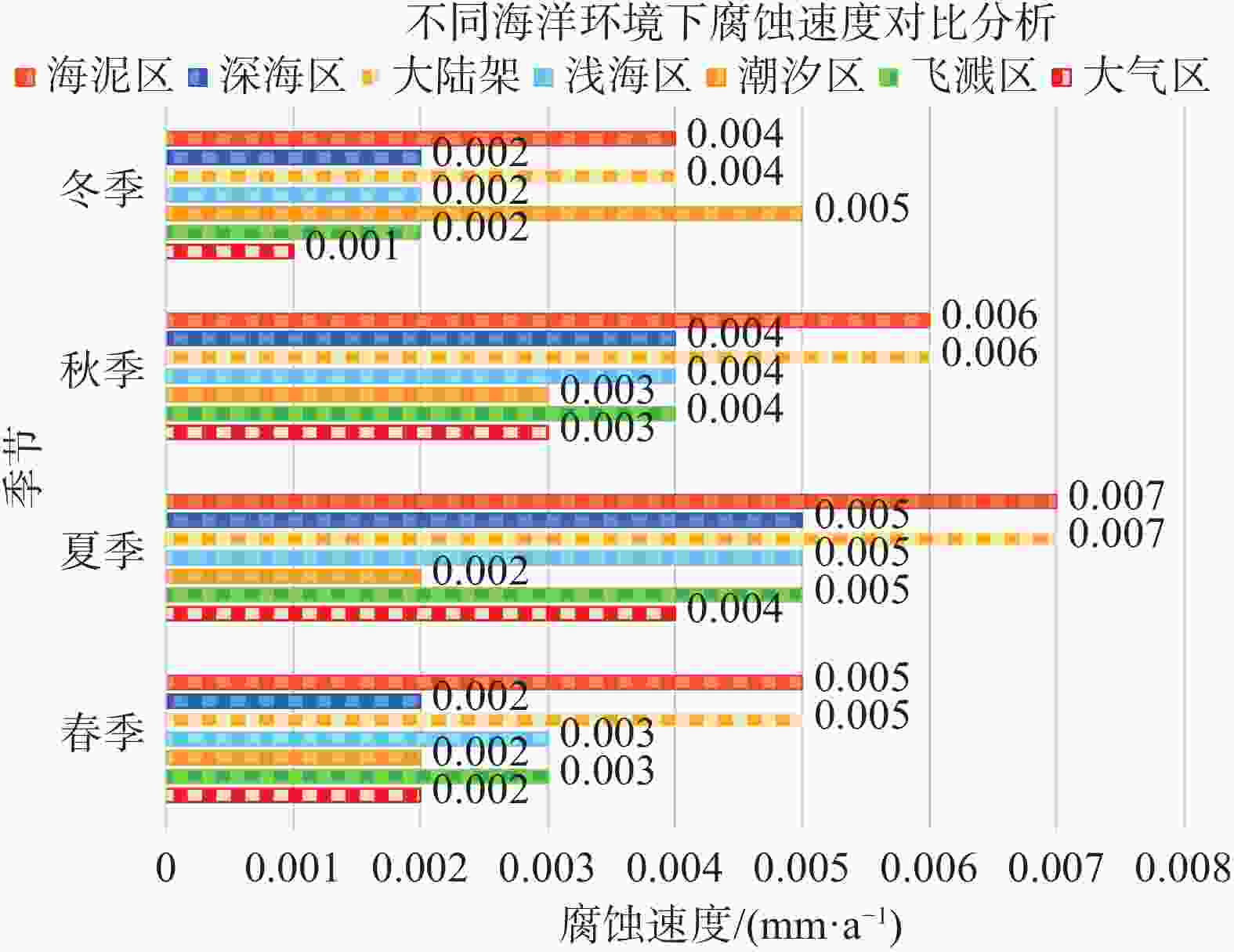
Figure 1. Comparative analysis of corrosion rates in different marine environments and different season
通过实际项目使用对比发现,在同样海水环境下,浸泡时间相同,其腐蚀特征区别如表2所示。
对比项目 镀铜钢绞线 包塑镀铜钢绞线 耐腐蚀性 8~10 a的使用寿命,腐蚀速率:0.005 67 mm/a 无腐蚀,腐蚀速率:0 mm/a 热稳定性 热稳定系数135 热稳定系数135 导电性 相当于铜的30% 相当于铜的30% 泄流能力 对高频电流的泄流能力是钢材的4倍 对高频电流的泄流能力是钢材的4倍 连接方式 放热焊接,电气性能稳定,没有接触电阻 放热焊接,电气性能稳定,没有接触电阻 接地效果 很稳定,接地电阻会保持在一个较稳定的水准 很稳定,接地电阻会保持在一个较稳定的水准 防盗性 其材料非铜看起来像铜容易被盗,防盗性差 由于外面包塑一层外皮,诱惑力不大,防盗性好 Table 2. Comparison of corrosion characteristics of copper-plated and plastic-coated copper-plated grounding in offshore floating photovoltaic power stations
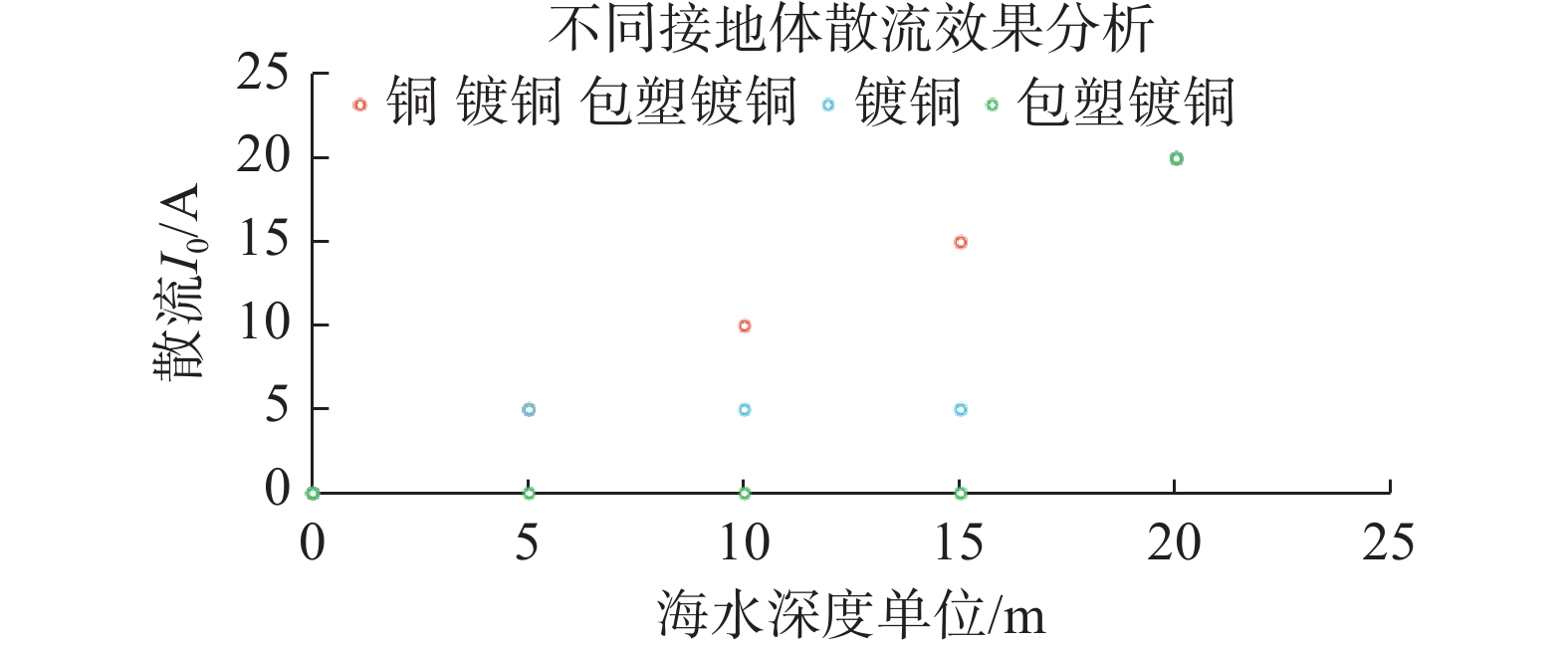
在海底电阻率均匀、接地体与海水紧密接触的情况下,流入海底的电流通过接地极向海底呈半球状散流,铜、镀铜、包塑镀铜3种接地材料在海上其散流效果如图4所示。试验证明:离接地体愈近,电流密度愈大,电压降也愈大;当电流流经距接地体很远的地方时,由于电流密度非常小,实际电压下降接近于0。其散流分布特性为,铜由径向逐步增大散流;镀铜由径向稳定一个数值散流;包塑镀铜直到接地极处散流。由于包塑与海水接触部分不散流,不会造成人员及海水中物体受电。

Figure 4. Comparison of dispersing the scattered current area effects of different offshore grounding electrodes
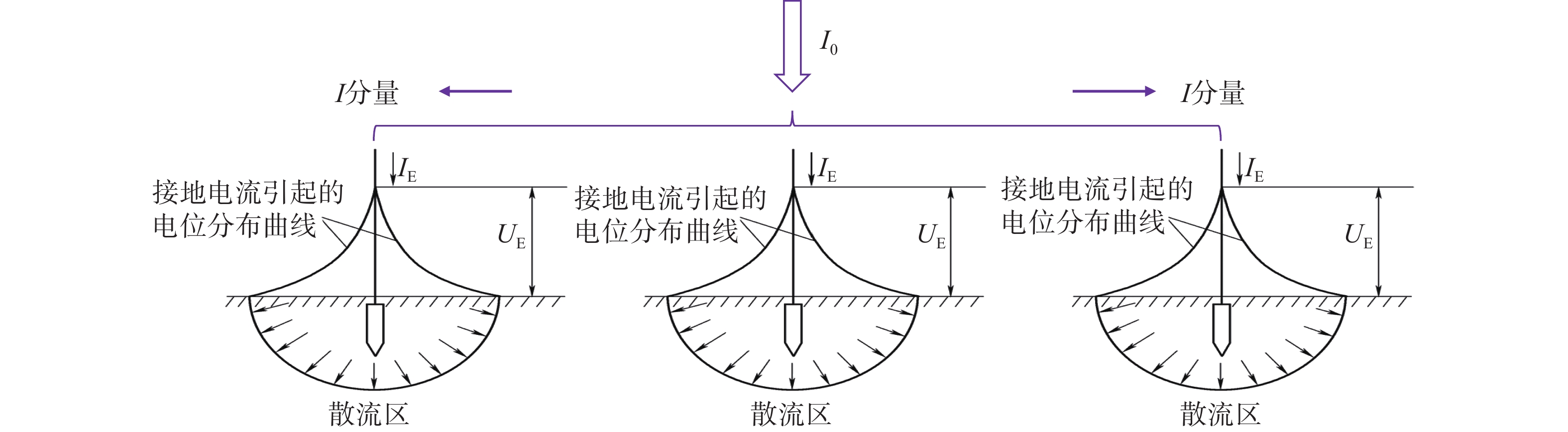
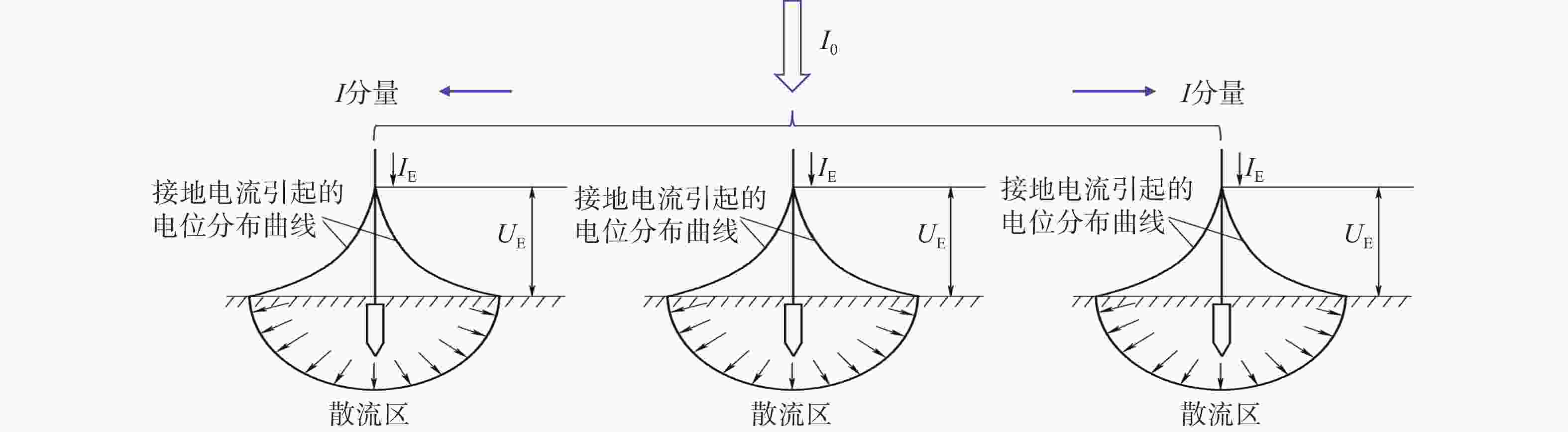
多根接地装置周围散流电阻分布如图5所示。由图5可知,多根接地装置由于屏蔽作用,其散流区更大,零电位的位置更远。
由此可以得出,零电位存在于散流区之外,接地体越多,散流区越大,零电位的位置也越远。散流区的大小取决于地网的形状、大小和尺寸。因此海上漂浮光伏电站使用包塑镀铜材质作为接地引下线不会对其散流效果产生影响。
1)铜:铜是一种良好的导电材料,适用于高电流和腐蚀性环境。在海水环境下,铜的耐腐蚀性较好,但长期浸泡在海水中也会被腐蚀,且价格昂贵。
2)镀铜:镀铜是通过在铜表面镀上一层薄薄的铜层来提高铜的耐腐蚀性和抗氧化性。在海水环境下,镀铜的耐腐蚀性较好,但长期浸泡在海水中也会被腐蚀,价格相对较便宜。
3)包塑镀铜:包塑镀铜是一种将镀铜层包裹在聚乙烯或聚氯乙烯塑料中的接地材料。包塑镀铜的耐腐蚀性较好,且能够有效地防止土壤和海水对铜层的腐蚀。同时,包塑镀铜还具有较好的柔性和耐久性,适用于各种复杂环境。且性价比最高。在海水环境下,包塑镀铜是一种较为理想的接地材料。
-
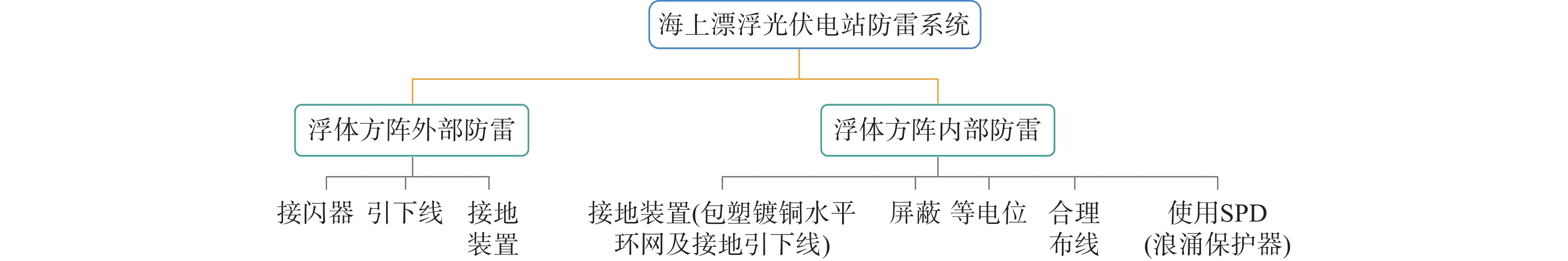
海上漂浮光伏电站是指在海面上建造的浮动式光伏电站,采用全柔性HDPE(High Density Polyethylene,高密度聚乙烯)浮体漂浮系统的漂浮电站,其主体结构均为HDPE浮筒,每个光伏组件与单个专有浮体相连接组成一个小单元,不与其他光伏组件产生联系,浮筒与浮筒之间通过相同材料的螺栓柔性连接,在应对各方向受力情况下,均能通过上下摆动进行卸力,在风浪流的耦合作用下可“随波上下浮动”,受力良好达到了以柔克刚的效果。它们的结构设计需要充分考虑海洋环境的特殊要求。其结构与固定式相似,但采用了动态浮体设计,光伏组件与浮体之间用支架连接,浮体采用高密度聚乙烯(HDPE)材质制成,抗风能力为60~70 m/s。该类型电站可以在水深50~100 m之间的海域安装。如图6所示,海上漂浮光伏电站通常由浮体、支架、组件、逆变器等部分组成。其中,支架和组件是电站的重要结构部分,也是易受雷击危害的部位。因此,在防雷设计中需要针对支架和组件进行设计和改进,采取更为可靠、坚固的材料和技术,保护这些部位。
-
海上雷电现象的发生时间具有明显的季节性和日变化。一般来说,夏季和秋季是海上雷电现象的高发季节,而白天比晚上更容易发生海上雷电现象。海上雷电现象的发生与海洋环境因素密切相关。例如,海面温度、海水盐度、海流、风速、湿度等环境因素的变化都可能影响海上雷电现象的发生。海上雷电现象的形式多样,包括云闪、云地闪、海底闪等。其中,云地闪是海上最常见的雷电现象,指的是云与地面之间的放电现象。海上雷电现象的电流和电压较高,可以达到数百千安培和数百万伏特。同时,海上雷电现象的能量也较大,可能会对光伏组件、逆变器设备及平台等海上漂浮光伏设施造成严重的破坏。海上雷电现象的发生具有随机性,难以预测,给海上漂浮光伏电站带来一定挑战。
以研究项目所处地理位置为例,天津滨海新区塘沽地处渤海湾,其特殊的地理位置和环境条件,导致夏季常常遭到雷暴的影响。塘沽地区近50年(1964-2013年)来雷暴日数在6~8月的夏季出现次数最多,占整年的47.8%,其次是春季的3~5月占整年的29.2%,秋季的9~11月占整年的13%,冬季的12月~次年2月没有雷暴发生[3]。
雷电天气时避雷系统的作用极为关键,避雷针、地网等设备能够起到重要的雷击保护作用[4-7]。在防雷设计中,需合理设计避雷系统,采取合适的避雷针高度、地网接地深度等参数,以达到最佳的防雷效果。
-
海上漂浮电站的雷电作用原理是指,在海上漂浮电站内部,当云层和大地之间的电位差增大时,就会形成电场,从而使电子在空气中移动形成电离层[8-10]。当电场足够强时,电子会沿着空气中的离子通道穿过电离层并击穿到海面上。
在这个过程中,电子和离子之间的碰撞会导致电荷的分离,形成电荷分离层[11-13]。当电场足够强时,这个层会形成电晕放电,从而将电荷释放到海上漂浮电站的导体表面。
当这些电荷在电站表面积累到一定程度时,就会产生放电现象,生成电流[14-16]。这个电流可以沿导体,通过导体向海底释放掉,从而保证了漂浮光伏电站的安全运行。
-
防雷设计的基本原理是通过建立保护设备和接地系统[17-18],以分散、吸收、放电或反射雷电电磁波,减小雷击对光伏电站带来的危害[19-20]。以5 MWp标准阵列为例,如图9所示,海上漂浮电站防雷设计原理包含以下几个方面:

Figure 9. Schematic diagram of the 5 MWp standard array of the offshore floating photovoltaic power station
1)建立地网:在海上漂浮电站浮体通道周围安装地网,将电站的金属结构与海底连接起来,形成一个低阻抗的路径,以便将雷击电荷导入海底。这有助于降低结构的感应电位和电压,并减少雷击损伤的概率。
2)安装避雷针:避雷针通常是在电站的顶部安装,可以将雷击电流导入地下设备中,防止雷击伤害电站结构和设备。
3)安装绝缘器:在电站内部,可以安装电气绝缘器来隔离电站的不同部分,以减少雷击电荷的传递。
4)使用合适的材料:电站结构和设备的材料应该具有优良的防雷性能,抗雷击能力强。例如,使用耐腐蚀的包塑镀铜材料等。
5)安装监测设备:在电站结构和设备中,安装合适的监测设备,以便及时发现雷击事件,并采取相应的措施。监测设备可以包括雷暴警报系统、感应电压监测装置、接地电阻测试设备等。
综上所述,海上漂浮电站的防雷设计是多方面的,需要综合考虑各种因素,采取合适的措施来减少雷击损伤的概率和影响。
-
首先需要进行光伏电站的地质勘探,掌握地质和土壤等基础信息。地质勘探和土壤电学特性研究是地球科学领域的重要方向之一,主要是研究土壤及地下岩石的导电性质。例如,地球物理勘探中的电阻率法、自然电位法、磁法都是基于土壤和岩石的导电特性来进行勘探的[21-22]。电阻率法能够探测到地下物质的性质、形状、空间分布等信息;自然电位法则以地下电位的分布规律来推断地质构造;磁法则能够探测到地下物质中磁性物质的含量、位置和分布。根据实测结果,确定合适的接地形式,包括单点、网状和集中等多种类型。
-
由于海水是一种良好的导体,在海水中安装的海上漂浮光伏电站的船体必须具有绝缘措施,降低雷击风险。船体绝缘措施可以大致分为以下几个方面:
1)船体涂漆:船体的涂漆可以增强其绝缘性能,减少电器设备的电磁干扰和静电干扰。
2)接地系统:对船体进行有效的接地处理可以提高其绝缘性能,减少电器设备的漏电和电击的风险。及时清洗和维护接地系统,保证接地系统的导电性能。
3)船体绝缘材料:对于一些高压设备,可以在其周围铺设绝缘材料提高安全系数。
-
加装避雷针是一种常见的防雷手段。在海上漂浮的光伏电站上,可在电站周围的海上增加一定数量的避雷针,以吸收雷电的电荷,从而减轻雷击力。
-
为了防止直接击中和雷电波的感应效应,可以设计引下系统和接地系统,并规范接地电阻的大小,以达到有效地吸收、放电、反射雷电电磁波的目的。海上漂浮式光伏发电系统应在每个漂浮方阵四周、电气设备主通道设置接地干线,接地干线宜采用铜包钢、接地电缆等,可在水中设置垂直接地极。
根据IEEE标准中接地导体截面选择计算,标准中所提供的接地导体最小截面的公式如下:
$$ {A_{{\rm{sc}}}} = \dfrac{{{I_f}}}{{\sqrt {\left( {\dfrac{{T_{CAP} \cdot {{10}^{ - 4}}}}{{{{{t}}_{\rm{c}}} \cdot {{{a}}_{\rm{r}}} \cdot {\rho _{\rm{r}}}}}} \right) \cdot {\rm{ln}}\left( {\dfrac{{{K_{\rm{o}}} + {T_{\rm{m}}}}}{{{K_{\rm{o}}} + {T_{\rm{a}}}}}} \right)} }} $$ (1) 式中:
If ——接地故障对称电流(A);
Asc ——导体截面积(mm2);
Tcap ——单位体积热容[J/(cm3·℃)];
tc ——故障持续时间,取0.6 s;
α0 ——电阻率热系数(t = 0 ℃);
αr ——参考温度Tr下电阻率热系数;
ρr ——参考温度Tr下导体电阻率(μΩ·cm);
Ko ——1/α0或(1/αr-Tr) ℃;
Tm ——导体允许最大温度(℃);
Ta ——环境温度(℃)。
采用式(1)计算的假想条件是短路为绝热过程。对于大多数金属,只要发生故障的时间足够短,对于大部分温度条件来说,这些假设都基本成立。将各种接地材料的相关参数带入IEEE标准里的导体截面选择公式中,可以得到如下公式:
$$ A_{{\mathrm{SC}}}= \frac{1}{{1.974}}{I_{\text{f}}}{K_{\text{f}}}\sqrt {{{{t}}_{\text{c}}}} $$ (2) 式中:
Kf ——材料在不同Tm值下的常数[23]。
通过以上公式计算得海上漂浮式光伏发电系统组件间宜采用不小于6 mm2的接地电缆,设备接地宜采用不小于50 mm2的电缆,主接地网宜采用不小于70 mm2的包塑镀铜钢绞线。漂浮式光伏发电系统中接地用连接线或电缆应考虑浮体波动及水位及海浪变化的影响[6]。
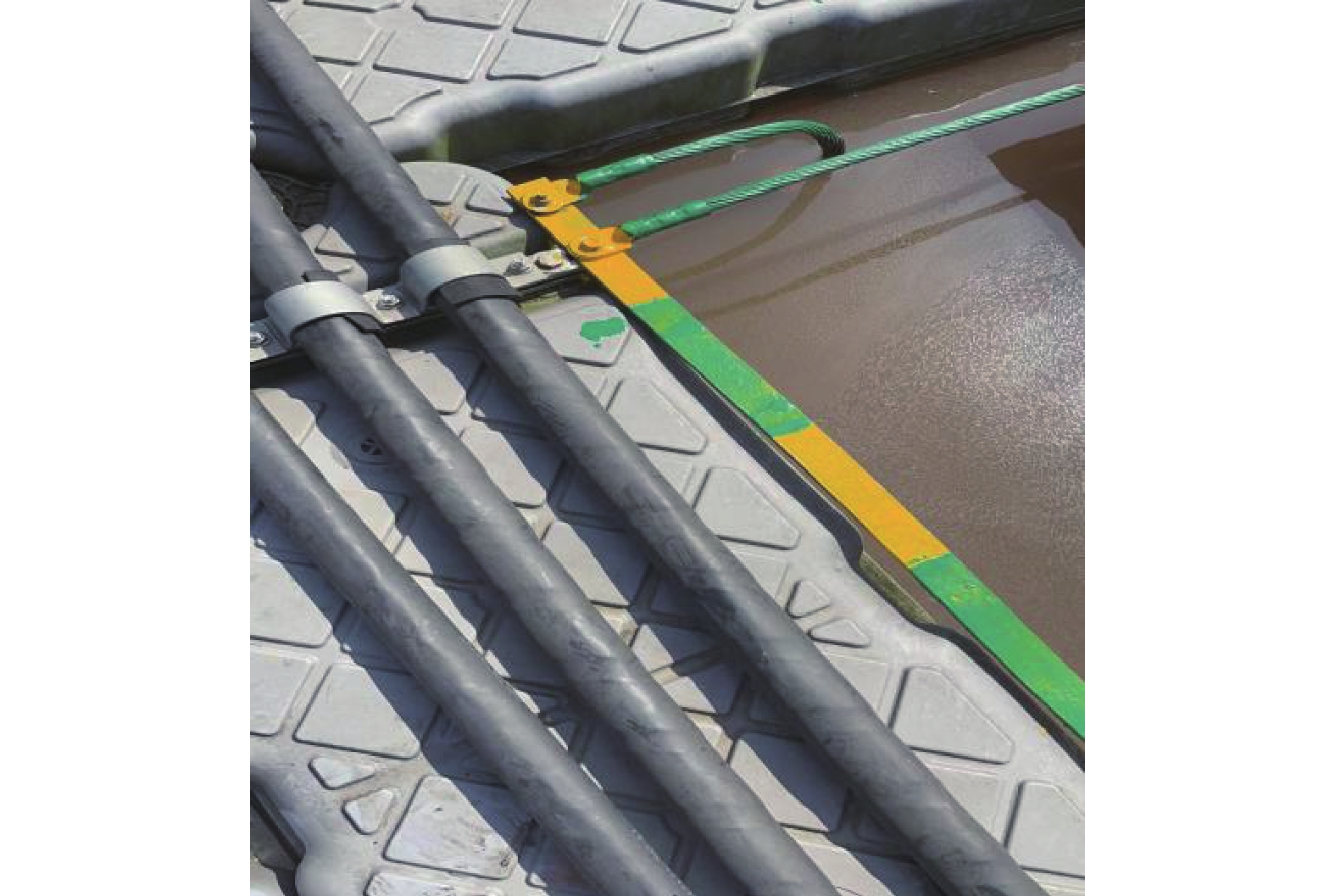
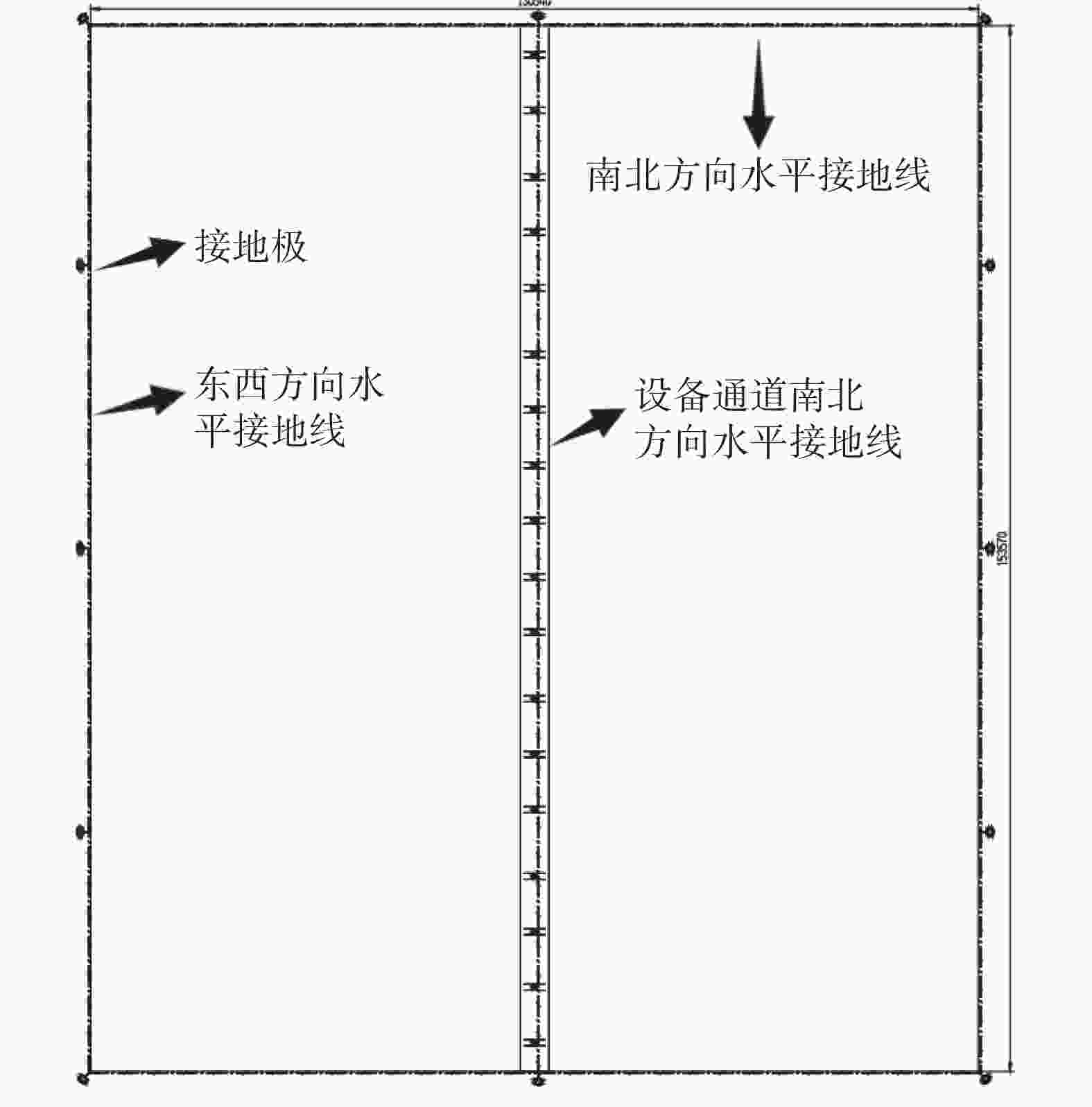
通过对天津某海上漂浮光伏电站进行设计,如图10所示,采取了一些接地防雷技术选取。水平接地采用120 mm2包塑镀铜钢绞线,沿检修通道浮体边沿敷设,在经常有人出入的地方采取穿管保护措施,利用方阵周边浮体耳朵螺栓进行固定。接地网的外缘应闭合且各角做成圆弧形,圆弧的半径不应小于均压带间距的一半。接地体采用HJ-Tm100不锈钢镁合金防腐地极,需确保打入海底,接地体与水平接地网通过一根120 mm2包塑镀铜钢绞线压接。电池组件支架间用镀铜接地扁钢进行两点可靠连接,每组光伏组件支架必须保证两点直接与主地网连接或通过其他光伏组件支架与主地网连接。接地线与接地网的连接点至35 kV及以下设备接地点的接地体长度(地中距离)大于15 m。箱变必须保证至少两点与主地网连接,箱变平台接地网引下线与主接地网采用120 mm2铜缆两点连接。组件支架间,组件支架和主接地网间接地扁钢的连接采用螺栓压接的方式,其压接截面必须大于或等于两倍镀铜扁钢宽度,需满足施工规范要求。组串式逆变器等需要有明显的接地线与主接地网连接,接地线采用25 mm²的包塑镀铜铜绞线。设备接地应有便于测量的断开点。接地黄绿标识应规范,所有明敷的接地线均应刷15~100 mm宽度相等的黄绿相间的条纹。光伏电池板无氧化层保证与支架可靠连接,形成电气通路,保证光伏组件与支架整体的电气联通。所有接地材料均要求包塑镀铜处理,现场连接处需做防锈处理。箱变单元接地网和光伏方阵接地网保证两点可靠连接,接地扁钢通过电缆浮体通道敷设。光伏场区工频接地电阻设计值不大于4 Ω,若实测值达不到设计值,需增加垂直接地极或接地装置。
-
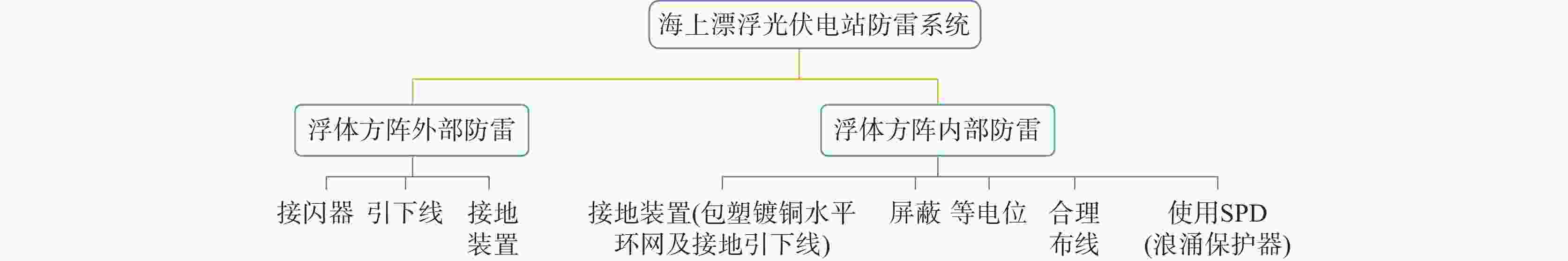
在海上光伏电站防雷设计过程中,也会遇到一些技术难题,例如避雷针、地网及接地装置的选择和定位、避雷系统一级保护、二级保护设计和布置等。针对这些难题,可以采取合理的设计思路,包括考虑系统的可靠性、实施时的安全性。可以采取以下措施来进一步提高海上漂浮光伏电站的防雷能力,如图11所示:
1)设置绝缘障碍:在电站结构和设备的周围设置绝缘障碍,如橡胶条、聚乙烯薄片等,防止雷击电流直接进入结构和设备。
2)定期维护光伏电池板:光伏电池板的表面一旦有脱落或损坏,会削弱防雷能力。因此,需要定期检查和维护光伏电池板表面,确保其完好无损[7]。
3)配备避雷保护装置:在电站的电气系统中,可以配备适当的避雷保护装置,如避雷器、耐压电缆等,以增强电气设备的防雷能力。
4)加强人员培训:加强工作人员的防雷意识和知识培训,培养工作人员发现和应对雷击风险的能力,避免疏忽大意导致意外事故的发生。
5)进行防雷设备的安装:根据防雷设计的方案和技术要求,进行防雷设备的安装,包括避雷针、接触网状焊接、接地体和导体等细节方案。
6)防雷设备的维护和检查:为了保证防雷设备能够长期有效工作,需要进行定期维护和检查。例如,定期检查避雷针和接地体的可靠性,定期测试接地电阻[8, 15-16]。
-
文章对海上漂浮光伏电站防雷设计进行研究,结论如下:
1)海上漂浮光伏电站防雷设计是非常重要的,因为在海上这种特殊环境中,雷击事件的发生概率非常高。
2)在国内和国外已经有相当多的关于光伏电站防雷设计的研究,但是在海上漂浮这种特殊环境下,还需要更多的研究和改进。
3)目前常用的防雷措施包括接地、避雷针、避雷带、防雷网和防雷模块等,这些措施都需要在海上环境下进行特殊的设计和使用。
4)在设计海上漂浮光伏电站的防雷措施时,需要考虑海上特殊的环境因素,如海水腐蚀、海风等,以确保防雷措施的长期有效性。
海上漂浮光伏电站的防雷设计涉及众多方面,需要全面考虑,采用多种手段相结合,才能有效地预防雷击风险,确保电站的安全稳定运行。海上漂浮光伏电站防雷设计是确保电站正常运行和减少安全事故的重要保障。通过正确的设计和技术实施,可以有效地减轻雷击对电站的危害,提高电站的安全性能和可靠性。海上漂浮光伏电站防雷设计既有面临的挑战,也有追求的目标和方向。通过综合应用多种防雷技术手段,加强对电站的管理和维护,可以更好地提高电站的防雷性能,实现海上漂浮光伏电站的安全稳定运行。
Lightning Protection Design of Offshore Floating Photovoltaic Power Station
doi: 10.16516/j.ceec.2023-132
- Received Date: 2023-05-21
- Accepted Date: 2023-07-21
- Rev Recd Date: 2023-07-20
-
Key words:
- offshore floating photovoltaic power station /
- lightning protection design /
- lightning protection measures
Abstract:
| Citation: | ZHOU Chengsheng. Lightning Protection Design of Offshore Floating Photovoltaic Power Station[J]. SOUTHERN ENERGY CONSTRUCTION. doi: 10.16516/j.ceec.2023-132 |









 DownLoad:
DownLoad: