-
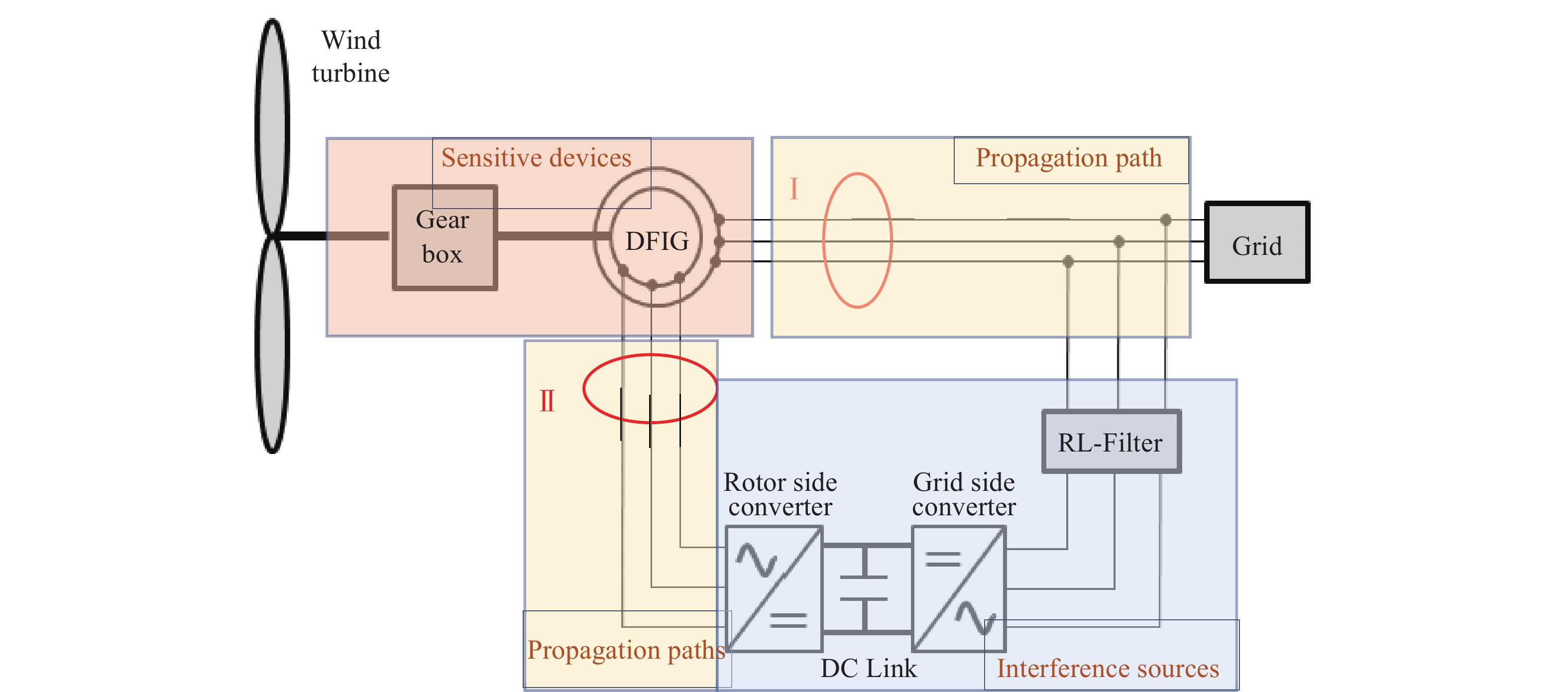
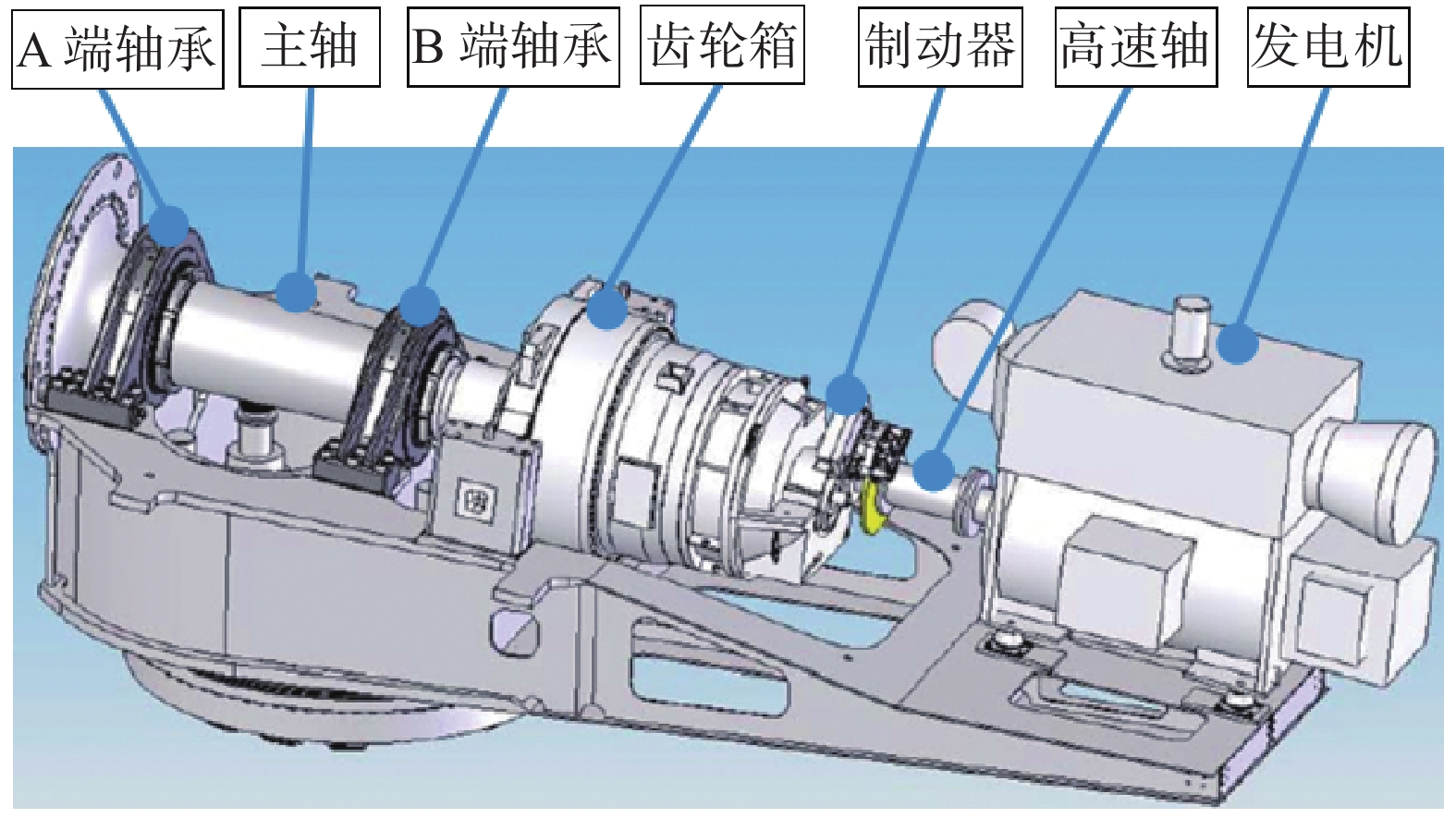
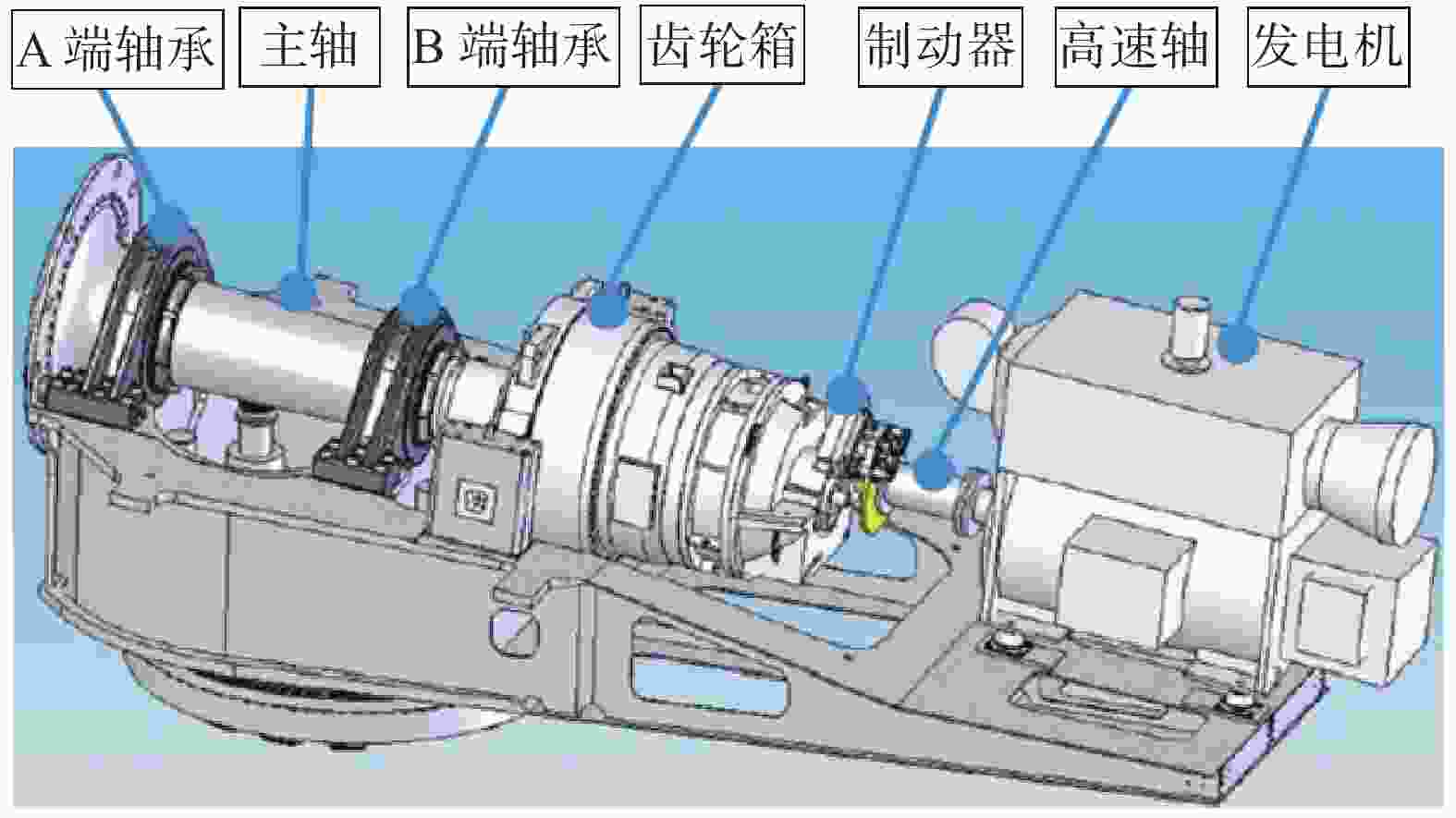
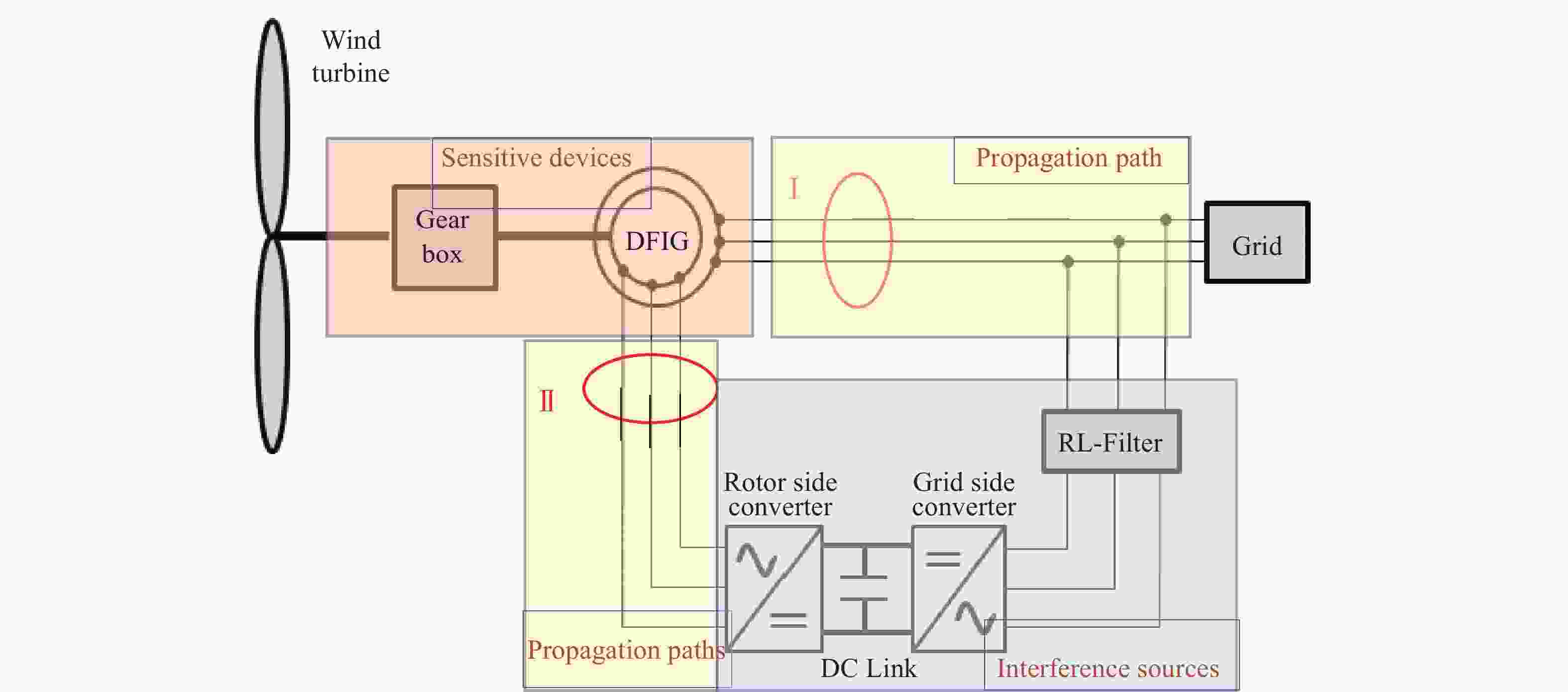
我国规划2030年前实现碳达峰,2060年前实现碳中和,政策陆续出台明确碳达峰碳中和目标及工作路线[1]。大力推进新能源发展,适应不断变化的能源供需格局和能源改革趋势[2],向提高能源利用效率,减少碳排放,满足各方能源需求的方向努力[3]。风力发电能源这种可再生清洁能源有着广阔的发展前景[4],随着风电单机容量不断提高,对风力发电机组主要部件的可靠性和安全性有了更高的要求[5]。我国南方沿海海岛上某风力发电场处在海岛山尖上,全场由22台机组型号为明阳MY1.5s-77/65双馈异步滑环陆上发电机组成,发电机定子直接与电网连接,转子功率通过逆变器输入到电网。通讯光纤网络和电线电缆沿山脉敷设,此机型主要零部件结构图如图1所示[6]。此风场全场风机到2014年初陆续完成正常网发电的,而文中描述的试验机组#11风机于2013年12月27日通过试运行,正常投入运行并网发电,截止2020年11月份对#11机组进行抽检测试时此风机运行约满7 a。风力发电机组主设备安全问题一直以来都是风力发电技术的重要研究对象[7]。本文对一起风力发电机组发生共模电流信号干扰破坏进行了原因分析[8],提出了改善方案,为以后减少此类故障提供解决方法和思路[9-10]。
-
本风电场由22台风机组成,此风机主要部件厂家/型号具体如表1所示,通过历史运行数据和现场实测发现此风电场发电机组存在高共模电流破坏设备问题[11-12]。根据以往经验,若系统长期运行可能导致以下问题,如输电线缆过热、用电转换变压器过热、保护检测设备的误动作/误报警及风电发电机组电机振动异常等。“高共模电流”是电力行业设备中存在的一种共性问题,只是干扰电流破坏设备的程度大与小的问题。
名称 厂家/型号 装机容量/MW 330 机组型号 MY1.5s-77/65 风机整机厂家 明阳 风机主要部件 叶片 明阳 变桨系统 OAT 主轴 江阴振宏/平湖中州/江阴南工 齿轮箱 南高齿/FD1160E-01-00R13 发电机 南汽轮/DASAA 5023-4UFB 变频器 艾默生/MYFvert-SH 1.5/A 主控系统 倍福 液压站 敏泰11FD004 Table 1. Manufacturers/models of main component of wind turbine
-
高频共模电流通过发电线路线缆时,产生了“集肤效应”现象,流过电缆表面的无序、不规则的电流趋向于导电体的表面,并不是均匀分布在导电体内芯[13-14]。若此电流频率越高,这种电流信号趋向于导体表层分布的现象越显著,而电流密度沿导体截面分布又不均匀,导致电导体的有效截面积减少,电阻值增大[15],产生过热,又长时间通流下,从而导致线缆容易老化,绝缘层损坏,造成线缆绝缘等级不合格,会引起不可估量的事故损失[16]。
-
高变压器发热主要由两方面导致:绕组铜损和变压器磁芯的铁损[17]。
1)铜损:由2.1的分析可知,当高频电流流过变压器绕组时,绕组发热加剧,会导致变压器铜绕组绝缘层老化,绝缘层损坏,造成变压器绝缘等级不合格,会引起事故故障。
2)铁损:当变压器中存在高频电流,磁芯产生涡流损耗,导致变压器发热增加,同样导致变压器铁磁芯绝缘层老化,绝缘层损坏,造成变压器绝缘等级不合格等,也会引起事故故障。
综上所述,若变压系统长期存在高频共模电流,则会导致变压器寿命缩短,降低变压器的有效容量,同时存在事故隐患。
-
为保证风机机组发电系统正常工作,变频器设有监控及保护模块[18]。而变频器在变频过程中产生的高频干扰电流(共模电流)在传输过程中,若耦合到监控或者保护线路中,则会导致系统报警或误动作。
-
发电机异常震动可能由高共模电流导致的局部熔化和波列纹理所引起。
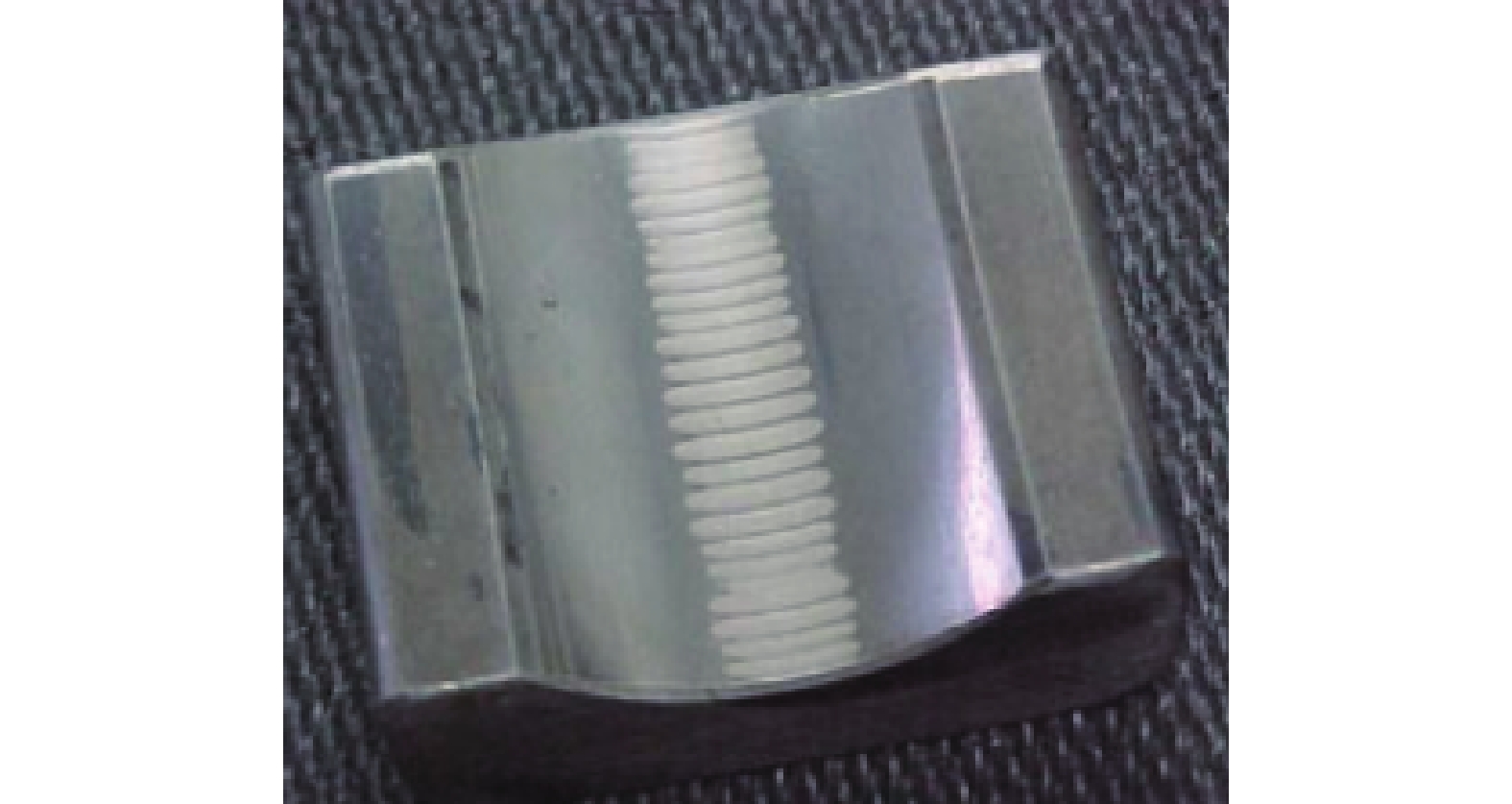
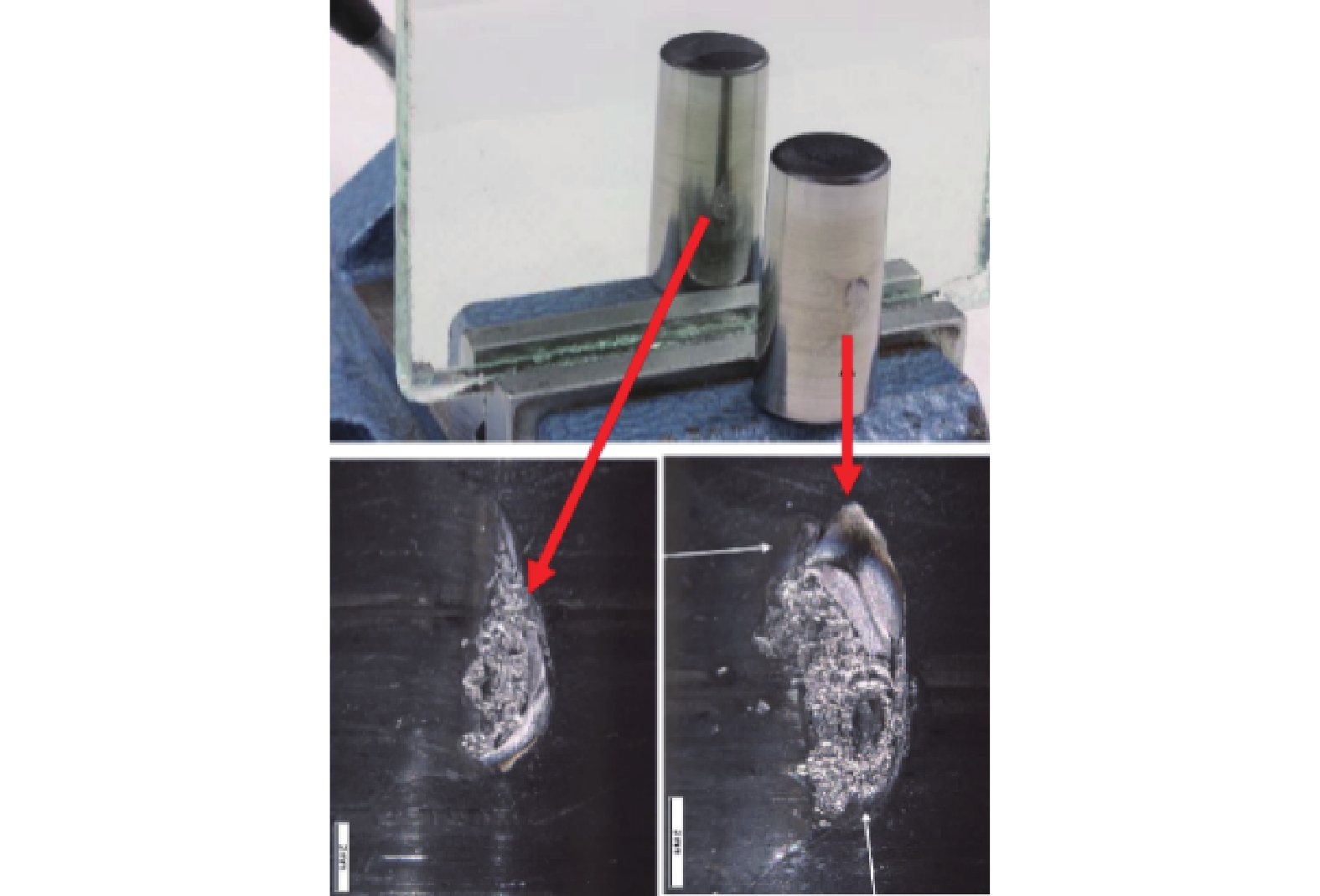
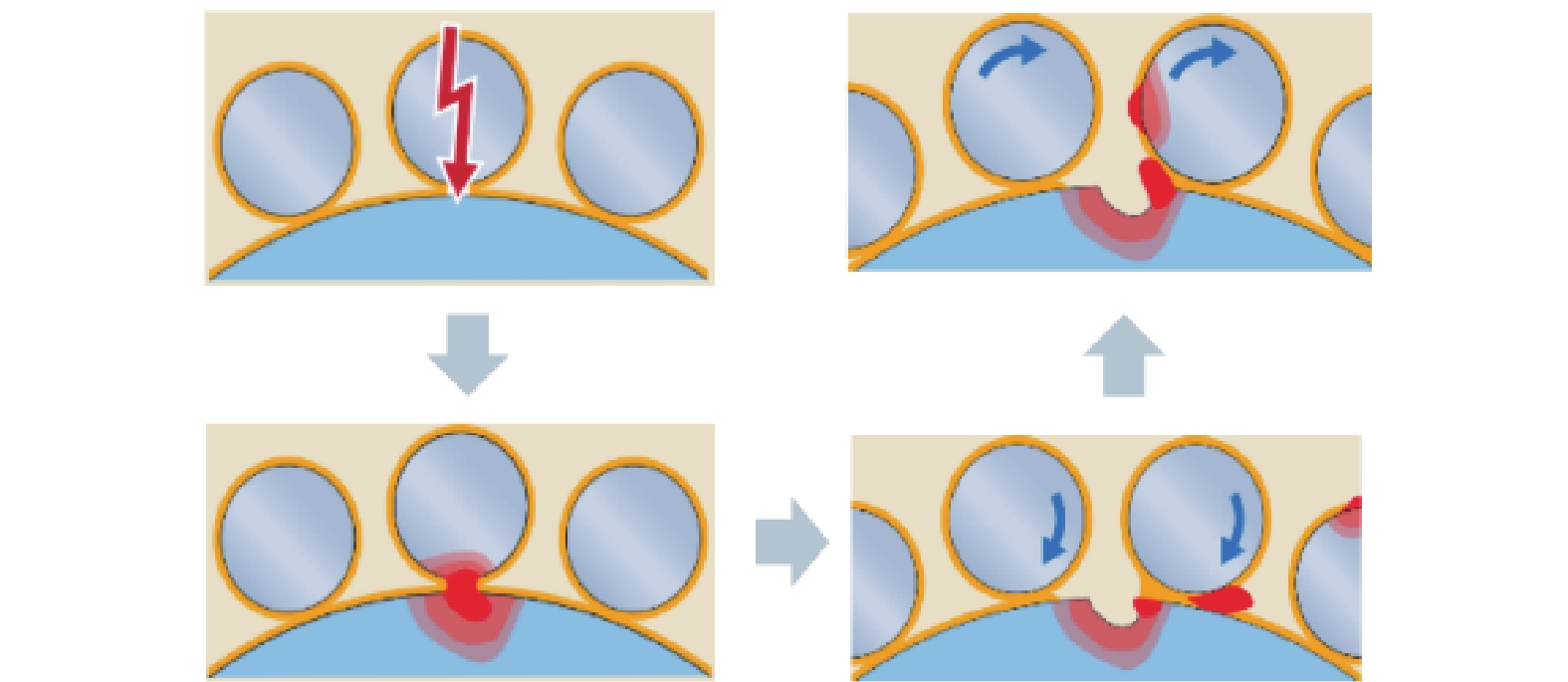
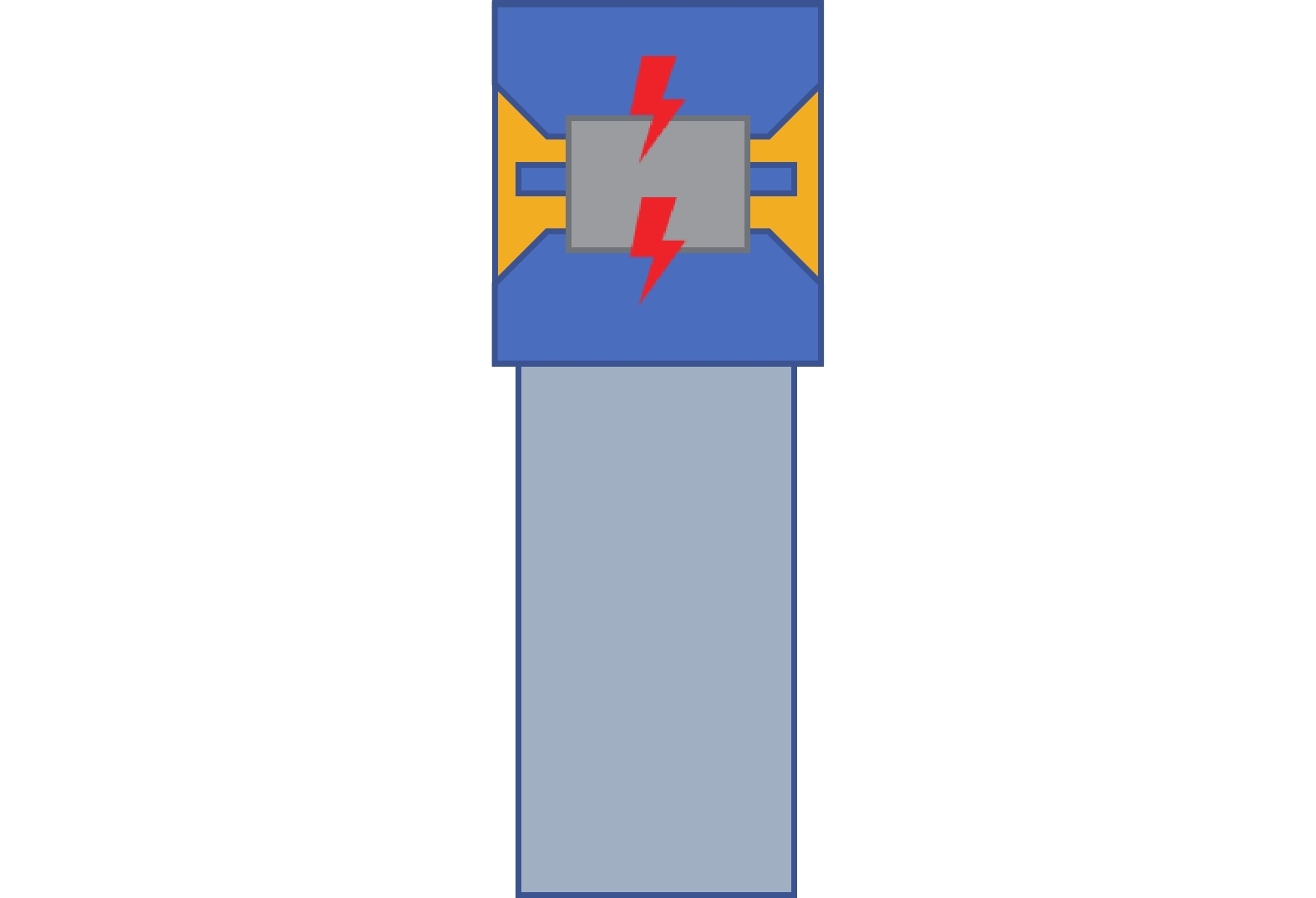
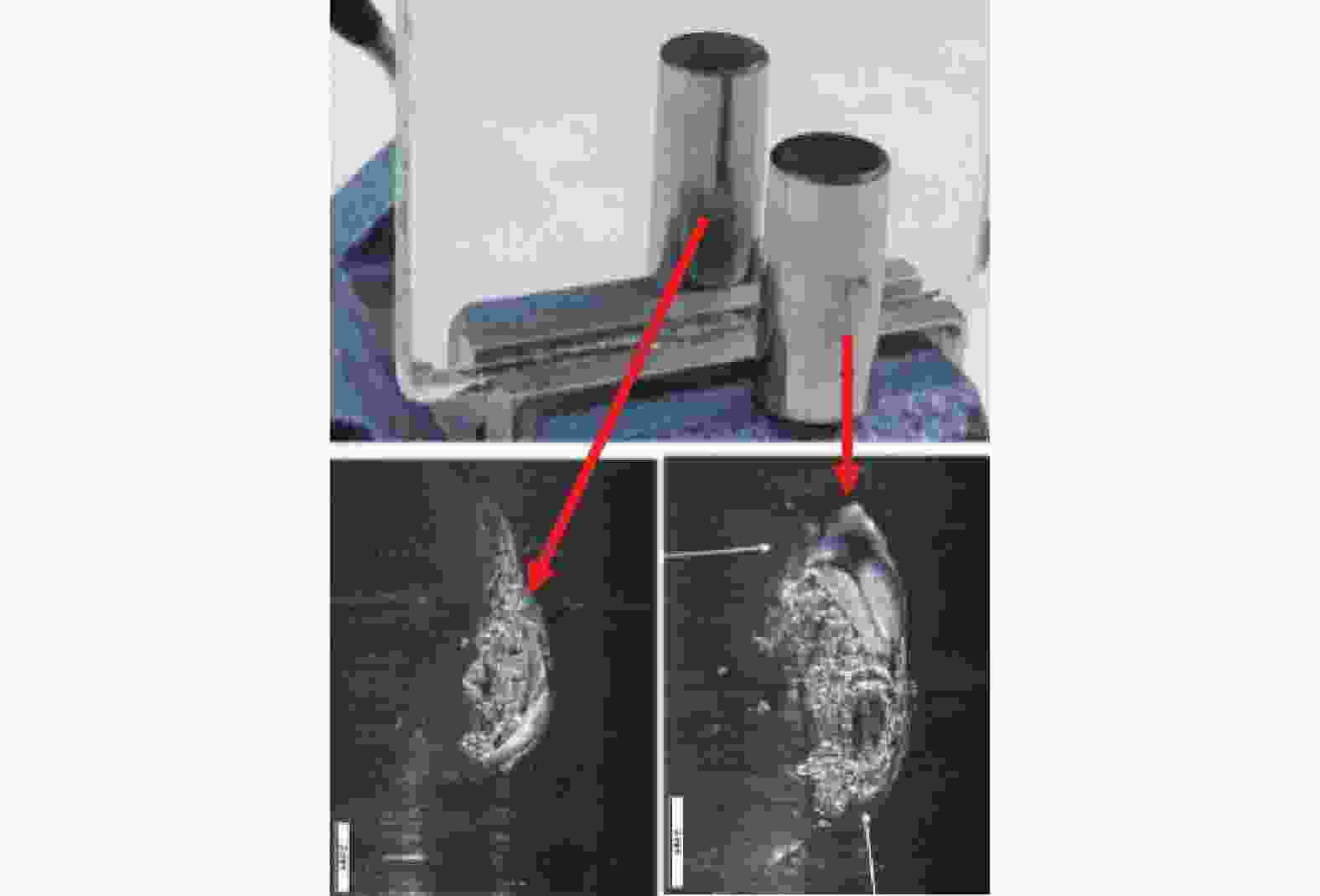
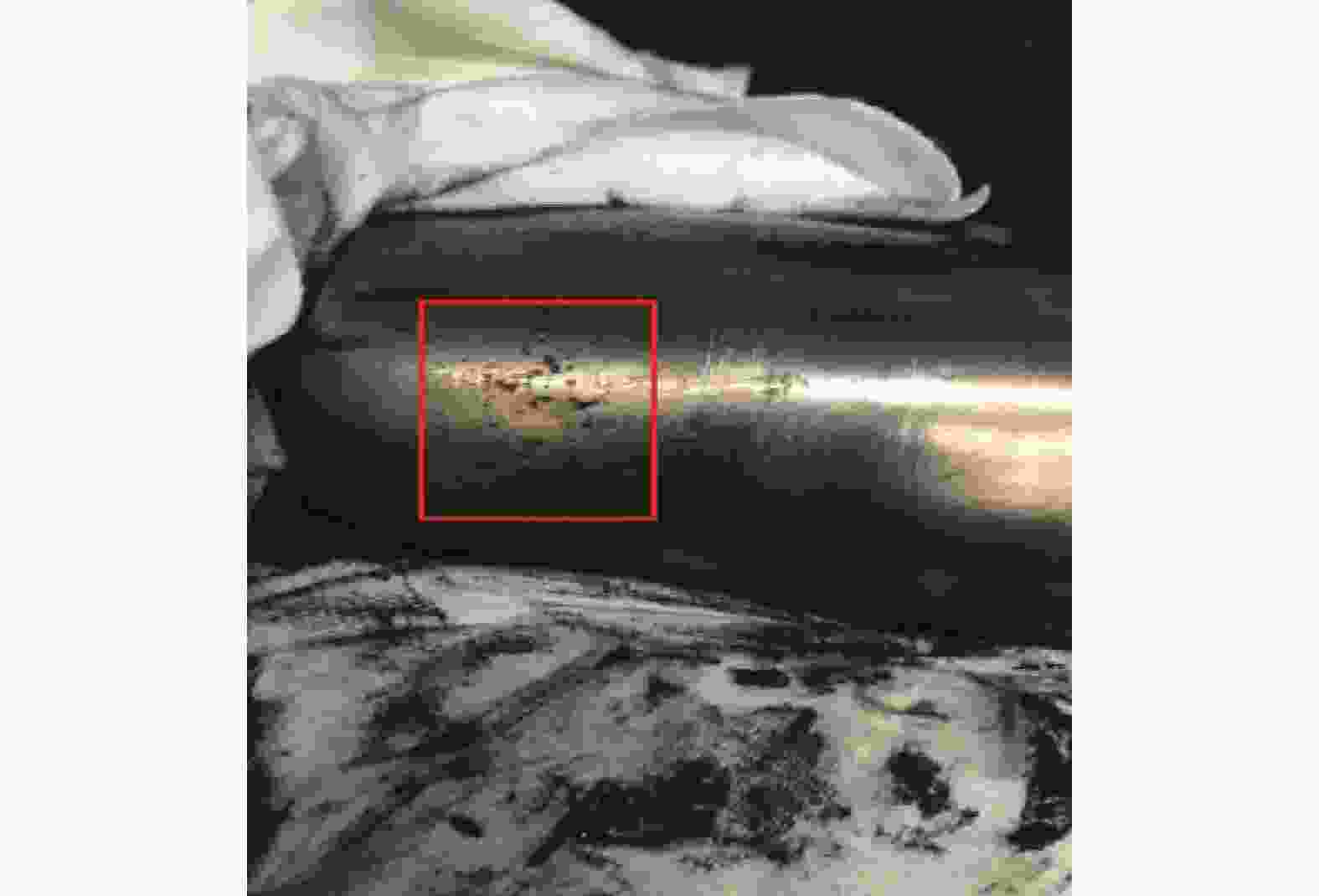
1)局部熔化:轴承局部熔化来源于电火花放电。风力发电机轴承滚动运转时,其滚动体与滚道之间存在感应电动势,而且产生了电势差,随着电动势的电能积累,电势差将自动寻找释放能量空间位置,当这电势差超过轴承表面润滑油膜固有击穿电压时候,产生放电现象,并对轴承表面产生了电洛现象如图2所示。由于放电效应的增强,并且电动势无法通过金属导体有效的释放,必将以火花的形式对轴承放电如图3所示。由于雪崩效应原理,当弧电压下降时候,弧电流并未能有效消失或减少,依然不断的增加,不断形成了1个负阻抗特性。当轴承周围局部电场电流强度逐渐减小时候放电将停止,而储藏在电容里的残余电能量也会慢慢被消耗掉,这就是常见的“放电加工”效应[19]。
润滑油膜的击穿电压与击穿电场电流强度、设备局部状态有着密切关联。该“放电加工”现象是1个局部的无规则可循的短期现象,风力发电机的长期运行,轴承一直处于运转状态,必将频繁发生放电现象,而且这种放电现象与轴承大小、形状、钢强度无关,重点是取决于局部电场的大小以及集聚电能量传输条件。轴承在静电放电(EDM)的作用下,总能量的转换有一部分(EEDM)会以放电形式消耗掉或被转化为热量[20]。一般情况下单个能量EEDM释放的时间持续30 ns左右,而这种能量释放是导致滚动体和滚道表面层润滑剂退化及局部熔融的基本原因,从而导致轴承整体结构的物理损坏,例如轴承保持架散架。
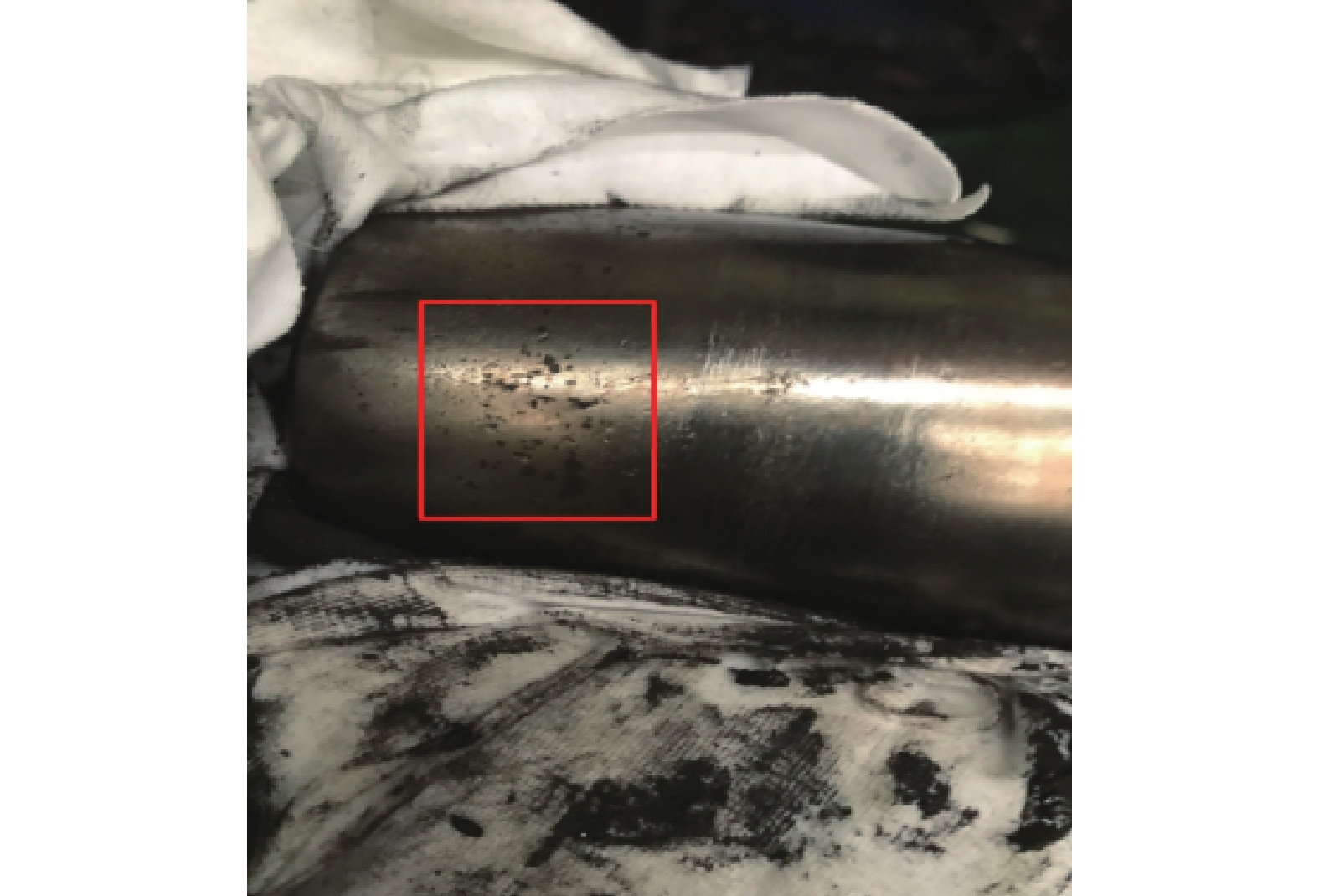
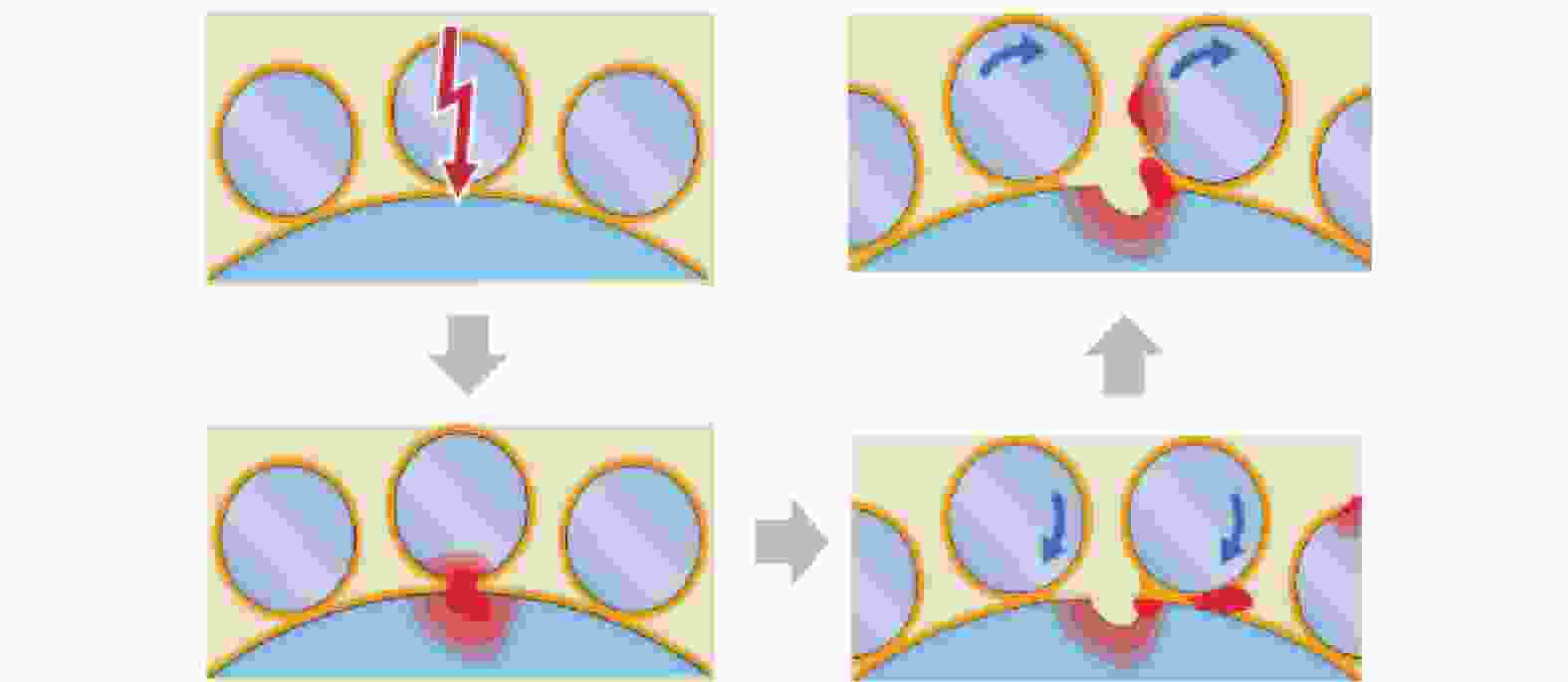
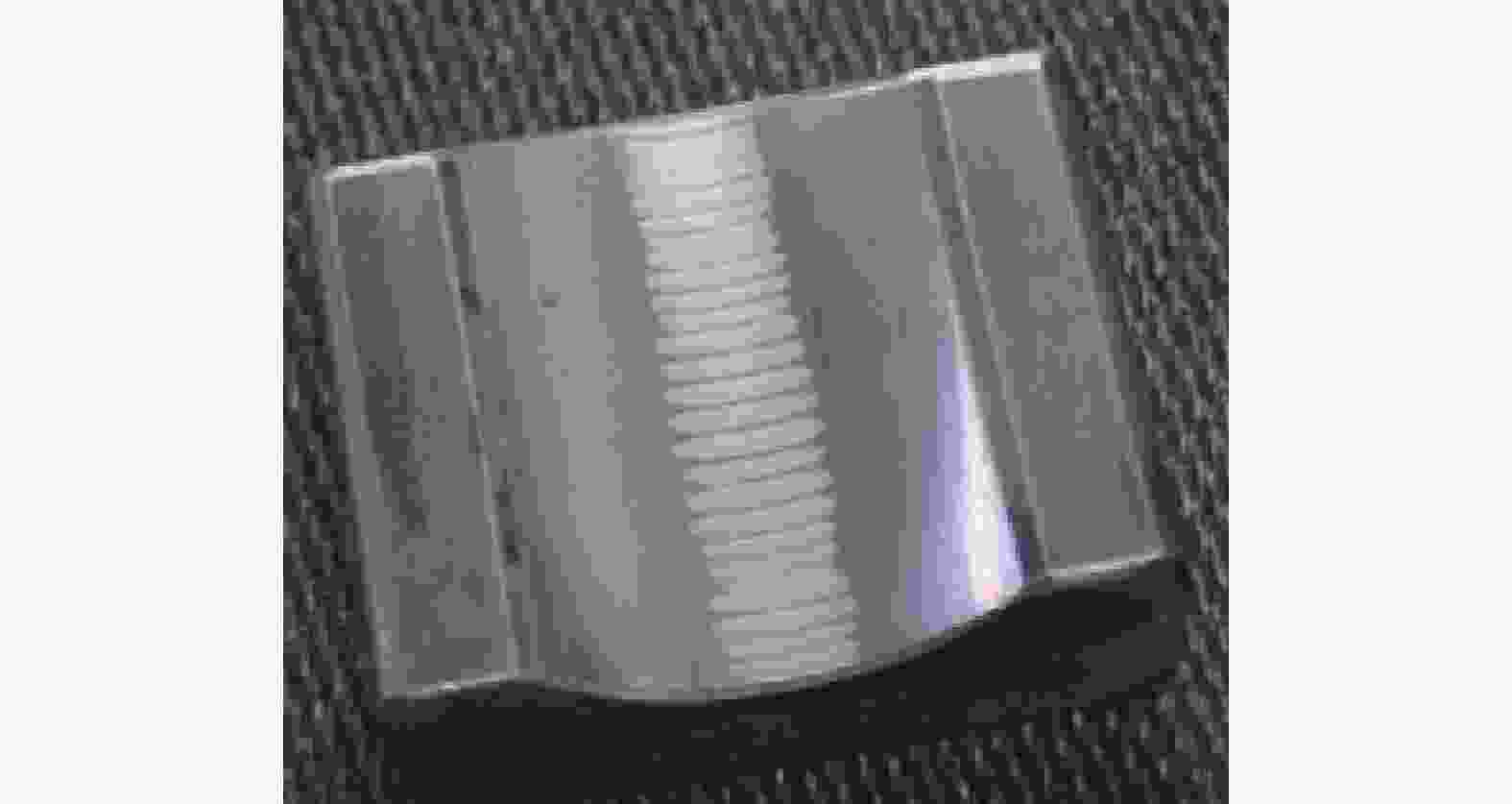
2)波列纹理:造成波列纹理的原因是通过轴承的持续过电流,导致各部件温度升高并使润滑脂加速劣化。过电流的频率会造成滚道上会出现规则的波浪纹理,导致滚道出现疲劳,表面失去硬度,润滑剂退化,滚动体损坏,如图4和图5所示,最终造成轴承失效。
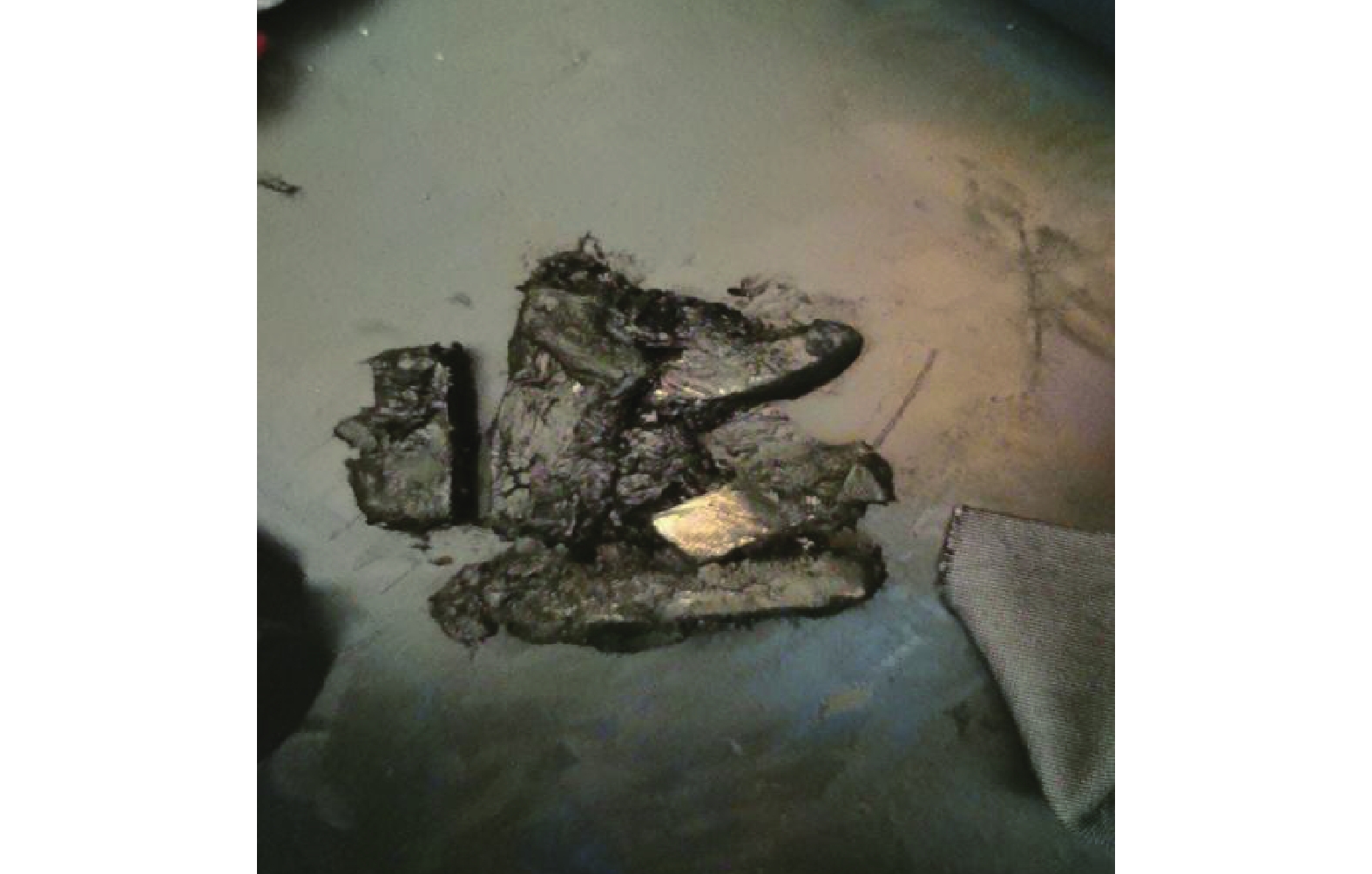
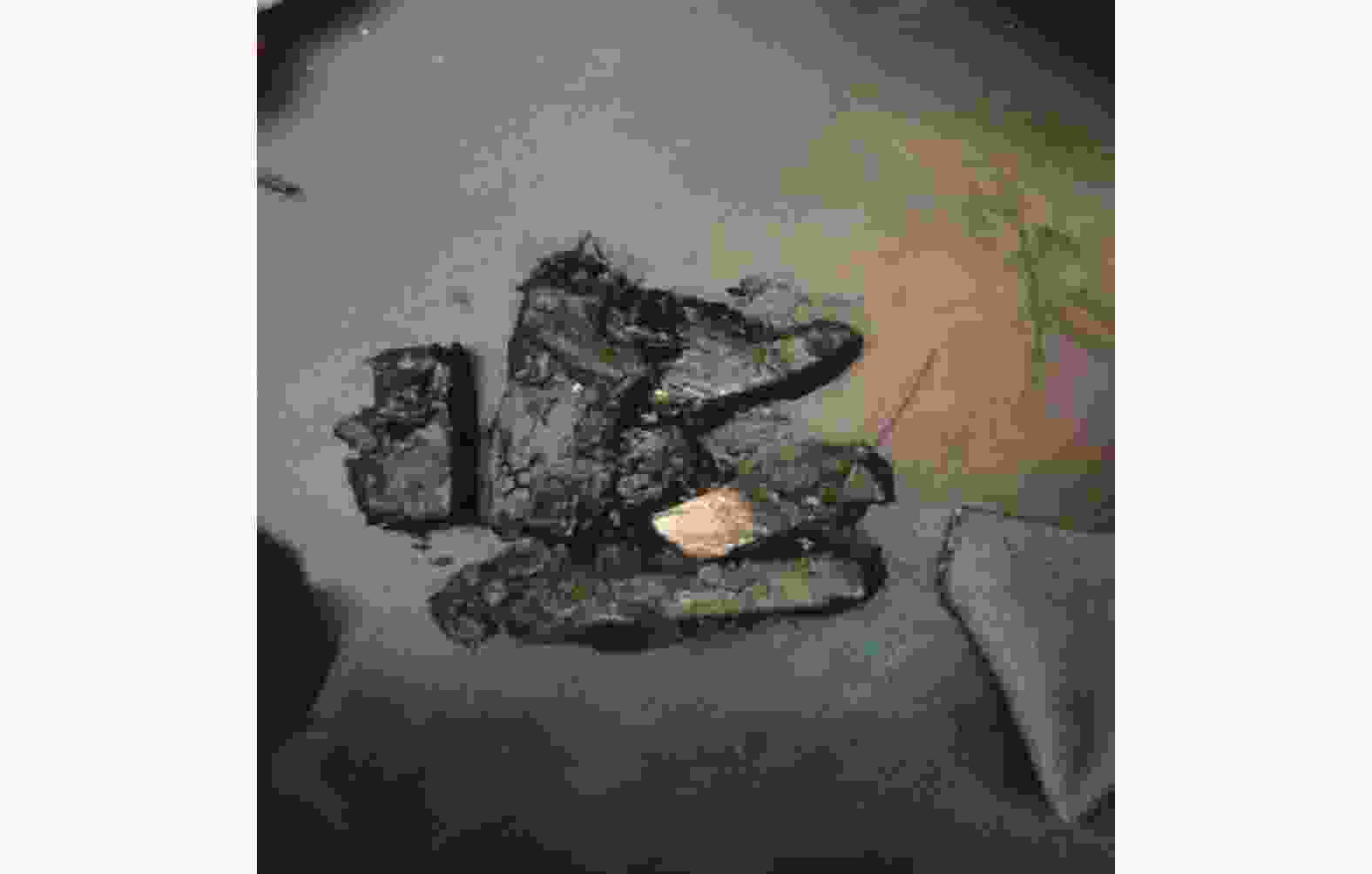
根据以上2个现象可以确认,高共模电流导致的局部熔化和波列纹理可能导致电机异常振动,会让轴承保持架断裂,从而会破坏主机轴承的使用寿命,如图6和图7所示。
-
1)测试示意图如图8所示。
2)于2020年11月,对现场机位地势比较高、具有代表性的#11机组进行抽检测试,结果如表2所示。
设备 测试点 共模电流${I}_{{\rm{peak}}}$/A 分析 #11 风机(4.3 m/s) Ⅰ 10.404 基于测量结果,系统中存在较大的共模电流,且共模电流随着风速的增加(功率增加)而增大。若风速达到10 m/s或以上,预计定子的控制系统中共模电流超过20 A,而控制转子的系统共模电流则超过30 A。长期运行较大概率出现以下问题:
(1)电缆过热;(2)变压器过热;(3)保护设备的误动作/误报警;(4)发电机异常振动。#11 风机(5.3 m/s) Ⅰ 12.024 #11 风机(4.3 m/s) Ⅱ 16.624 #11 风机(5.3 m/s) Ⅱ 19.180 Table 2. Measurement result of #11 wind turbine
3)现场仪器测量截图如图9所示。
-
1)经过现场测量,确认由该变频系统产生的共模干扰电流过大,该问题可导致电缆过热、变压器过热、保护设备的误动作/误报警、电机异常震动问题。
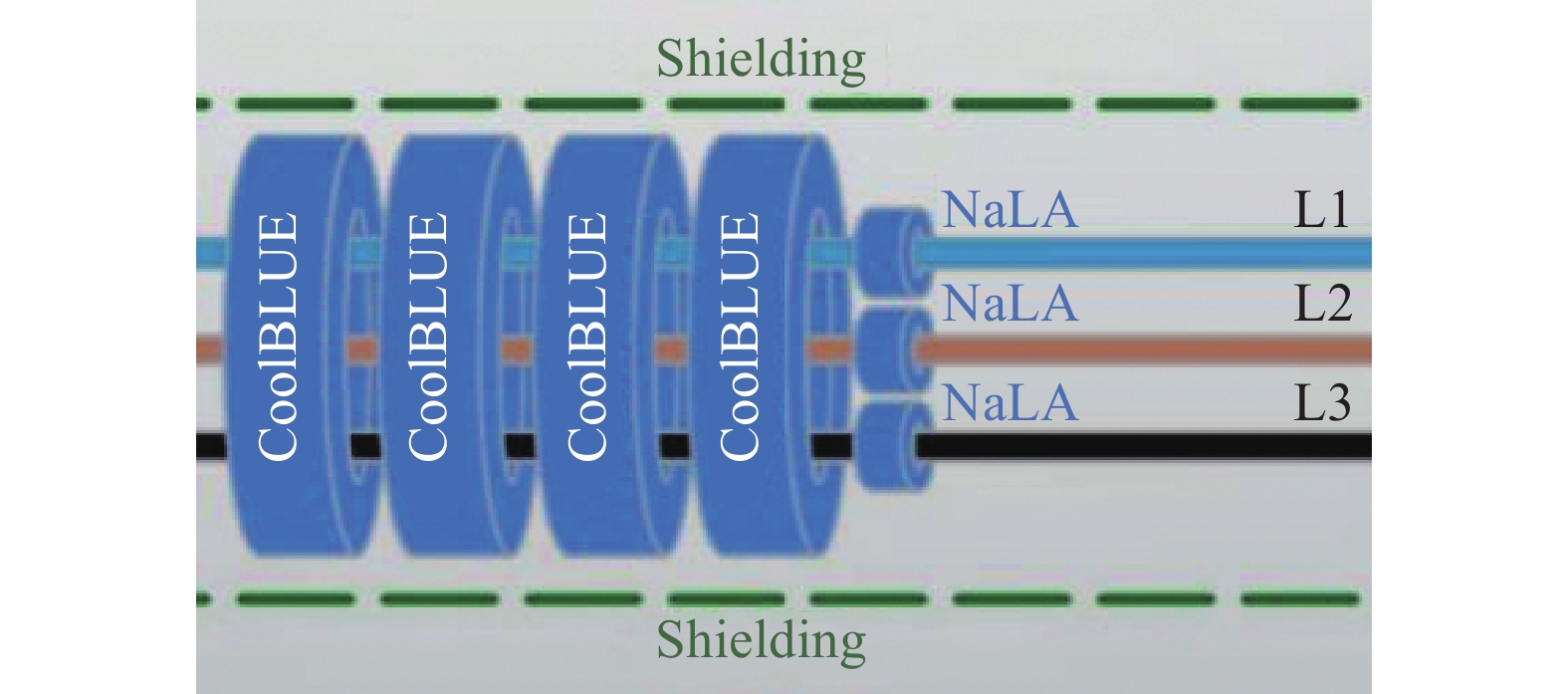
2)由于该项目为已投产项目,设备及电缆布置均已固定,难以改动,因此,建议采用在母线上加装抗干扰线圈CoolBLUE®系列的解决方案[21]。该方案的优点在于:
(1)无需改变原有设备及线路,不需接入系统,对系统可靠性无任何影响。
(2)利用材料高频阻抗特性将高频干扰在源头转化为热量,对工作电流无影响,不会造成其他处的杂散电流。
(3)本技术改造可免维护维修,并可长期有效使用。
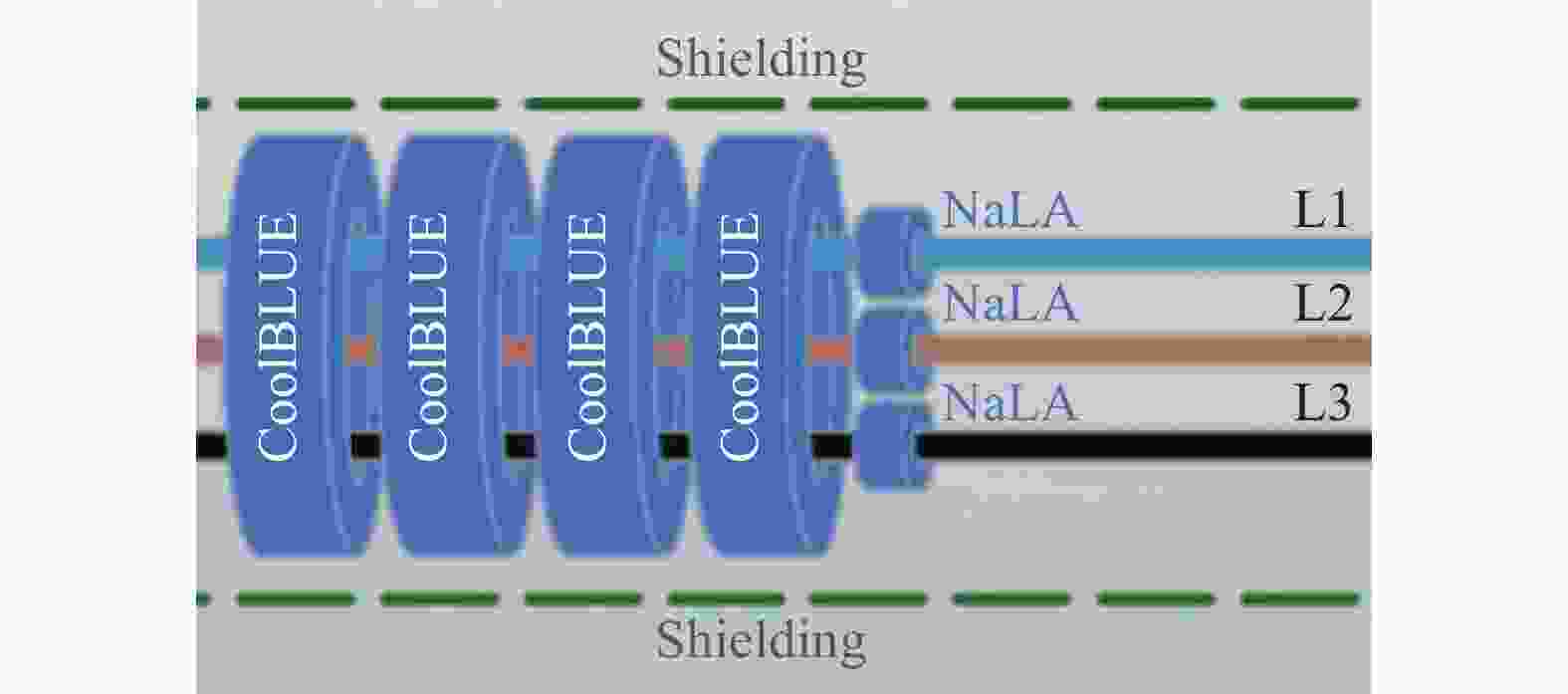
3)本次安装,应将CoolBlue®安装在变频器出口,电缆无屏蔽层处。将三相电缆穿过CoolBlue®,接地线不可穿过CoolBlue®。安装示意图如图10所示。
-
风力发电设备发生高共模电流时产生的磁通量大小和方向均相同,两者相互叠加,使“CoolBlue®”装置产生较大的共模阻抗,因此共模电感对共模干扰信号具有很好的滤除作用,而差模电流通过“CoolBlue®”共模线圈时磁力线方向相反,感应磁场削弱,共模电流通过共模线圈,磁力线方向相同,感应磁场加强。对于共模电感,当共模电流流过线圈时,由于磁力线方向相同,在不考虑漏感的情况下磁通量叠加,当磁通量翻倍时匝数和电流均没有发生变化,意味着电感量增加为原来的2倍,所以在互感模式下等效电感量与共模感抗均成倍增加,因而对共模信号有良好的滤除的作用,即将共模信号用大阻抗阻挡,不让其通过共模电感,也就是不让此信号传输到电路的下一级,从而起到遏止和解决高共模电流的作用。
-
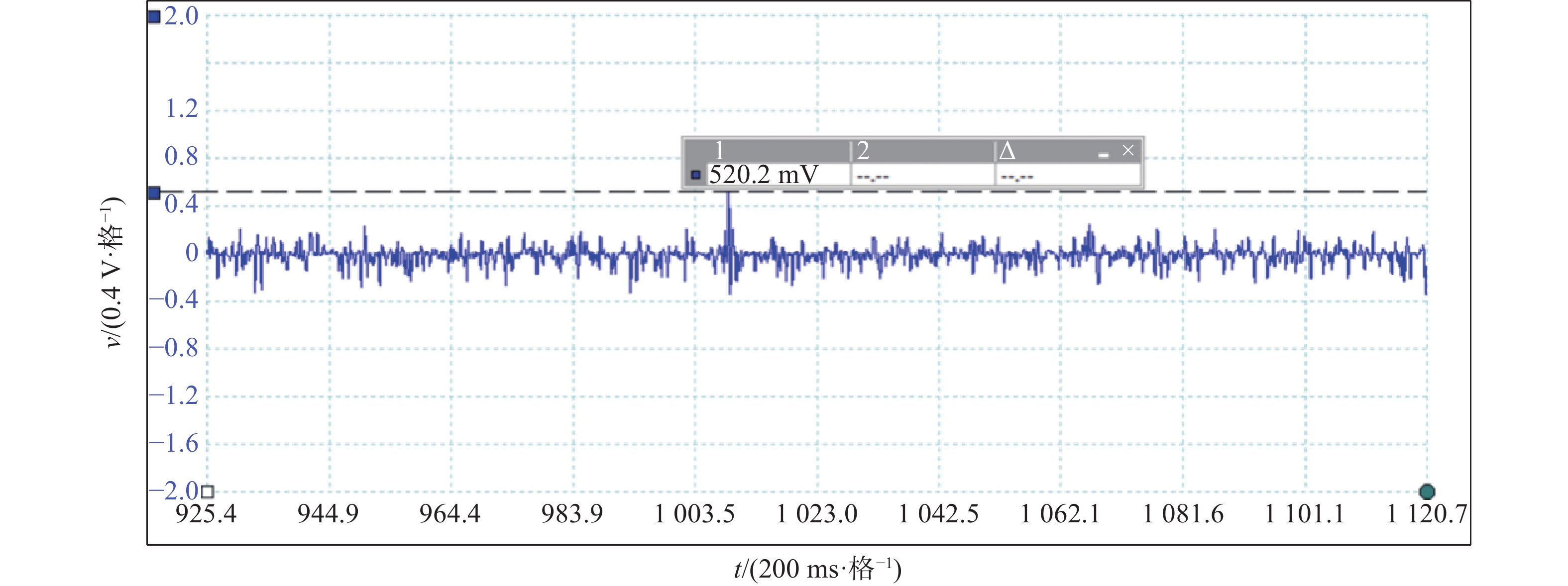
通过本次采用在试验机组#11风机母线上加装抗干扰线圈CoolBlue®系列的解决方案后现场测试结果如表3和图11所示。
风机/时间 主轴轴承B温度/℃ 次数/次 最高温度/℃ 占比/% Y向振动实时值/mm 次数/次 最大值/mm #11风机
11月21日~12月21日<40 5 108 39 100.0 <0.8 4 936 — ≤40<50 0 — 0.0 <0.8<1 139 — ≤50<60 0 — 0.0 <1<1.2 29 — ≤60<65 0 — 0.0 >1.2 4 1.53 ≥65 0 — 0.0 — — — Table 3. Measurement result after rectification of #11 wind turbine
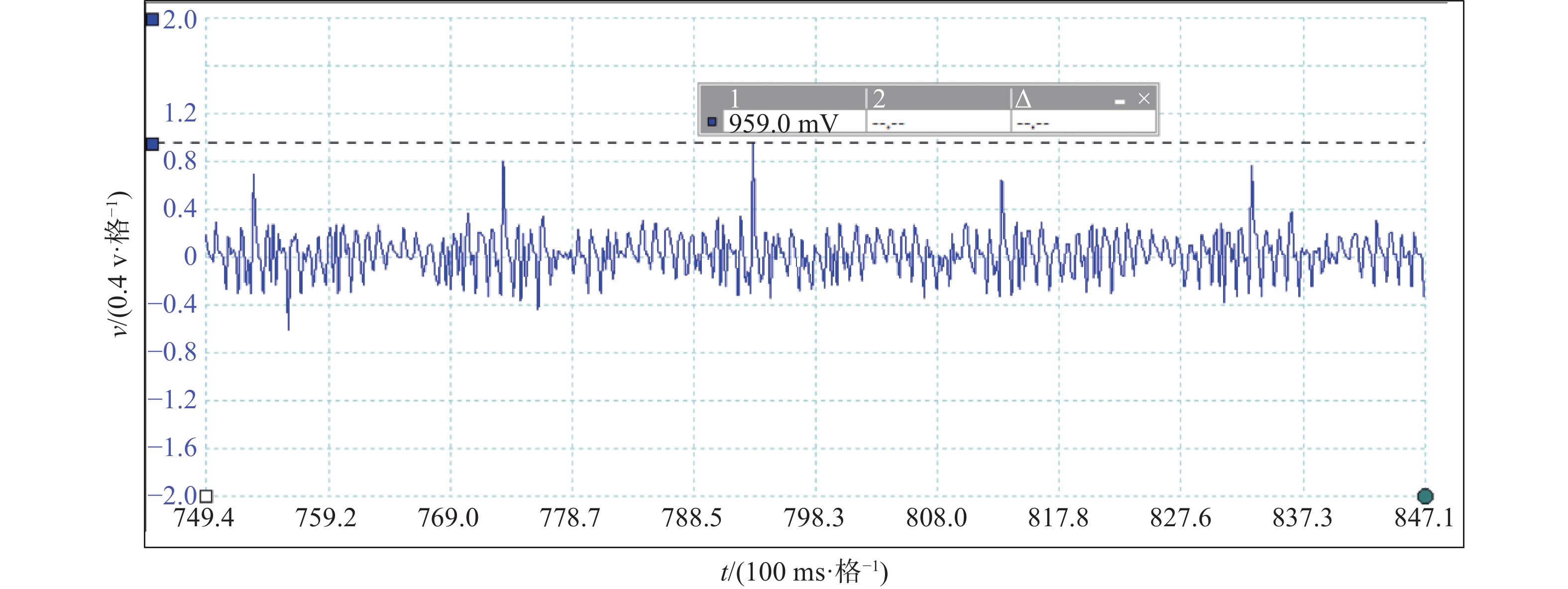
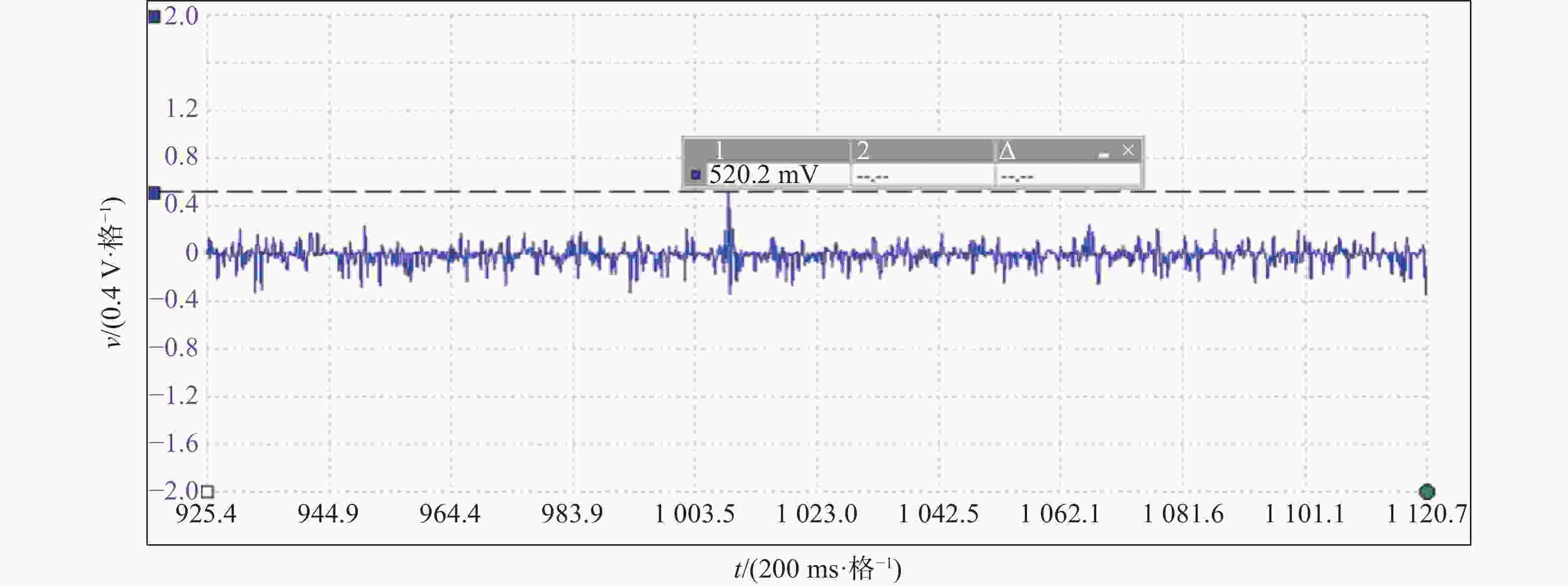
由此可见,在#11风机母线上加装抗干扰线圈CoolBlue®系列前的实测波形图扰动频繁,干扰电压最高值为959.0 mv(如图9所示),而加装抗干扰线圈后实测波形图扰动稀少,干扰电压低至520.2 mv(如图11所示),风机主轴温度和Y轴振动值也都在正常范围内,因此,本次测试整改安装前后效果对比明显可见。
-
随着风力发电技术的大力发展,新能源发电领域的电量需求不断提升。本文通过对一起风电机组发电系统中存在高共模电流,从而引起的一系列问题进行系统分析,现场检测,找出了根本原因,并提出改善方案和实践验证,技术整改后效果明显。为日后类似故障提供参考思路与解决方法,并可避免类似故障重复出现,提高风力发电机组的安全性,极大降低设备机器损耗与运维人员的工作量,提高了风场发电效益。该设备对风力发电机组起到一定的抗干扰作用,可以推广到其他陆上风电机组和海上风电项目使用,目前还没有其他风力发电场的应用场景及业绩,值得推广应用。
Analysis of the Influence of Common Mode Current on Wind Turbine
doi: 10.16516/j.gedi.issn2095-8676.2023.04.016
- Received Date: 2023-03-04
- Rev Recd Date: 2023-04-14
- Available Online: 2023-07-25
- Publish Date: 2023-07-10
-
Key words:
- common mode current /
- cable overheating /
- transformer overheating /
- anti-interference coil CoolBLUE /
- fault
Abstract:
| Citation: | WANG Xiaofeng. Analysis of the Influence of Common Mode Current on Wind Turbine[J]. SOUTHERN ENERGY CONSTRUCTION, 2023, 10(4): 158-165. doi: 10.16516/j.gedi.issn2095-8676.2023.04.016 |






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: