-
随着大规模分布式电源和电动汽车等负荷的接入[1],配电网运行状态更加复杂多变,传统终端的测量面临谐波、间谐波、噪声、阶跃等干扰,测量结果的准确性和快速性均面临巨大挑战[2-3]。
同步相量测量装置(Phasor Mearsurement Unit,PMU)已在电力系统发电和输电网中得到广泛应用[4-6],目前也正积极向配电网推广[7-9]。不同于传统的测控装置,PMU具备三个显著的特征:“快”、“准”和“全”。“快”指PMU需支持的上传速率和动态响应速度快;“准”指无论动态还是稳态情况,PMU均需满足严格的精度考核指标;“全”指PMU不仅可以测出幅值、频率和功率等,同时可测出全网的同步相角和功角,同时量测数据带全网统一的时标。正是由于这三个特征,PMU已不仅仅是其发明初期仅用来监测同步相角的装置,而已经成为电力系统不可或缺的工具。在向配电网进行推广的过程中,配电网同步相量测量装置与配网传统终端进行了融合,形成一种配电网新一代配电网微型同步相量测量装置(Distribution Micro Synchronous Phasor Measurement Unit,D-PMU),具有传统测控保护类终端的功能,同时具有快速性、准确性、可靠性和扩展性,应用领域也从监测推广到辨识、分析、控制和保护。
为在配电网推广应用此新技术,亟需设计D-PMU安装部署方案和典型应用场景的示范工程,本文将从D-PMU的技术原理及作用、系统及安装部署方案和工程案例分析三个部分进行介绍。
HTML
-
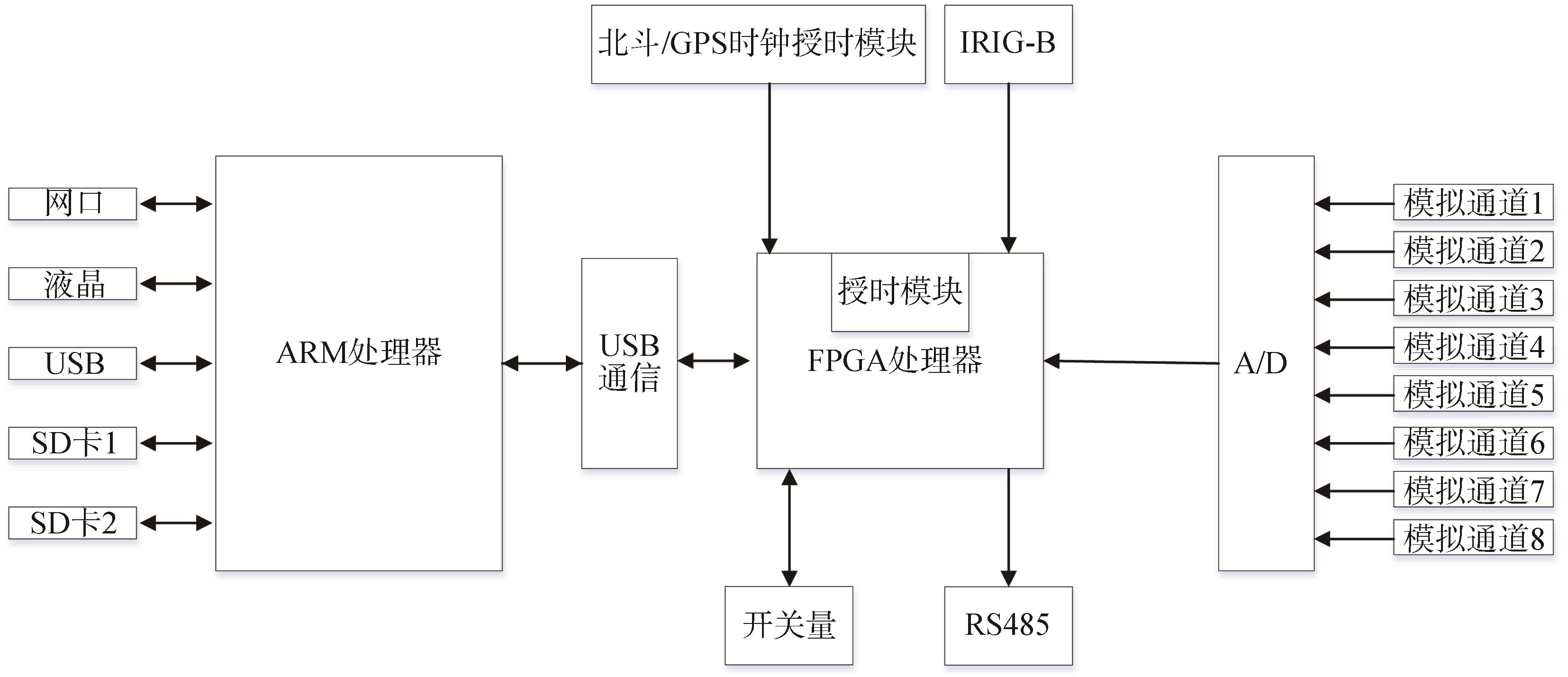
D-PMU能以微秒级采样周期采集配电网运行过程中的电流、电压等相量信息,计算并获得测点功率、相位、功角等信息,通过GPS/北斗提供时间同步信号,D-PMU可将每个状态量同步到同一个时间断面上,对配电网运行信息进行实时同步监测。
通常D-PMU包含以下几个模块:
1)处理器模块。
2)通信模块。
3)北斗/GPS时钟授时模块。
4)模拟和数字量模块。
D-PMU的系统总体结构如图1所示。
全面掌握配电网运行状态,是协调优化、正确决策的关键前提条件。D-PMU的量测精度和采样频率均高于传统常规量测手段。因此,已在配电网多个领域得到关注和研究,主要应用领域包括:
配电网中大规模的风电、光伏等分布式电源以及电动汽车的接入,导致配电网谐波、间谐波、电压暂升暂降、频率偏差等电能质量问题更加突出。同时新能源的随机冲击和负荷的动态波动,对配电网的安全可靠运行带来了新的挑战。因此,需要建立以高精度和快响应的同步相量测量装置为基础的适用于配电网的新一代状态估计和态势感知系统,以保障配电网安全可靠运行。配电网状态估计的难点主要在于配电网谐波噪声等干扰严重导致量测点的误差较大,同时量测数据较少,而增加高精度的同步相量测量数据将有利于解决这些问题。
当前配电网故障诊断和精确定位难点主要如下:(a)配电网运行方式和网络拓扑动态变化,随着分布式电源接入,线路潮流的方向大小等随机变化,导致故障机理难以分析;(b)配电网谐波噪声干扰严重,加大了故障信息提取难度;(c)配电网节点分支较多,增加了故障线路和非故障线路的区分难度。传统故障诊断和定位技术是基于电流幅值,并综合多点的量测结果来确定故障点,但系统中需要的量测节点众多,且各节点不具备同步性,仅能利用故障电流的幅值信息。同步相量测量装置引入,增加了高速率的量测数据和同步相角等信息。
3)协调控制[16]
基于同步量测数据的多维信息融合的配电网协调控制,主要集中在:继电保护、配网自动化、电压无功控制和低周减载等方面。考虑配电网电动汽车和大规模分布式电源(光伏、风机等)接入及用户与电网的供需互动,基于PMU的同步实时数据与分布式电源、柔性负荷、用电营销等系统信息融合的协调控制技术,目前也正在研究中。多维信息融合的协调控制的一个基础是准确快速获取电力系统各节点的电压电流信息,而同步相量测量装置由于其快速的相量上传和高精度的相量测量,同时可以测出各节点的同步信息并带有全网统一的时标,所以可以快速反映电力系统动态运行状态,是多维信息体系中重要的基础数据。
-
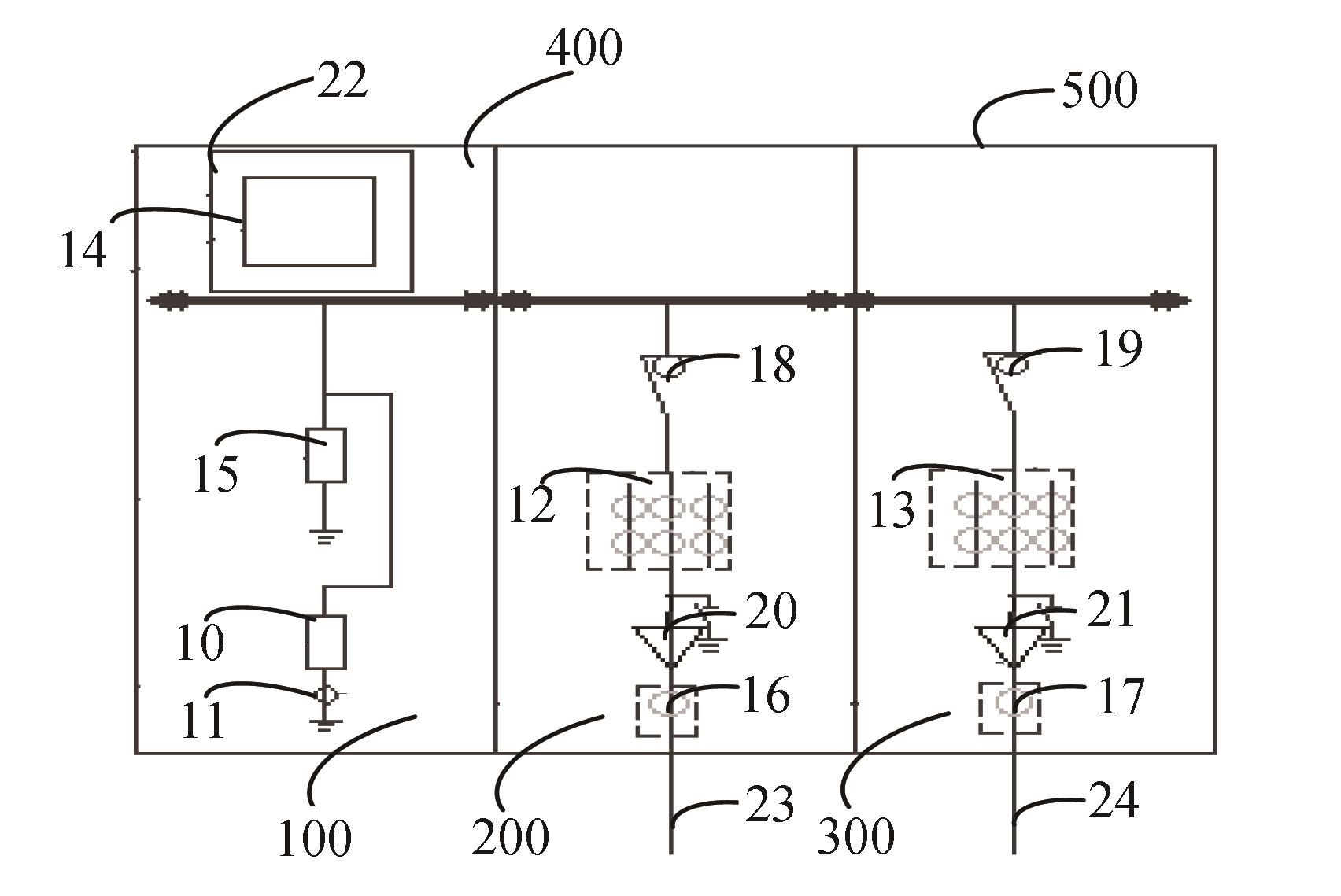
典型配电网运行监控开关柜结构如图2所示,主要包括柜体500、三相五柱式电压互感器10、行波传感器11、进线三相双绕组电流互感器12、出线三相双绕组电流互感器13和同步相量测量装置14。具体地,三相五柱式电压互感器10的第一端连接母线,第二端连接行波传感器11的一端,行波传感器11的另一端接地;进线三相双绕组电流互感器12的第一端连接母线,第二端通过连接电缆23连接外部电力设备;出线三相双绕组电流互感器13的第一端连接母线,第二端通过出线电缆24外部设备;三相五柱式电压互感器10的第三端、行波传感器11的第三端、进线三相双绕组电流互感器12的第三端和出线三相双绕组电压互感器13的第三端均通过控制电缆连接到同步相量测量装置14,将所采集的数据传输到同步相量测量装置14进行分析,从而能够实现对配电网的运行调度。采用上述配电网运行监控开关柜对配电网进行监控和运行调度,在适应配电网不断发展的需求的同时,能够不对原有的开关柜进行改造,造成的停电时间较少,大大提高了配电网的可靠性。
通过航空插头22把同步相量测量装置接入开关柜中,有效地提高了操作便利性,并且,在同步相量测量装置14发生故障时,可以直接替换,不用停电维修。
根据功能的不一样,将配电网运行监控开关柜内的各个器件按照功能划分,分别置于不同的间隔内,每一间隔内的器件均组成完整电路。电压互感间隔100内的电路、进线间隔200内的电路、出线间隔300内的电路和二次小室400。相互之间独立工作,在其中一个间隔内的电路出现故障时,不会对另外间隔的电路产生影响,增强了配电网运行监控开关柜的可靠性。
-
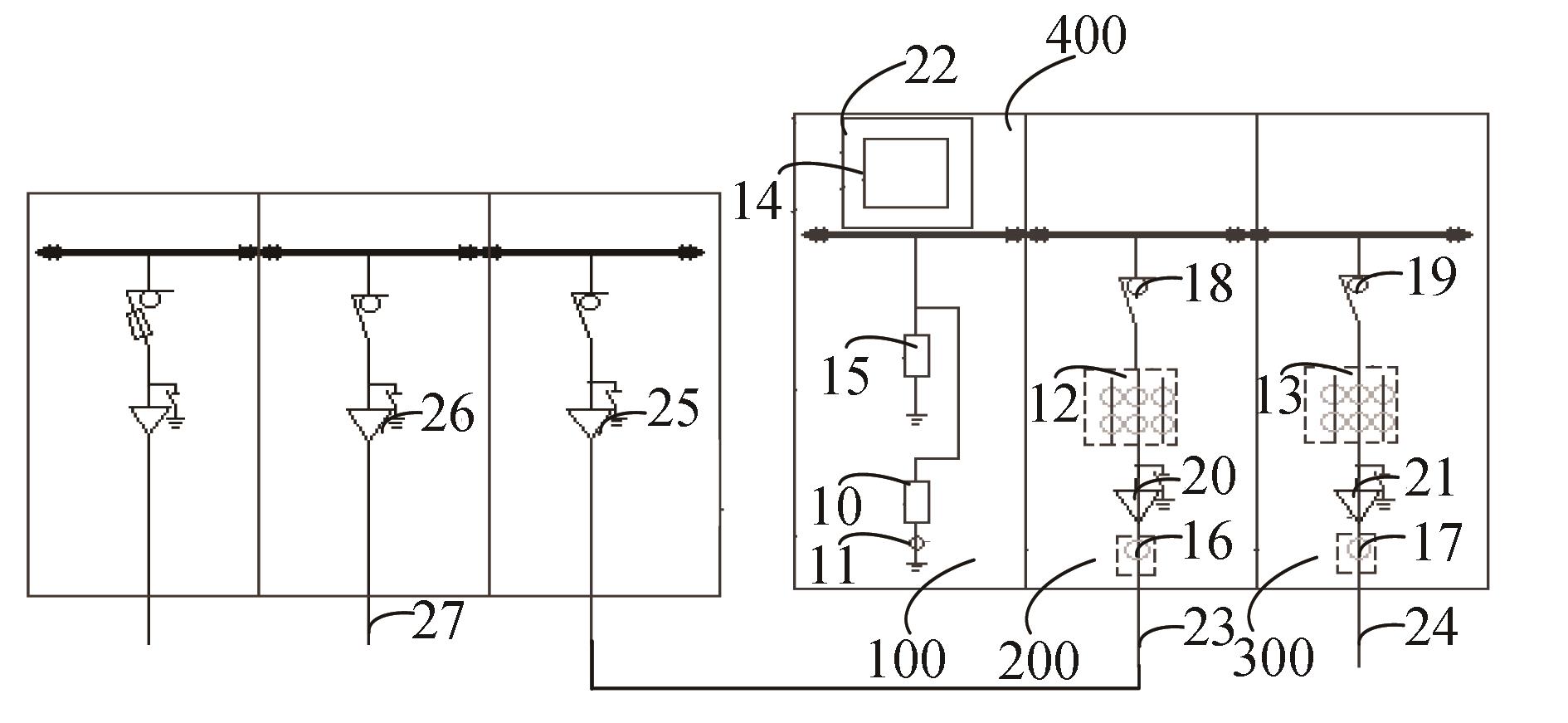
配电网同步相量测量系统结构示意图如图3所示,章节2.1所述的配电网运行监控开关柜,还包括待改造开关柜,配电网运行监控开关柜通过连接电缆23与待改造开关柜的出线间隔的冷缩电缆头25相连接。待改造开关柜的进线间隔的冷缩电缆头26的一端通过待改造开关柜的进线开关与母线连接,另一端连接进线电缆27,进一步地通过进线电缆27与外部设备相连。待改造开关柜通过进线间隔的冷缩电缆头26与外部电力系统连接,从而采集外部电力系统的电压与电流,对外部电力系统的电压与电流进行监控。
在将配电网运行监控开关柜接入配电网时,步骤如下:将待改造开关柜出线间隔的负荷开关打开,使得待改造开关柜的出线电缆失压断电;将配电网运行监控开关柜的进线电缆23与待改造开关柜的出线间隔的冷缩电缆头25相连接;打开待改造开关柜的出线间隔的出线开关闭合。这样,将配电网运行监控开关柜接入待改造开关柜,从而实现对配电网的运行监控与调度。通过这种方式接入配电网运行监控开关柜,只需将配电网的进线电缆23连接,造成很短的停电时间,提高用户体验。
配电网同步相量测量系统还包括以太网交换机,以太网交换机与配电网运行监控开关柜通信连接,用于配电网运行监控开关柜与外部设备进行数据交互。以太网交换机可以设置在配电网运行监控开关柜的内部,还可以设置在待改造开关柜的内部,可以理解,以太网交换机还可以设置于配电网同步相量测量系统以外,只要能实现配电网同步相量测量系统与外部设备之间的数据交互即可。通过设置以太网交换机,实现配电网同步相量测量系统与外部实时进行数据交互,提高配电网同步相量测量系统对电力系统的监控和调度能力。
2.1 典型配电网运行监控开关柜
2.2 配电网同步相量测量系统安装部署方案
-
根据示范区域的业务需求,提出配电网广域测量控制系统的体系架构及部署方案。在终端方面,充分考虑示范区域配电网的网架架构现状及规划、负荷分布、开关设备情况以及现场实施条件,提出D-PMU安装部署方案。在上述基础上,进行示范工程高级功能设计,并开展示范工程建设工作。
-
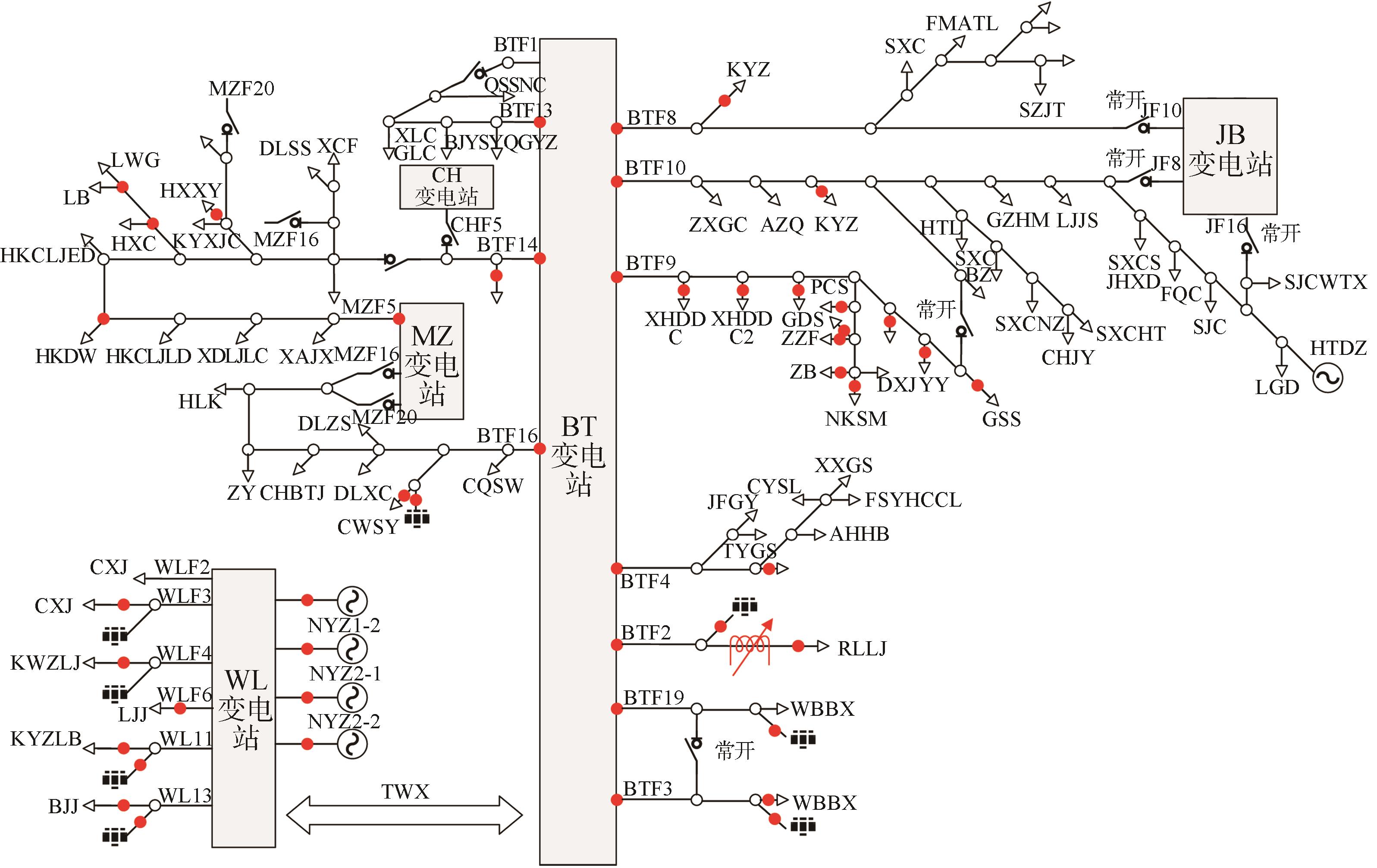
以广州某地区示范工程系统为例,说明自适应状态估计、精确故障定位和源网荷协调控制功能的应用。示范区占地约25 km2,共涉及变电站3座,10 kV馈线13回,为国家第一批分布式光伏发电应用示范区。2020年光伏发电总计规模大于30 MW,电动汽车充换电站(桩)大于5 MW,负荷规模达到40 MW。示范工程D-PMU安装点网络接线图如图4所示。
-
示范工程功能应用主要包括:自适应状态估计、精确故障定位、源网荷协调控制等功能。
-
在示范区分别设置配网同步相量测量装置覆盖率达100%、SCADA+PMU覆盖率达100%以及量测不足三种情况,用于对比测试不同配置下状态估计效果。所以选取WL站部分和BTF2、BTF3、BTF19配网PMU覆盖率达100%,可验证量测充足情况下的快速状态估计效果。选取BTF9作为SCADA和配网PMU覆盖率达到100%示范区域,以验证量测充足情况下的高精度状态估计效果。选取BTF1、BTF4、BTF8、BTF10、BTF13、BTF14、BTF16以验证量测不足情况下的鲁棒状态估计效果。
-
示范区考虑MZF5线路较长,分支较多,电缆和架空线混合,多T接,所以选取为从化示范区的精确故障定位高级应用功能示范点。选取线路首端即MZ变电站F5馈线端,分支末端HKCLJLD配变、HXC配变、KYXJC和HXXY专用高压房安装带有行波功能的同步相量测量装置,以示范高精度故障定位功能。
-
示范区考虑BT变电站为主要供电电源,选取BT变电站及下属各馈线示范源网荷协调控制高级应用功能和孤岛切换及稳定控制功能。考虑工业园区含光伏电源容量为17.8 MWp,CCHP(Combined Cooling Heating and Power,冷热电联产系统)容量为30 MW,充电桩容量为0.8 MW,工业大负荷容量为66.1 MW,所以此示范区重点示范源网荷协调控制。考虑BTF8、BTF9、BTF10涵盖医院、政府、派出所、客运站等重要负荷,选取此示范区重点示范孤岛切换及稳定控制功能。
-
示范区建成后,示范区内状态估计精度高于95%;故障检测准确率高于99%;故障定位精度小于0.2 km;源-网-荷快速协调控制系统的闭环控制平均时延小于200 ms。
通过配电网故障诊断与精确定位技术,可大幅提高故障检测准确率,平均缩短故障处理时间48.25 min,年减少用户停电损失约314万元。
通过源荷协调控制,实现配电网与用户的灵活互动,削减示范区柔性负荷峰值约13%,延缓输配电基础设施投资约416万元,减少调峰备用电源建设费用约1 170万元。
-
建成涵盖柔性负荷、分布式电源、充电桩等配网典型负荷,涵盖变电站、配电房、集装箱、户外杆塔等配网典型安装环境,涵盖基于D-PMU的自适应状态估计、故障精确定位和源网荷协调控制及孤岛运行等配网典型高级应用功能的示范工程,对国家重点研发计划项目相关内容进行试验,为后续大规模推广和复制积累工程经验。
3.1 示范工程概况
3.2 示范工程高级功能设计
3.2.1 自适应状态估计
3.2.2 精确故障定位功能
3.2.3 源网荷协调控制及孤岛运行
3.3 示范工程建设成效
3.4 示范工程意义
-
本文详细介绍了配电网同步相量测量装置的技术原理及作用、系统及安装部署方案和工程案例。本文的先进性和主要工作如下:
1)分析了配电网微型同步相量单元的工作原理和典型的应用场景。
2)提出了一种配电网同步相量测量系统及安装部署方案,该方案不需要对原有的开关柜进行改造,造成的停电时间较少,可大幅提高配电网的可靠性。
3)提出了D-PMU高级功能示范设计方案,通过关键技术的示范应用,全面提升配电网的安全与经济运行水平,具有显著的经济效益。
本文工作为D-PMU进一步与配网其他传统领域融合推广提供了丰富的工程经验。在进一步推广应用时,需要针对不同的区域特点和功能需求,研究D-PMU的最优布点方案,提高经济性。










 DownLoad:
DownLoad: