-
实时动态仿真分析是现代电网实时控制的重要依据[1,2,3]。要进行有效的电力系统实时动态仿真分析,必须采用准确的电力模型[4,5]。尤其是对于时变性较强的电力负荷模型,若在实时动态仿真分析过程中采用固定的模型参数,所得的结果将可能与实际情况出现较大的偏差,在某些情况下甚至会出现截然相反的结论[6,7,8]。在这种背景下,本文开展动态电力负荷建模的研究。
负荷建模主要描述的是负荷功率与电压或者频率之间的关系,可视作一个系统辨识问题。从已有的研究情况看,负荷建模主要包含模型结构选择以及参数辨识两部分内容[9]。在模型结构方面,相关学者进行了大量研究并提出了多种模型结构,具体可分为静态负荷模型和动态负荷模型两类。其中,静态负荷模型中最具代表性的是ZIP模型[10],其结构简单,便于理解和应用,目前已得到大量应用。然而静态负荷模型无法准确描述电力负荷的动态特性,因此在实时动态仿真分析中的应用受到了限制[11]。为此,一些专家提出了动态负荷模型,其中目前应用较为广泛的是电动机模型[12]或电动机并联ZIP模型[13,14]。这种动态负荷模型在离线的动态仿真分析中具有较好的效果,但其参数过多,在线辨识的难度较大。为此,一些学者只对其中灵敏度较高的某些参数进行辨识,但这又降低了模型的精度。指数型动态负荷模型作为另一种典型的动态电力负荷模型也得到了较多的研究和广泛的认可[15,16]。该模型既能比较准确地描述负荷恢复或者过渡过程的非线性动态特性,其相对简单的结构也有利于在线参数估计,因而适用于实时动态仿真分析。
在参数辨识方面,最小二乘法在早期得到了较为广泛的应用[17]。但是由于电力负荷模型的非线性较强,最小二乘法在参数辨识时容易陷入局部最优。为了解决这个问题,近年来遗传算法[18]、粒子群算法[19]、人工蜂群算法等人工智能算法也被大量地用于负荷模型的参数辨识,但该类方法耗时较长,因而无法用于在线建模。为了实现参数的在线辨识,某些学者又引入了扩展卡尔曼滤波算法[20,21]。该方法可根据实时量测进行参数的在线更新,有助于描述电力负荷的实时变化特性,但扩展卡尔曼滤波算法属于线性滤波算法,在对非线性动态电力负荷模型进行参数辨识时仍然容易陷入局部最优问题。
因此,本文基于不敏卡尔曼粒子滤波(UKPF)提出一种动态电力负荷在线建模方法,目的是实时跟踪电力负荷的变化特性,更好地满足电力系统实时动态仿真分析的需求。
HTML
-
UKPF算法主要用于解决动态系统的滤波问题。对于一般的动态系统,其离散形式可表示为
((5)) ((6)) 式中:X(k)、Z(k)为状态向量和量测向量;W(k)、V(k)为过程噪声和量测噪声。本文假定W(k)、V(k)为高斯噪声,即W(k)~N(0,Q(k)), V(k)~N(0,R(k))。
对于上述的系统,UKPF算法的滤波步骤可描述如下[22]。
-
1)根据概率分布p(x0)抽取N个粒子
((7)) ((8)) ((9)) 2)初始化各粒子的状态和协方差
((10)) -
对于i=1,…,N:
1)用UKF更新粒子
(1)计算似然点
((11)) ((12)) ((13)) 式中:
(2)状态及协方差预测
((14)) ((15)) ((16)) (3)状态及协方差更新
((17)) ((18)) ((19)) ((20)) ((21)) ((22)) ((23)) 2)采样
-
1)计算误差方差
((24)) 2)重要性权值递推更新
((25)) 3)重要性权值归一化
((26)) -
((27)) ((28)) -
若
-
判断量测数据输入是否结束,若是则退出本算法,否则设k=k+1并转向步骤2。
-
由上述分析可知,利用UKPF算法进行动态负荷模型的参数辨识时,需要将式(1)~式(4)描述的模型转化为式(5)~式(6)所示的离散化形式。采用二阶龙格库塔法进行离散化,同时将待辨识的参数向量扩展为特殊的状态向量,即X(k)=[Pr(k),αps(k),αpt(k),Tp(k)] ,则式(1)~式(2)描述的有功负荷的动态变化特性可转化为
((29)) 式中:
此外,模型观测方程为:
((30)) 式(3)~式(4)描述的无功负荷的动态变化特性可进行类似的转化,此处不再赘述。对于上述离散化的动态负荷模型,利用式(7)~式(28)描述的UKPF进行滤波,即可掌握所有状态的变化情况,包括扩展为状态向量的参数变化值,这就实现了动态电力负荷的参数辨识。
2.1 UKPF算法
2.1.1 步骤1——初始化
2.1.2 步骤2——重要性采样
2.1.3 步骤3——重要性权值计算
2.1.4 步骤4——状态及协方差计算
2.1.5 步骤5——重采样
2.1.6 步骤6
2.2 基于UKPF的参数辨识
-
为了验证本文所提方法的有效性,基于Matlab平台搭建了一个动态仿真平台。给定其中的负荷模型参数,设置一个恒定的电压降落,采集相应的电压和功率变化数据,人为添加一个噪声序列后作为最终的量测数据,最后利用本文所提方法进行参数的跟踪辨识。其中,动态负荷模型的参数分别设置为:
其它一些假定和细节具体如下:
1)在t=0时刻负荷母线发生一个电压降落,幅度为ΔV/V0=-20%。
2)总仿真时长为4 min,仿真步长为0.01 s。
3)采取任意值随机初始化状态向量和协方差矩阵,如式(8)~式(9)所示。
4)观测噪声协方差Rk=1.0×10-4,过程噪声协方差Qk=1.0×10-6×I4。
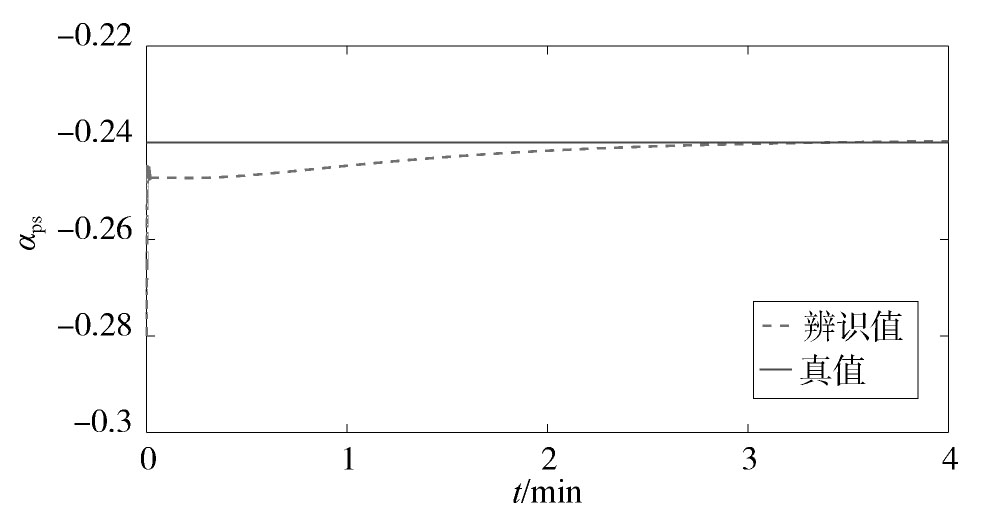
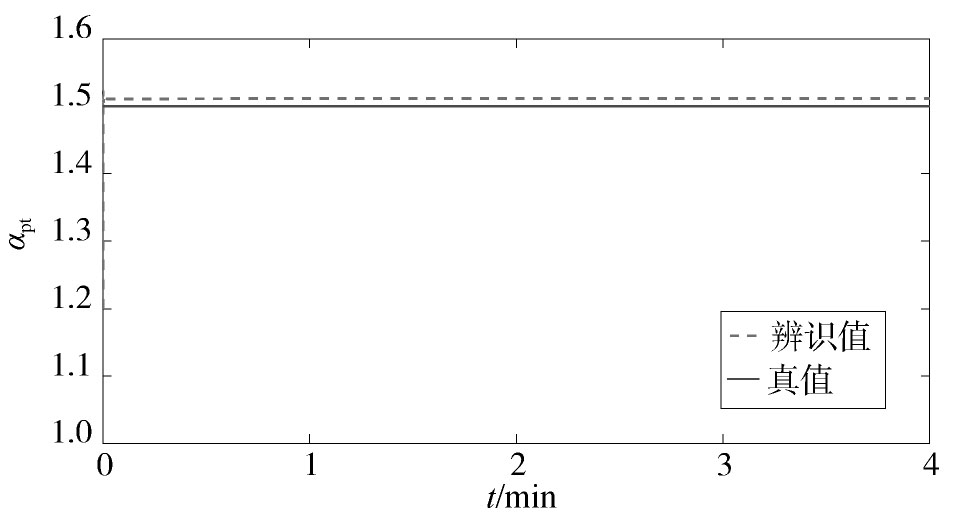
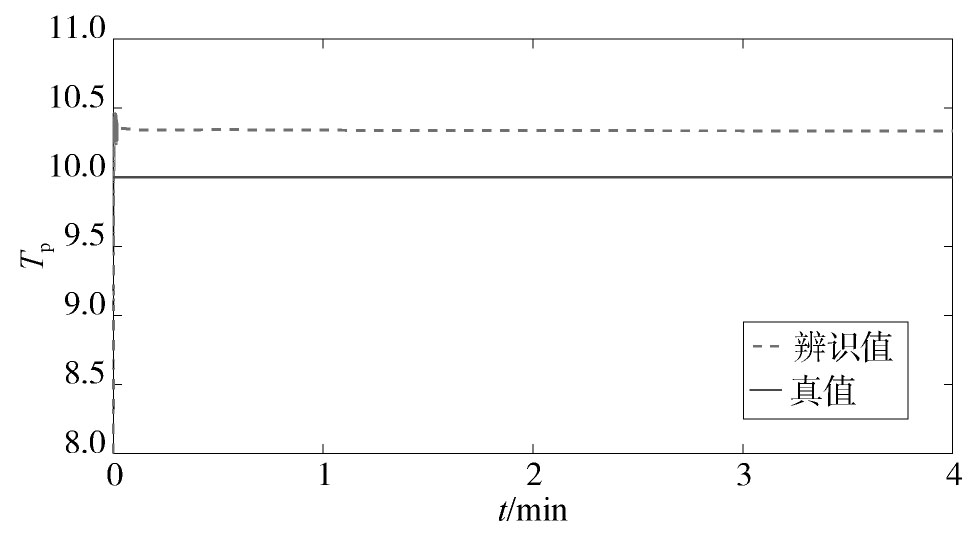
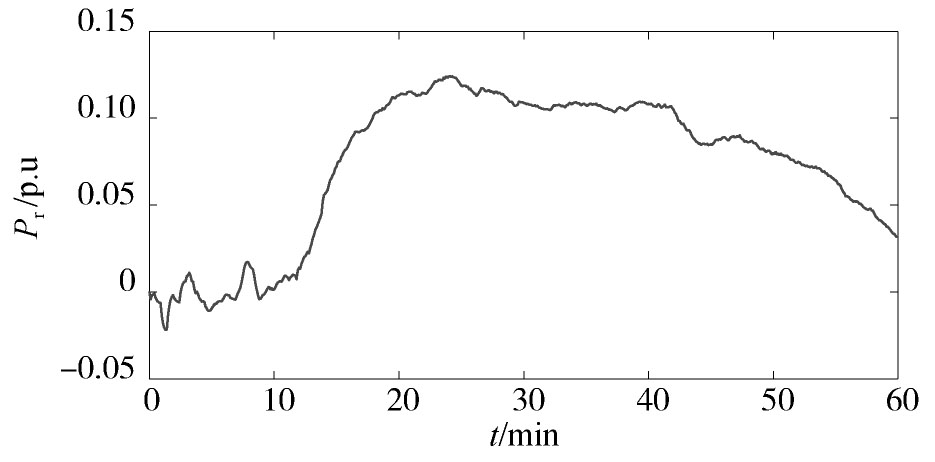
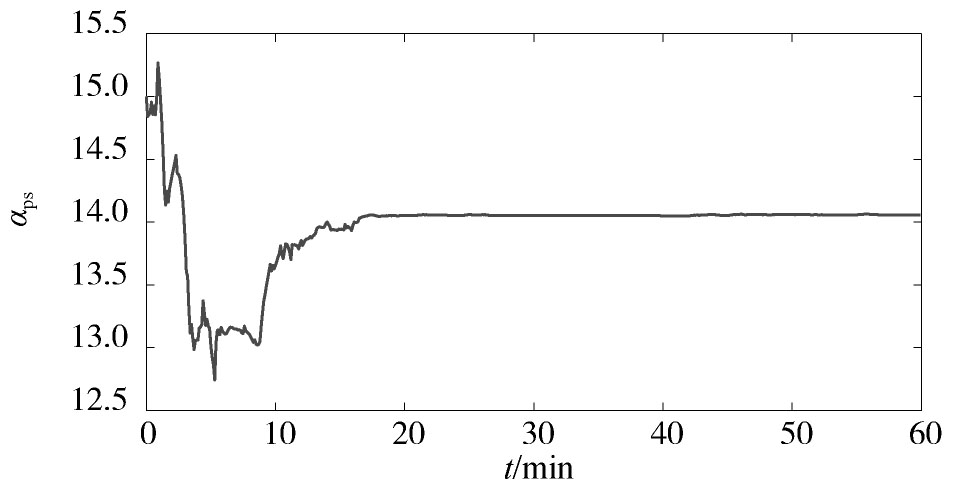
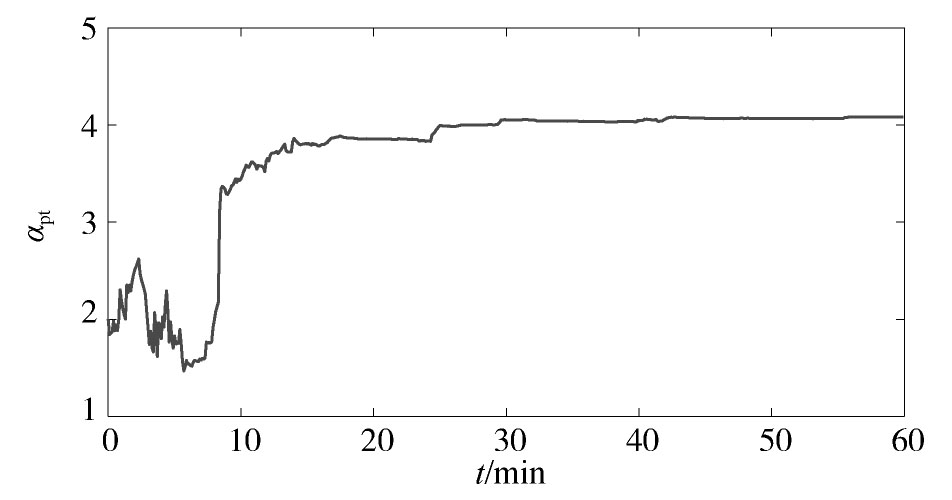
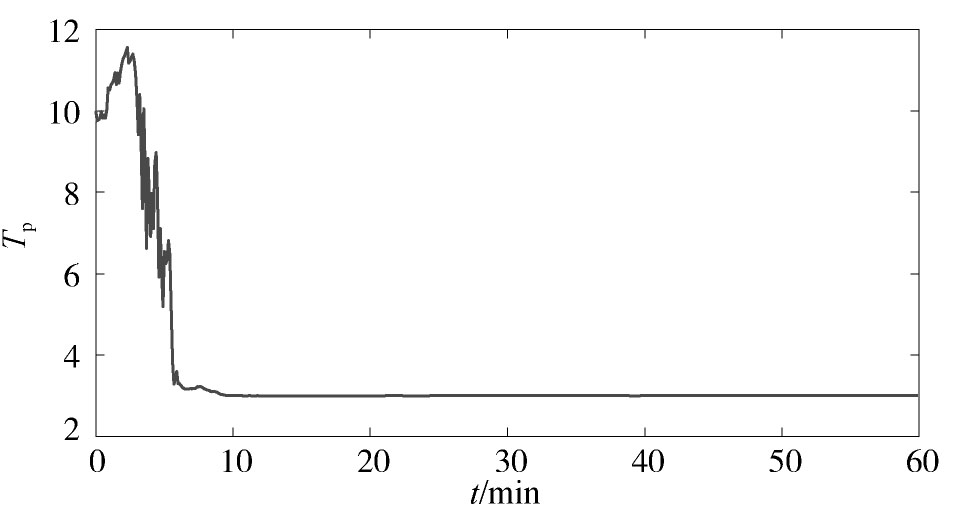
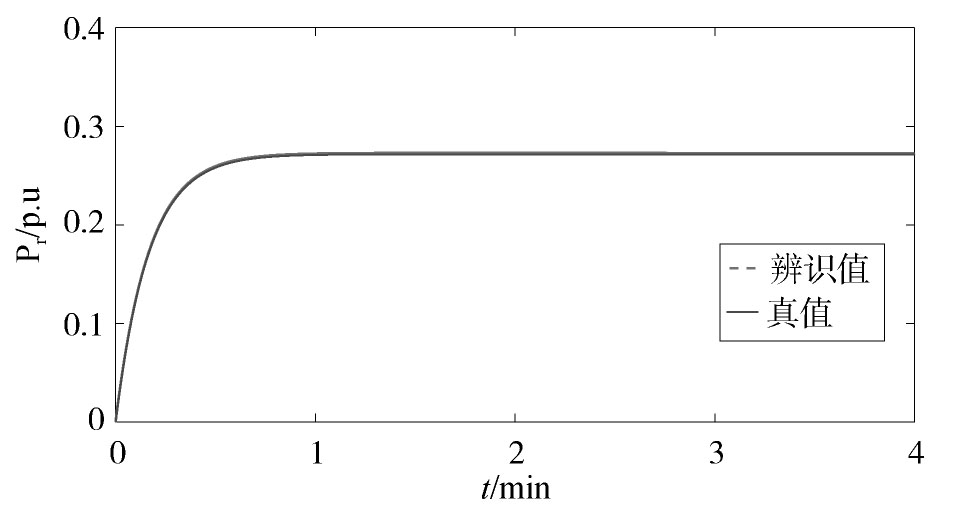
所提方法的参数辨识结果如图1,图2,图3,图4所示。从中可以看出,随着迭代的进行,αps和αpt这两个参数具有较高的辨识精度。Tp虽然在迭代过程中具有一定的偏差,但最大仅为3.4%。通过大量的仿真发现,Tp的允许偏差范围为5%左右。因此,该辨识精度仍在可接受的范围内。在这种情况下,Pr的辨识曲线与真实值较为接近,这说明本文所提方法可以较好地对电力负荷参数进行在线辨识,并实时跟踪电力负荷的动态变化特性。
-
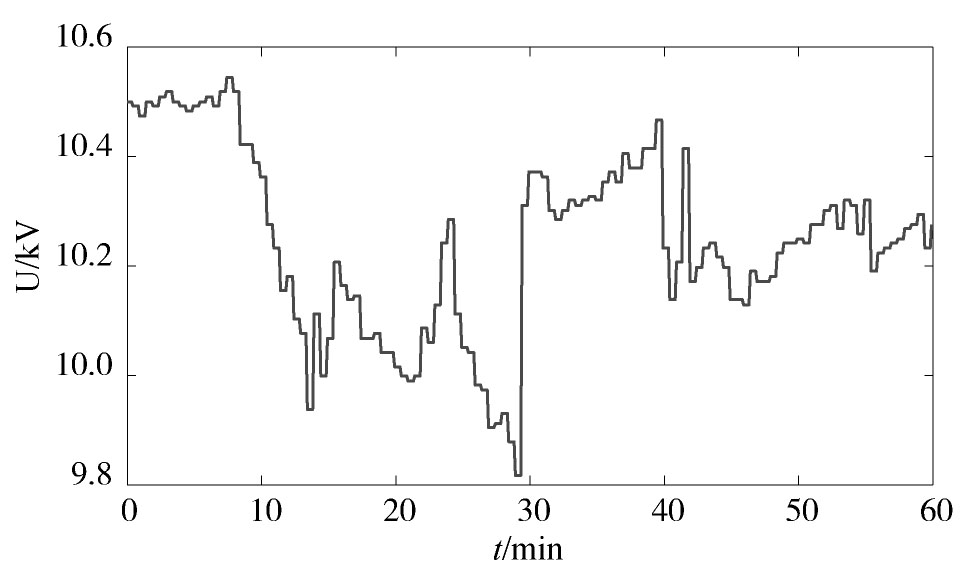
采集某一地级市的变电站量测数据进行动态电力负荷在线建模分析。每隔1 s采集一次变电站母线上的电压和功率数据,总采样时长为60 min。所采集到的实际电压变化曲线如图5所示,其中电压幅值大部分落在10~10.4 kV之间。
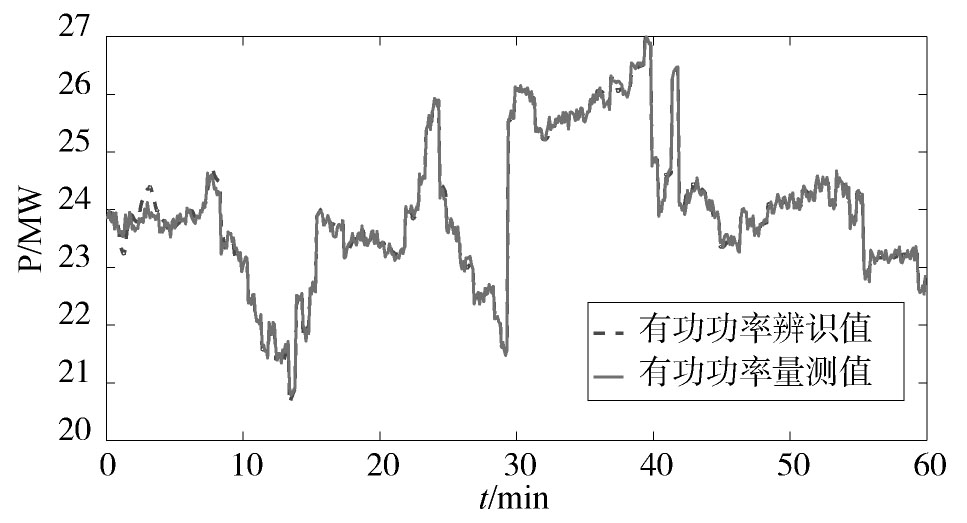
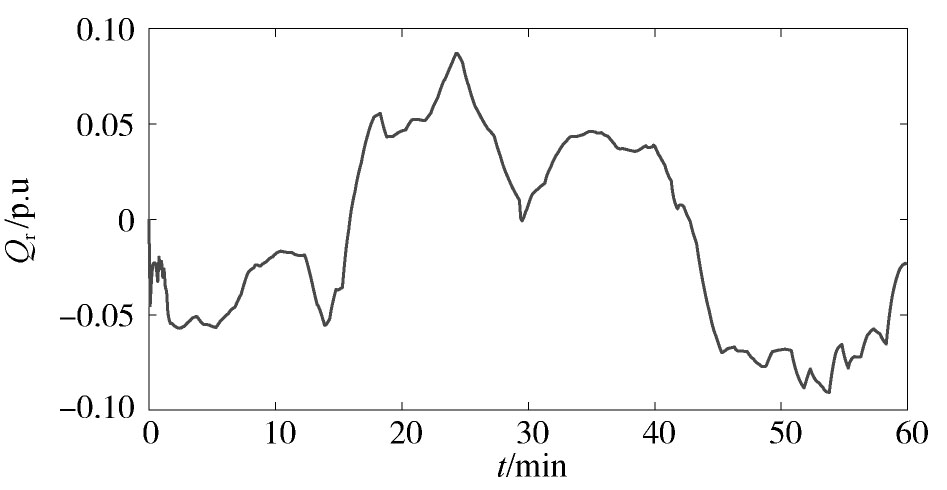
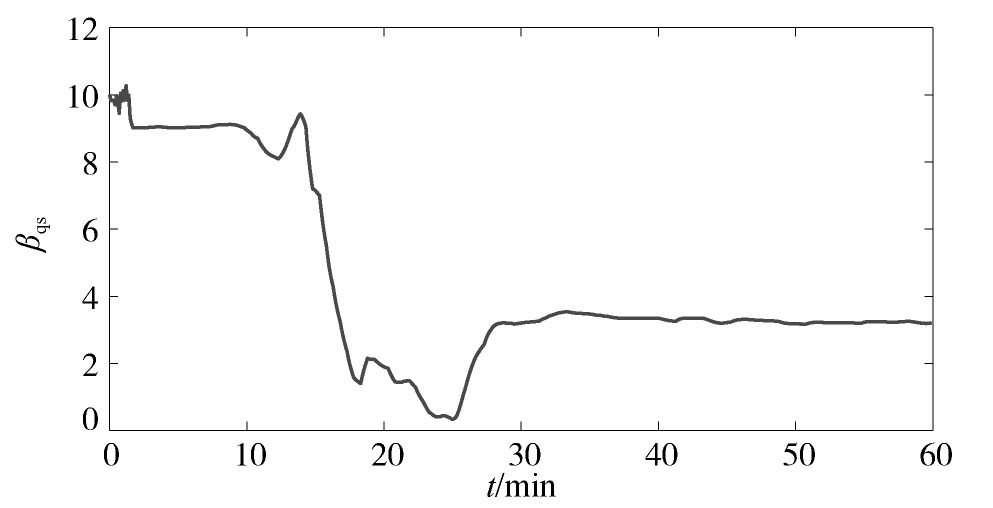
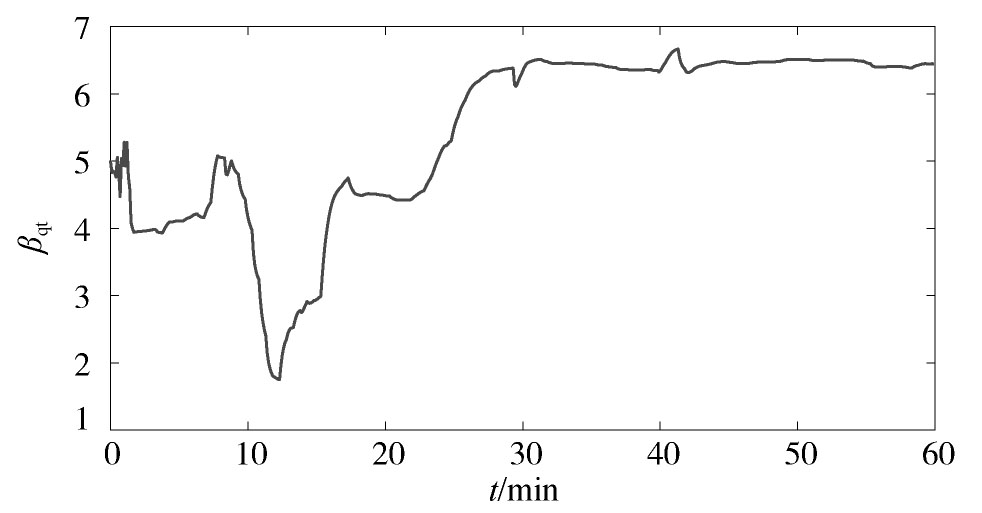
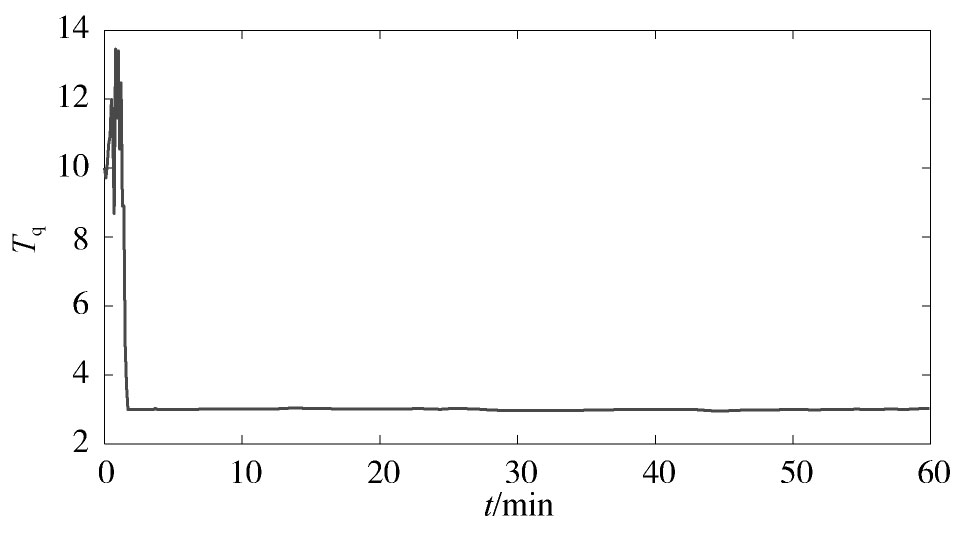
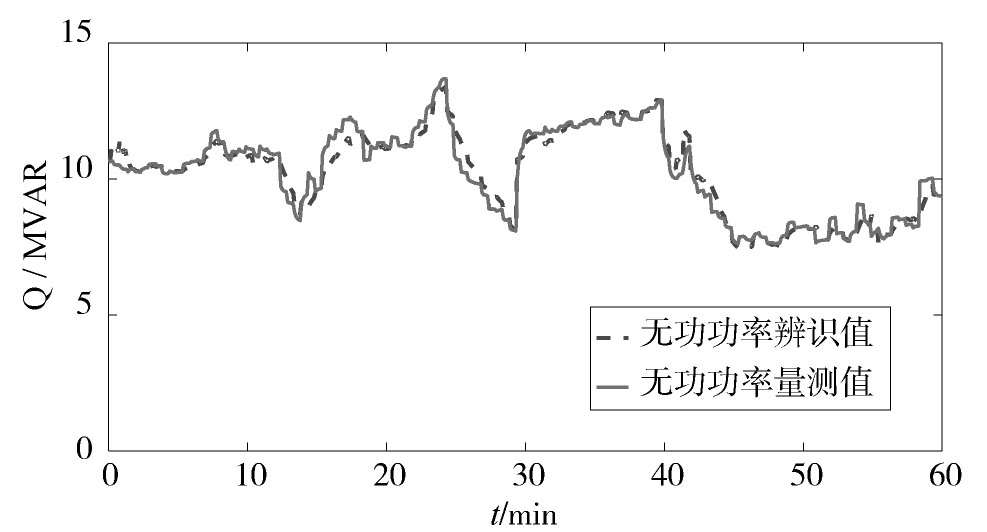
利用本文所提方法进行在线参数辨识,辨识结果如图6,图7,图8,图9,图10,图11,图12,图13,图14,图15所示。从可以看出,动态负荷模型的参数在整个辨识过程中动态变化,这符合实际电力负荷的时变性特点。图10和图15分别给出了负荷的有功功率和无功功率的跟踪情况,从中可见,本文所提方法能较好地反映电力负荷的实际变化特性。
3.1 基于仿真平台量测数据的仿真分析
3.2 基于实际量测数据的算例分析
-
本文重点探讨动态电力负荷模型的参数辨识问题。所采用的指数型动态负荷模型结构简单,可降低在线参数辨识的计算复杂度。利用UKPF算法对指数型动态负荷模型的参数进行辨识,能对电力负荷的实时变化特性进行准确描述,有利于提高实时动态仿真分析的精度。如何将所提方法用于其它动态负荷模型的在线参数辨识,将是后续的一个研究重点。





















































 DownLoad:
DownLoad: